How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Detailed Analysis of possible future aircraft of the BAF
- Thread starter Zabaniyah
- Start date
Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
Radar and electronics:
Gonna take the MKK variant as an example since there are many variants out there. But all are very similar, they are only configured along with non-Russian components to suit end-user's needs.
The radar used in most SU-30 variants in use today is that NIIP N001VE, which use a twisted Cassegrainian antenna arrangement, borrowed from the MiG-29 N019 multimode radar.
It is referred to as a fire-control radar.
That's a lot of flares

References:
CHINESE AIR POWER - PEOPLE'S LIBERATION ARMY AIR FORCE
N001 Mech Fire-Control Radar (FCR) (Russian Federation) - Jane's Avionics
Flanker Radars in Beyond Visual Range Air Combat
---------- Post added at 04:47 PM ---------- Previous post was at 04:44 PM ----------
Um...fighting catfish?
Gonna take the MKK variant as an example since there are many variants out there. But all are very similar, they are only configured along with non-Russian components to suit end-user's needs.
The radar used in most SU-30 variants in use today is that NIIP N001VE, which use a twisted Cassegrainian antenna arrangement, borrowed from the MiG-29 N019 multimode radar.
It is referred to as a fire-control radar.
The PLA SU-30 MKK is equipped with the Tikhomirov NIIP N001VE radar which can range up to 90-110 km in counter-air mode, 70-80km against ground targets and 200-250 km against large ships. The MKK2 version is possibly equipped with the Phazotron Zhuk-M-S which has a 140km in counter-air mode, and 300km against large ships. The SU-30 can be equipped with the Kupol M400 side-looking radar pod that can control up to 10 fighters. The MKK3 is equipped with a Tikomirov “Panda,” radar that has a 190 km counter air mode or may be equipped with the new version of Zhuk-M-S.
The SU-30 is equipped with an extensive electronics suite including the OLS-30 IRST (Infrared Search and Track) system that has a 80-100km range. SU-30 pilots are equipped with the Surya-K Helmet Sight for close in air-to-air combat. SU-30 also have the Sapsan-E ir/laser targeting pod for ground attack, a APK-9 data link pod for Kh-59ME missile, A-737 satnav system, the L-150 Pastel RWR Radar Warning system, a 96x chaff/flare dispenser, the Sorbitsya ECM and the Spektr data link.
That's a lot of flares

During 1974, the Soyuz Programme was instigated to develop advanced radars for the MiG-29 Fulcrum and Su-27 Flanker fighter aircraft. Both radar sets were to have maximum commonality, with the only main difference being antenna size and power output. They were to use flat, slotted-array antennas, digital signal processing and employ Pulse-Doppler (PD) processing and Track-While-Scan (TWS) for enhanced look-down, shoot-down performance against multiple targets. The maximum ranges were to be 100 and 200 km, for the MiG-29 and Su-27 respectively. The MiG-29 radar was to be developed by NIIR, while NIIP would tackle the Su-27 system.However, both programmes failed to meet their performance requirements and in the late 1970s, both companies produced less capable radars - NIIR designed and built the N019 Rubin (see separate entry) radar for the MiG-29, while NIIP developed the N001 Mech radar for the Su-27. Both radars carry the NATO designation Slot Back and feature mechanically scanned Cassegrain antennas, combined with advanced solid-state technology and digital signal processing. Initial performance of the N001 was rather disappointing - head-on maximum detection range was 140 km against a large aircraft and 100 km against a fighter-size target. At low aspect, the ranges decreased by over 50 per cent. Compared to earlier Russian radars, however, look-down, shoot-down ranges were relatively good. After much work, the N001 radar was accepted into service in the early 1990s.In the Su-27, the N001 radar forms part of the RLPK-27 integrated radar sighting system.The radar computer (BTsVM) Ts100 enables the N001

References:
CHINESE AIR POWER - PEOPLE'S LIBERATION ARMY AIR FORCE
N001 Mech Fire-Control Radar (FCR) (Russian Federation) - Jane's Avionics
Flanker Radars in Beyond Visual Range Air Combat
---------- Post added at 04:47 PM ---------- Previous post was at 04:44 PM ----------
Sorry for going offtopic but i think designers got idea from catfish



Um...fighting catfish?

Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
Final, and probably the best contender: 
SAAB JAS-39 Gripen:

More at : Gripen - a multirole fighter of the latest generation
Specifications:
-Crew: One (Two for the JAS-39B)
-Powerplant: One Volvo Flygmotor RM12 turbofan (General Electric F404-GE-400) rated at 5,507 kg dry and 8,210 kg with afterburning.
-Weights: Operating Empty 6,700 kg (JAS 39B: 7,000 kg); Normal Take-off about 8,000 kg - 8,500 kg); Maximum Take-off 12,700 kg. (Pretty light)
-Armament:
>27-mm Mauser BK27 cannon semi-recessed under centre fuselage next to port air intake with 120 rounds;
>Wingtip launch rails for Rb 74 (AIM-9L) Sidewinder or similar missiles;
>Four underwing hardpoints and one under-fuselage centre-line pylon for a maximum of 6500 kg.
-Performance:
>Speed: Mach 2.0 at high altitude, Mach 1.15 at low level;
>Maximum rate of climb at sea level: ~5,000 meters per minute;
>Time to 33,000 ft (10,000 m) 2 mins;
>Service ceiling: ~15,240 m;
>Ferry range: 3,000 km with drop tanks;
>Combat radius for interception 900 km at high altitude with typical stores load and external fuel, for air-to-surface 1200 km in hi-lo-hi mission with with typical stores load and external fuel, or 750 km all low altitude with typical stores load and external fuel.
References:
Global Aircraft -- Saab 39 Gripen
Aeroflight » SAAB JAS 39 Gripen
SAAB JAS-39 "Gripen"

SAAB JAS-39 Gripen:

In designing the aircraft, several layouts were studied. Saab ultimately selected an unstable canard design. The canard configuration gives a high onset of pitch rate and low drag, enabling the aircraft to be faster, have longer range and carry a larger payload.
The combination of delta wing and canards gives the Gripen significantly better takeoff and landing performance and flying characteristics. The totally integrated avionics make it a "programmable" aircraft. It also has a built-in electronic warfare unit, making it possible to load more ordnance onto the aircraft without losing self defence capabilities.
The Gripen affords more flexibility than earlier generations of combat aircraft used by Sweden, and its operating costs are about two thirds of those for JA 37 Viggen.
More at : Gripen - a multirole fighter of the latest generation

Specifications:
-Crew: One (Two for the JAS-39B)
-Powerplant: One Volvo Flygmotor RM12 turbofan (General Electric F404-GE-400) rated at 5,507 kg dry and 8,210 kg with afterburning.
-Weights: Operating Empty 6,700 kg (JAS 39B: 7,000 kg); Normal Take-off about 8,000 kg - 8,500 kg); Maximum Take-off 12,700 kg. (Pretty light)
-Armament:
>27-mm Mauser BK27 cannon semi-recessed under centre fuselage next to port air intake with 120 rounds;
>Wingtip launch rails for Rb 74 (AIM-9L) Sidewinder or similar missiles;
>Four underwing hardpoints and one under-fuselage centre-line pylon for a maximum of 6500 kg.
-Performance:
>Speed: Mach 2.0 at high altitude, Mach 1.15 at low level;
>Maximum rate of climb at sea level: ~5,000 meters per minute;
>Time to 33,000 ft (10,000 m) 2 mins;
>Service ceiling: ~15,240 m;
>Ferry range: 3,000 km with drop tanks;
>Combat radius for interception 900 km at high altitude with typical stores load and external fuel, for air-to-surface 1200 km in hi-lo-hi mission with with typical stores load and external fuel, or 750 km all low altitude with typical stores load and external fuel.
References:
Global Aircraft -- Saab 39 Gripen
Aeroflight » SAAB JAS 39 Gripen
SAAB JAS-39 "Gripen"
Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
More info on the weapons:
Loadout:

Meteor beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile:
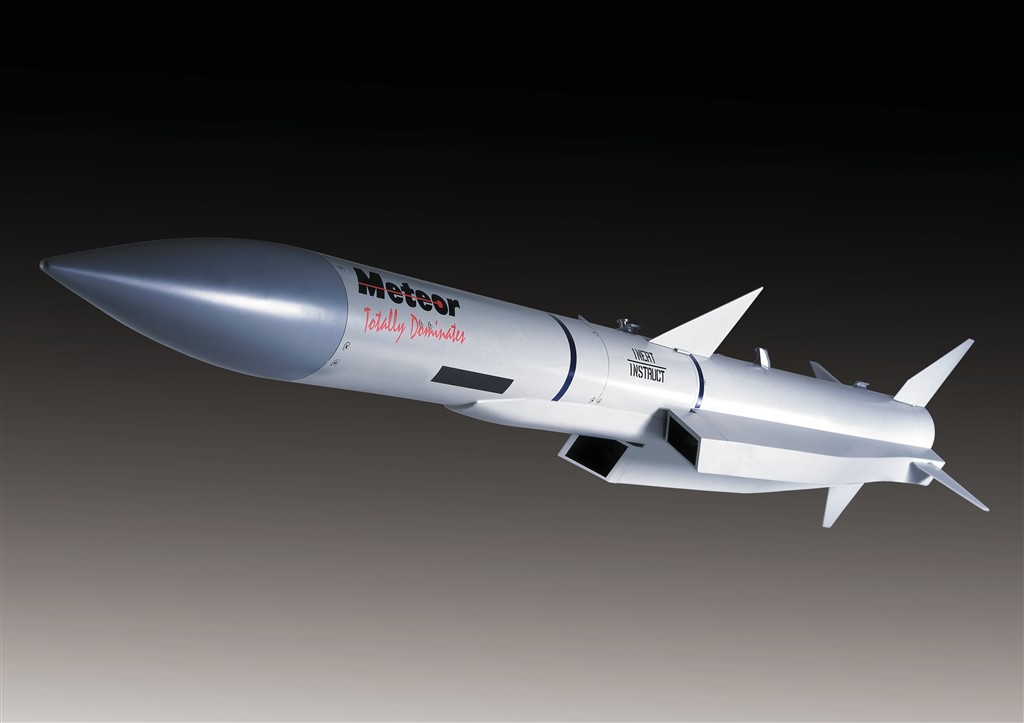

Specifications:
-Warhead: High Explosive Blast-Fragmentation
-Detection mechanism: Proximity / Impact
-Operational range: 100+ km (60+ mi)
-Speed: Mach 4+
-Guidance system: Inertial Mid-course with Datalinked Updates, Active Radar
-Applications: Eurofighter Typhoon, Dassault Rafale, JAS 39 Gripen
The missile is still under development.
IRIS-T Short-range air-to-air missile:

HAF (Greece) F-16 armed with IRIS-T


Specifications:
-Max range: ~30 km
Interesting reading:
More reading at:
http://knygos.sprogmenys.net/knygos-2/Rocketry/Missiles and Warheads/Jane's Missiles and Rockets.pdf
References:
Ministry of Defence | Fact Sheets | Project Factsheets | Beyond Visual Range Air to Air Missile (BVRAAM)
Meteor - Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile
IRIS-T Short Range Air-to-Air Missile - Technical specifications
The Gripen has seven external hardpoints for carrying payloads: one at each wingtip, two under each wing and one on the fuselage centreline.
The air-to-air missiles include MBDA (formerly Matra BAe Dynamics) MICA, Raytheon AIM-120B AMRAAM and Lockheed Martin / Raytheon Sidewinder AIM-9L (Swedish Air Force Designation RB74).
Sidewinder, mounted on the wingtips, is an all-aspect attack, short-range missile for enhanced dogfight capability. Air-to-surface missiles include the radar-guided Saab RBS15F anti-ship missile and Raytheon Maverick missile.
Later versions of the aircraft for Sweden will be armed with the short-range Diehl BGT Defence IRIS-T air-to-air missile and the MBDA Meteor beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile. Deliveries of IRIS-T began in December 2005.
The Swedish Defence Material Administration awarded an Skr312m ($42m) contract to Saab in September 2010 for incorporating the active radar guided beyond visual range (BVR) missile, meteor as well as radar and displays on Gripen Fighters. Saab will execute test flight and test firing as part of the contract. The aircraft will also be equipped with support and maintenance systems such as simulators and planning computers.
The Saab Bofors / MBDA Taurus KEPD 350 long-range stand-off missile, with a range of 350km, has been successfully flight tested on the Gripen.
In May 2008, South Africa placed an order for the IRIS-T air-to-air missile to equip its Gripen fleet until the indigenous Denel A Darter missile enters service.
The internally mounted 27mm Mauser high-energy gun can operate in an automatic radar-guided aiming mode. The stand-off dispenser is the DWF39 from EADS (formerly DaimlerChrysler Aerospace) and Bofors. The Bofors ARAK 70 rocket pod is cleared for carriage on the Gripen.
Loadout:
Meteor beyond visual range (BVR) air-to-air missile:

Meteor is an active radar guided beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) superior to other missiles of its type, and capable of engaging air targets autonomously, day or night, in all weathers and in harsh electronic warfare environments.
The missile’s ramjet propulsion system gives Meteor its high-speed performance and the energy to defeat fast, moving targets at long range.
The Meteor programme sees the UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain and Sweden joining together to provide access to technology and expertise across Europe. MBDA is the Prime Contractor.
Specifications:
-Warhead: High Explosive Blast-Fragmentation
-Detection mechanism: Proximity / Impact
-Operational range: 100+ km (60+ mi)
-Speed: Mach 4+
-Guidance system: Inertial Mid-course with Datalinked Updates, Active Radar
-Applications: Eurofighter Typhoon, Dassault Rafale, JAS 39 Gripen
The missile is still under development.
IRIS-T Short-range air-to-air missile:

HAF (Greece) F-16 armed with IRIS-T
Control is everything in an air-to-air combat situation. And control means confidence – offered by Saab's IRIS-T.
Procured by six nations, The IRIS-T is a short-range, highly manoeuvrable, all-aspect air-to-air missile. A sophisticated imaging infra-red seeker, thrust-vector control and a powerful motor allows for the engagement of any target from point-blank all the way to maximum range.
The IRIS-T programme sees the Germany, Greece, Norway, Italy, Spain and Sweden joining together to provide access to technology and expertise across Europe. Diehl BGT Defence is the Prime Contractor.
IRIS-T has both lock-on before launch (LOBL) and lock-on after launch (LOAL) capabilities, enabling it to be cued by any sensor input or a helmet-mounted sight.


Specifications:
-Max range: ~30 km
Interesting reading:
On 24 April, a missile fired from a German Air Force F-4F test aircraft, from a near head-on position and a distance of slightly
under 10km, scored a direct hit against a Meteor Mirach 100/5 target drone and destroyed it. The target and launch aircraft
were flying at high subsonic speed and medium altitude. This trial demonstrated missile performance against low infrared (IR) signature targets under difficult head-on engagement conditions.
A third firing conducted at the Salto di Quirra range on 3 May was designed to demonstrate the hit capability of IRIS-T in
the presence of IR flares and under difficult head-on engagement conditions. Conditions were similar to these on the 24 April firing, but on this occasion the F-4F test aircraft (from the German WTD 61 Test Centre in Manching) launched the missile from a range of slightly under 7km. The round intercepted a Mirach 100/5 drone, which was flying a maximum-g evasive manoeuvre, and
dispensing flare countermeasures.
IRIS-T/GL meets all MEADS requirements for an affordable and cost-effective secondary missile able to complement Patriot
PAC-3, defeating aircraft, helicopters, cruise and other tactical aerodynamic missiles flying at low and medium altitudes. BGT
says that an independent assessment carried out by IABG (a consulting company to the German MoD) showed that IRIS-T/GL was superior to competing solutions in terms of technical performance and cost-effectiveness.
More reading at:
http://knygos.sprogmenys.net/knygos-2/Rocketry/Missiles and Warheads/Jane's Missiles and Rockets.pdf
References:
Ministry of Defence | Fact Sheets | Project Factsheets | Beyond Visual Range Air to Air Missile (BVRAAM)
Meteor - Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile
IRIS-T Short Range Air-to-Air Missile - Technical specifications
Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
Sorry about being sluggish guys, I'll post more, and reach a solution in the conclusion 
A2G weapons:
Saab RBS15F anti-ship missile devil
devil :
:
Specifications:
-Country: Sweden
-Class: SLCM
-Target: Ship
-Length: 4.35 m
-Diameter: 0.50 m
-Wingspan: 1.40 m
-Launch Weight: 790-805 kg
-Payload: 200 kg HE, fragmentation
-Propulsion: Turbojet w/ solid boosters
-Range: 100-200 km
-Guidance: INS, radio altimeter, active radar
-Status: Operational
-In Service: 1985-Present
-Associated Country: Germany
-Exported: Finland, Germany, Poland, Serbia, Montenegro, Croatia
The Gripen is also capable of firing the Raytheon Maverick missile which I have discussed in the F-16 part.
References:
MissileThreat :: RBS-15
RBS15 Antiship missile system

A2G weapons:
Saab RBS15F anti-ship missile
 :
:Specifications:
-Country: Sweden
-Class: SLCM
-Target: Ship
-Length: 4.35 m
-Diameter: 0.50 m
-Wingspan: 1.40 m
-Launch Weight: 790-805 kg
-Payload: 200 kg HE, fragmentation
-Propulsion: Turbojet w/ solid boosters
-Range: 100-200 km
-Guidance: INS, radio altimeter, active radar
-Status: Operational
-In Service: 1985-Present
-Associated Country: Germany
-Exported: Finland, Germany, Poland, Serbia, Montenegro, Croatia
The Gripen is also capable of firing the Raytheon Maverick missile which I have discussed in the F-16 part.
References:
MissileThreat :: RBS-15
RBS15 Antiship missile system
Last edited by a moderator:
Lighting_Fighter
FULL MEMBER

- Joined
- Nov 25, 2011
- Messages
- 566
- Reaction score
- 0
Sorry about being sluggish guys, I'll post more, and reach a solution in the conclusion
A2G weapons:
Saab RBS15F anti-ship missiledevil
:
Specifications:
-Country: Sweden
-Class: SLCM
-Target: Ship
-Length: 4.35 m
-Diameter: 0.50 m
-Wingspan: 1.40 m
-Launch Weight: 790-805 kg
-Payload: 200 kg HE, fragmentation
-Propulsion: Turbojet w/ solid boosters
-Range: 100-200 km
-Guidance: INS, radio altimeter, active radar
-Status: Operational
-In Service: 1985-Present
-Associated Country: Germany
-Exported: Finland, Germany, Poland, Serbia, Montenegro, Croatia
The Gripen is also capable of firing the Raytheon Maverick missile which I have discussed in the F-16 part.
References:
MissileThreat :: RBS-15
RBS15 Antiship missile system
phew....I was glued to the screen.
---------- Post added at 01:02 AM ---------- Previous post was at 01:00 AM ----------
Sorry for going offtopic but i think designers got idea from catfish



yum yum, fried cat fish meat yum yum
Last edited by a moderator:
Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
Saab Bofors / MBDA Taurus KEPD 350:
Applications:
-Panavia Tornado
-Eurofighter Typhoon
-Gripen
-F-18 Hornet
Performance:
Max Launch Altitude 7,620 m (25,000 ft), Max Range 350 km (189 nm), Top Speed 276 mps (Mach 0.83)
Additional reading:
http://www.mbda-systems.com/mediagallery/files/TAURUS-KEPD-350_background.pdf
http://www.mbda-systems.com/mediagallery/files/taurus_ds.pdf
References:
Taurus KEPD 350
The Saab Bofors/MBDA Taurus KEPD 350 long-range standoff missile, with a range of 350km, has been successfully flight tested on the Gripen.
Applications:
-Panavia Tornado
-Eurofighter Typhoon
-Gripen
-F-18 Hornet
Highly demanding air operations require the ability to strike with accuracy and penetrate dense air-defences on the ground.
The TAURUS KEPD 350 is an advanced, modular stand-off missile system for precision strikes against bunkers and other hardened, deeply buried targets, as well as high-value point and area targets such as large radar stations.
The TAURUS KEPD 350 is a product of TAURUS Systems GmbH, a joint venture between LFK-Lenkflugkörpersysteme GmbH and Saab Dynamics AB, for the development, production and global marketing of the TAURUS stand-off missile family for long-range precision strikes.
Performance:
Max Launch Altitude 7,620 m (25,000 ft), Max Range 350 km (189 nm), Top Speed 276 mps (Mach 0.83)
Additional reading:
http://www.mbda-systems.com/mediagallery/files/TAURUS-KEPD-350_background.pdf
http://www.mbda-systems.com/mediagallery/files/taurus_ds.pdf
References:
Taurus KEPD 350
Last edited by a moderator:
Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
Engine:
The engine, a General Electric F414G turbofan, is a modular, fuel-efficient low-bypass ratio, afterburning turbofan with the latest technology. With a thrust rating of more than 22,000lb (98kN), the F414G produces 20% more thrust than Gripens current Volvo Aero RM12 power plant, and will enable super-cruise performance of Mach 1.1 with air-to-air weapons.

The engine is American, so there'd be strings attached to that one.
Radar:
ES05 RAVEN AESA:


The engine, a General Electric F414G turbofan, is a modular, fuel-efficient low-bypass ratio, afterburning turbofan with the latest technology. With a thrust rating of more than 22,000lb (98kN), the F414G produces 20% more thrust than Gripens current Volvo Aero RM12 power plant, and will enable super-cruise performance of Mach 1.1 with air-to-air weapons.

The engine is American, so there'd be strings attached to that one.
Radar:
ES05 RAVEN AESA:


With the worlds only 2nd generation AESA radar, ES 05 Raven, Gripen NG will secure its advantages in situational awareness. The ES 05 Raven developed by Selex-Galileo, together with Saab and Brazilian Industry, is the only fighter radar on the market with a moving swash plate allowing cover of scan angles up to ±100°. The new radar will improve all aspects compared to legacy radars, such as:
-Improved target tracking
-Wide field of regard
-Mode flexibility
-Increased detection range
-Improved electronic support measurements
-Increased operational availability together with lower life cycle costs.
Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
Bludgeon, i see that you are being a slightly bias towards the Gripen, so many tasty functions compared to the others

It's not bias. Just plain facts!
Avisheik
SENIOR MEMBER
- Joined
- Mar 21, 2011
- Messages
- 2,770
- Reaction score
- 1
- Country
- Location
It's not bias. Just plain facts!
Whatever floats your boat man. ME wants GRIPEN

Zabaniyah
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 24, 2011
- Messages
- 14,925
- Reaction score
- 7
- Country
- Location
The aircraft is equipped with a Saab Avitronics electronic warfare system that gives the NG a unique active and passive electronic attack (EA) capability – which adds the AESA to the vital EA mission. The NG is also equipped with a missile approach warning and self defence system. These systems give Gripen a self-defence system that is extremely hard to beat, in any combat situation.
The fully integrated avionic mission system, including the AESA radar, IRST sensor, and an advanced active and passive EW system, provides superior sensor fusion and decision support capabilities. These together with a missile approach warning system, laser warning system, towed decoys and built in jamming capability provide excellent offensive and defensive characteristics.
The outstanding agility of the Gripen NG is achieved through a combination of an advanced aerodynamic layout utilising a combined close-coupled canard delta configuration and a digital fly-by-wire system. The new, more powerful, General Electric F414 G engine not only gives Gripen supercruise but also unbeatable low life cycle cost.
Note: The Gripen does not implement AESA yet. Currently in service are using Ericsson PS-05/A pulse-doppler radar.
PS-05/A - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Ericsson PS-05 long-range multi-purpose pulse Doppler radar has air-to air operating modes covering long-range search, multi-target track-while-scan, multiple priority target tracking, air combat quick search modes, raid assessment and beyond visual range (BVR) missile mid-course updates.
The air-to-surface modes include long-range search/target identification, multiple priority target tracking, high-resolution, real beam mapping, air-to-surface ranging and Doppler beam sharpening (DBS).
The aircraft is equipped with a forward-looking infrared (FLIR) sensor and will have the Saab IR-Otis infrared search and track system (IRST).
Nine Swedish Air Force Gripens have been fitted with the Saab Avitronics modular reconnaissance pod, which includes a recon / optical CA270 infrared sensor. The system entered service in 2006.
Swedish Defence Material Administration awarded a four year SEK 400m contract to Saab in April 2010 for developing modular reconnaissance pod system (MRPS) which will be fitted in the Gripen fighter aircraft.
Future:
Integration of an AESA radar in place of the present mechanically-scanned PS-05 is an important future selling point, and has been promised in several of Saab’s recent foreign bid submissions. Development has been less smooth. Saab bought Ericsson’s radar group, which makes the Erieye AWACS radar, and began the “Nora” AESA project in 2006. In autumn 2007, Saab changed course and began a radar partnership with Thales for the RBE2-AA AESA radar that will equip Dassault’s Rafale. Then Dassault bought a large stake in Thales, and scuttled the deal in order to cripple a competitor. Saab is now partnered with Selex Galileo to design an ES-05 Raven AESA radar that builds on Selex’s experience with the Vixen 500 AESA, and Ericsson’s PS-05 MESA and Nora experiments. The new radar will use an active electronically scanned array that can be moved mechanically, increasing its total field of view and improving “lock and leave” maneuvers.
SpArK
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- May 5, 2010
- Messages
- 22,519
- Reaction score
- 18
- Country
- Location
The engine is American, so there'd be strings attached to that one.
What are the strings attached to it?
Similar threads
- Article
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 509
- Replies
- 65
- Views
- 5K
- Replies
- 394
- Views
- 22K

