Haq's Musings: History of Literacy in Pakistan 1947-2014
The parts that now constitute Pakistan were among the least developed regions of India and the rest of the world prior to 1947, and the last to be conquered by the British, according to an eminent Pakistani economist Dr. Kaiser Bengali. The British rule in Sind, Baluchistan and NWFP lasted about 100 years and these regions were considered the periphery of the British Raj in India. At the time of the first census in 1950, the overall literacy rate was 20% in India and 14% in Pakistan, according to UNESCO. As of 2012, India has achieved 75% literacy rate while Pakistan is at 58%. Pakistan Youth (15-24 years) literacy rate is 79.1% for males and 61.5% for females. Each new generation of Pakistanis is more literate than its predecessors:
Over 55 years 30% literate
45-55 years 40%
35-45 years 50%
25-35 years 60%
15-25 years 70%

Literacy Rates in 1950. Source: UNESCO
Pakistan has come a long way in terms of literacy but it still lags its neighbors, particularly Iran, which had lower literacy rate than Pakistan in 1950s, now has well over 90% of its adult population literate. Education was a key focus of the Shah Reza Shah Pehlavi, the Shah of Iran from 1941 to 1979. The Shah invested a significant chunk of his country's oil revenues to improve education, health care and infrastructure. Iran's education spending increased 1800% during the Shah's rule.

Although literacy in Pakistan has grown by about 13% during President Mushsarraf's rule to about 56%, it still remains woefully low when compared to its neighbors.
However, Pakistanis now spend more time in schools and colleges and graduate at a higher rate than their Indian counterparts in 15+ age group, according to a report on educational achievement by Harvard University researchers Robert Barro and Jong-Wha Lee.
As of 2010, there are 380 out of every 1000 Pakistanis age 15 and above who have never had any formal schooling. Of the remaining 620 who enrolled in school, 22 dropped out before finishing primary school, and the remaining 598 completed it. There are 401 out of every 1000 Pakistanis who made it to secondary school. 290 completed secondary school while 111 dropped out. Only 55 made it to college out of which 39 graduated with a degree.

Barro-Lee data shows the following:
1. India's overall schooling rate of 67.4% exceeds Pakistan's 61.9% in 15 and over age group.
2. Pakistan's primary schooling rate of 21.8% is slightly higher than India's 20.9% of 15+ age group
3. India has a big edge with its secondary enrollment of 40.7% over Pakistan's 34.6%, but India's completion rate at this level is a dismal 0.9% versus Pakistan's 22.5% of the population of 15+ age group.
4. India's tertiary education enrollment rate of 5.8% is higher than Pakistan's 5.5%, but Pakistan's college and university graduation rate of 3.9% is higher than India's 3.1% of 15+ age group.
5. Pakistan's combined graduation rate at all three levels is 45.7% versus India's 22.9% among the population age group of 15 years or older.
6. UNESCO's Global Education Digest shows that, as of 2009, nearly 16% of Pakistan's adult population has completed higher education, higher than the figures of 12% for India and 8% for Indonesia among emerging markets.
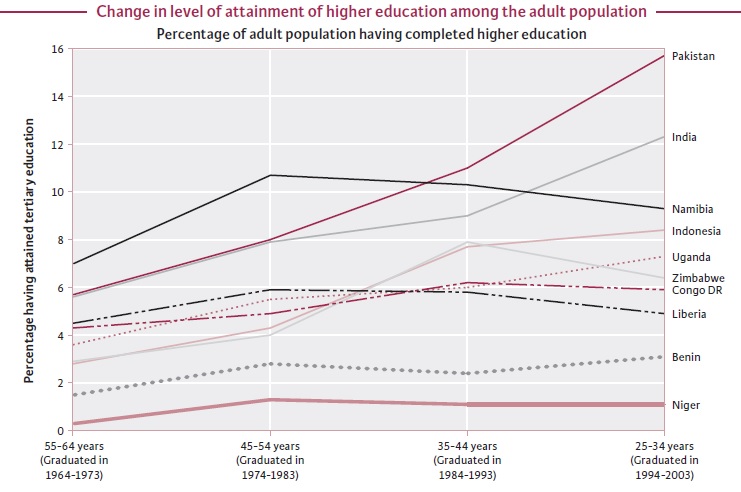
College Graduation Data. Source: Global Education Digest
Barro-Lee data also shows that the percentage of 15+ age group with no schooling has gone down in both nations in the last decade, particularly in Pakistan where it dropped dramatically by a whopping 22% from 60.2% in 2000 to 38% in 2010. In India, this percentage with no schooling dropped from 43% to 32.7% of 15+ age group.

Here's some data on out-of-school children in Pakistan:
1. The actual number of out of school children of primary age in Pakistan is 5.1 million.
2. The out-of-school figures of 50% in Punjab, 61% in Sindh, 65% in KP and 78% in Balochistan are for pre-primary children ages 3 to 5 years, not for ages 6-16 years.
3. In 6-16 years age group, 7% of urban and 23% of rural children are out of school.
4. The number of out-of-school children has declined from in 8.4 million in 2001 to 5.1 million in 2010.
5. According to Pakistan Standards of Living Measurements PSLM 2011-12, the country's literacy rate is 58%.

Source: 2012 Global Monitoring Report
6. Data from Harvard researchers Rober Barro and Jhong-Wa Lee shows that Pakistan has been increasing enrollment of students in schools at a faster rate since 1990 than India. In 1990, there were 66.2% of Pakistanis vs 51.6% of Indians who had no schooling. In 2000, there were 60.2% Pakistanis vs 43% Indians with no schooling. In 2010, Pakistan reduced it to 38% vs India's 32.7%.

UNESCO data also shows that a significant percentage of out-of-school children in Pakistan are expected to enter school:

I do not see any justification for the usual expressions of extreme pessimism that follow every alarmist report in the media. I do, however, see an urgent need for higher spending and greater focus on education by Pakistani government to make faster progress, particularly in closing the gender gap in school enrollment. A recent report about significant education successes in Punjab prepared by Sir Micheal Barber gives me hope that the PML (N) will perform better than the last government in responding to the challenge.
Haq's Musings: History of Literacy in Pakistan 1947-2014
The parts that now constitute Pakistan were among the least developed regions of India and the rest of the world prior to 1947, and the last to be conquered by the British, according to an eminent Pakistani economist Dr. Kaiser Bengali. The British rule in Sind, Baluchistan and NWFP lasted about 100 years and these regions were considered the periphery of the British Raj in India. At the time of the first census in 1950, the overall literacy rate was 20% in India and 14% in Pakistan, according to UNESCO. As of 2012, India has achieved 75% literacy rate while Pakistan is at 58%. Pakistan Youth (15-24 years) literacy rate is 79.1% for males and 61.5% for females. Each new generation of Pakistanis is more literate than its predecessors:
Over 55 years 30% literate
45-55 years 40%
35-45 years 50%
25-35 years 60%
15-25 years 70%

Literacy Rates in 1950. Source: UNESCO
Pakistan has come a long way in terms of literacy but it still lags its neighbors, particularly Iran, which had lower literacy rate than Pakistan in 1950s, now has well over 90% of its adult population literate. Education was a key focus of the Shah Reza Shah Pehlavi, the Shah of Iran from 1941 to 1979. The Shah invested a significant chunk of his country's oil revenues to improve education, health care and infrastructure. Iran's education spending increased 1800% during the Shah's rule.

Although literacy in Pakistan has grown by about 13% during President Mushsarraf's rule to about 56%, it still remains woefully low when compared to its neighbors.
However, Pakistanis now spend more time in schools and colleges and graduate at a higher rate than their Indian counterparts in 15+ age group, according to a report on educational achievement by Harvard University researchers Robert Barro and Jong-Wha Lee.
As of 2010, there are 380 out of every 1000 Pakistanis age 15 and above who have never had any formal schooling. Of the remaining 620 who enrolled in school, 22 dropped out before finishing primary school, and the remaining 598 completed it. There are 401 out of every 1000 Pakistanis who made it to secondary school. 290 completed secondary school while 111 dropped out. Only 55 made it to college out of which 39 graduated with a degree.

Barro-Lee data shows the following:
1. India's overall schooling rate of 67.4% exceeds Pakistan's 61.9% in 15 and over age group.
2. Pakistan's primary schooling rate of 21.8% is slightly higher than India's 20.9% of 15+ age group
3. India has a big edge with its secondary enrollment of 40.7% over Pakistan's 34.6%, but India's completion rate at this level is a dismal 0.9% versus Pakistan's 22.5% of the population of 15+ age group.
4. India's tertiary education enrollment rate of 5.8% is higher than Pakistan's 5.5%, but Pakistan's college and university graduation rate of 3.9% is higher than India's 3.1% of 15+ age group.
5. Pakistan's combined graduation rate at all three levels is 45.7% versus India's 22.9% among the population age group of 15 years or older.
6. UNESCO's Global Education Digest shows that, as of 2009, nearly 16% of Pakistan's adult population has completed higher education, higher than the figures of 12% for India and 8% for Indonesia among emerging markets.

College Graduation Data. Source: Global Education Digest
Barro-Lee data also shows that the percentage of 15+ age group with no schooling has gone down in both nations in the last decade, particularly in Pakistan where it dropped dramatically by a whopping 22% from 60.2% in 2000 to 38% in 2010. In India, this percentage with no schooling dropped from 43% to 32.7% of 15+ age group.

Here's some data on out-of-school children in Pakistan:
1. The actual number of out of school children of primary age in Pakistan is 5.1 million.
2. The out-of-school figures of 50% in Punjab, 61% in Sindh, 65% in KP and 78% in Balochistan are for pre-primary children ages 3 to 5 years, not for ages 6-16 years.
3. In 6-16 years age group, 7% of urban and 23% of rural children are out of school.
4. The number of out-of-school children has declined from in 8.4 million in 2001 to 5.1 million in 2010.
5. According to Pakistan Standards of Living Measurements PSLM 2011-12, the country's literacy rate is 58%.

Source: 2012 Global Monitoring Report
6. Data from Harvard researchers Rober Barro and Jhong-Wa Lee shows that Pakistan has been increasing enrollment of students in schools at a faster rate since 1990 than India. In 1990, there were 66.2% of Pakistanis vs 51.6% of Indians who had no schooling. In 2000, there were 60.2% Pakistanis vs 43% Indians with no schooling. In 2010, Pakistan reduced it to 38% vs India's 32.7%.

UNESCO data also shows that a significant percentage of out-of-school children in Pakistan are expected to enter school:

I do not see any justification for the usual expressions of extreme pessimism that follow every alarmist report in the media. I do, however, see an urgent need for higher spending and greater focus on education by Pakistani government to make faster progress, particularly in closing the gender gap in school enrollment. A recent report about significant education successes in Punjab prepared by Sir Micheal Barber gives me hope that the PML (N) will perform better than the last government in responding to the challenge.
Haq's Musings: History of Literacy in Pakistan 1947-2014








