IRS-P3
IRS-P3 was launched by PSLV-D3 on March 21, 1996 from SHAR Centre, Sriharikota, India. IRS-P3 carries two remote sensing payloads - Wide Field Sensor (WiFS) similar to that of IRS-1C, with an additional Short Wave Infrared Band (SWIR) and a Modular Opto-electronic Scanner (MOS). It also carries an X-ray astronomy payload and a C-band transponder for radar calibration.
Mission completed during January 2006 after serving 9 years and 10 months.
Mission : Remote sensing of earth's natural resources. Study of X-ray Astronomy. Periodic calibration of PSLV tracking radar located at tracking stations.
Weight : 920 kg
onboard power : 817 Watts
Communication : S-band
Stabilization : Three axis body stabilized
RCS : Combinations of bladder type and surface tension type mass expulsion monopropellant hydrazine system
Payload : WideField Sensor (WiFS), Modular Opto - electronic Scanner (MOS), Indian X-ray Astronomy Experiment (IXAE), C-band transponder(CBT)
Launch date : March 21, 1996
Launch site : SHAR Centre, Sriharikota, India
Launch vehicle : PSLV-D3
Orbit : 817 km. Circular polar sun-synchronous with equatorial crossing at 10.30 am (descending node)
Inclination : 98.68o
Repetivity : WiFS : 5 days
Mission completed during : January 2006
__________________________
IRS-P3 (Indian Remote-Sensing Satellite-P3)
IRS-P3 is an ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) experimental EO (Earth Observation) mission, a follow-up mission to IRS-P2, considered to be preoperational and serving in parallel for technology evaluation and scientific methodology studies. A portion of the payload is provided by DLR (German Aerospace Center) in the framework of a cooperative agreement between ISRO and DLR. In addition, DLR provides data reception support (Neustrelitz) and launch phase support. The objectives of the mission are:
• Technological test of the PSLV launch vehicle
• Scientific remote sensing applications and algorithm development based on joint interpretation of MOS and WiFS data
• Preoperational test of data processing and algorithm concepts
• Radioastronomy experiments using the X-ray payload
Spacecraft:
The IRS-P3 spacecraft structure is of IRS-P2 heritage. The bus design consists of four vertical panels and two horizontal decks supported on a central load-bearing cylinder of 930 mm diameter and 1188 mm height. The payload is accommodated on the outer side of the upper deck, it is oriented in flight direction. The onboard power generation is achieved by a pair of deployable, sun-tracking, uncanted solar panels (9.636 m2), which generates a power of 873 W. Two NiCd batteries (21 Ah/24 Ah) cater to the eclipse and peak load demands.
The S/C is three-axis stabilized. The AOCS employs Earth sensors, sun sensors and dynamically tuned gyros as attitude sensors; actuation is provided by reaction wheels, magnetic torquers and an RCS (Reaction Control System). An Earth pointing accuracy of better than 0.20º in all axes and better than 0.05º in all axes for stellar pointing (X-ray observation mode) is provided. In addition to these attitude sensors, AOCS also employs a star sensor in control loop in order to maintain the attitude during stellar pointing mode. The star sensor is an area array CCD imager of 288 x 384 pixels (FOV of 6º x 8º). It works as a star tracker with respect to a set of optical stars, identified a priori in conjunction with the X-ray package. The star sensor is mounted on positive roll axis and co-aligned with the X-ray payload's optical axis. When the spacecraft is inertially oriented and locked to a specified X-ray source, the star sensor works in a static mode. Therefore, the star sensor always locks to a specific scene about the roll axis. 1) 2)
Total S/C mass = 922 kg, a hydrazine propulsion system (84 kg of fuel sufficient for three years) with 16 thrusters is used for orbit maintenance.
Launch: A launch of IRS-P3 took place on March 21, 1996 on an ISRO PSLV-D3 (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle-Developmental flight 3) launcher from SHAR (Sriharikota Range), India, a launch site on India's east coast, representing the second successful test launch of PSLV. 3)
Orbit: Sun-synchronous circular orbit, altitude = 817 km, inclination = 98.7º, repeat cycle = 24 days, period = 101.35 min, local equatorial crossing at 10:30 hours on a descending node.
RF communications: The TT&C-system is operating in S-band with PCM/FSK/FM/PM modulation. The telemetry system uses PCM/PSK modulation in S-band (2203 MHz). The payload data is transmitted in S-band (2280 MHz) with BPSK modulation at a data rate of 5.2 Mbit/s. The spacecraft features in addition a C-band transponder (CBT) which acts as a dynamic target for calibrating PCMC (Precision Coherent Monopulse C-band) radars, supporting the Indian launches.
MOS instrument science data are being received at the following ground stations:: Hyderabad (ISRO, India), Neustrelitz (DLR, Germany), Maspalomas (ESA, Spain - since 1998), Wallops Island (NASA, USA - since April 1999).
Mission status:
Mission operations of the spacecraft at ISRO were terminated in the fall of 2004. The operational life of the spacecraft represented more than twice the design life of 3 years.
• In the fall of 2003, IRS-P3 encountered increasing energy problems (insufficient electrical power) and also orbit maintenance problems (the equatorial crossing time moved into the early morning hours between 8 and 9 AM).
• The contracts for MOS data reception (DLR, ESA, and NASA) were terminated for the end of 2003, this meant also the near end for MOS instrument operations.
• There were only sporadic MOS data receptions in 2004 (for instance, ESA had its last MOS data reception in March of 2004). DLR declared the final end of MOS operations as of May 31, 2004. ISRO continued operations of the IRS-P3 spacecraft until the fall of 2004. 4)
http://archive.is/V69Fl/6eb772463fea577965ef12061339aeb48244fd12.jpg ; https://archive.is/V69Fl/bd23946713e16a75469c3d990cd608301adf4537/scr.png ; http://web.archive.org/web/20200624...0-b48b21191bf2&groupId=163813&t=1338992697541
▲ 1. The IRS-P3 spacecraft during pre-launch tests.
__________________________
History of On-orbit Satellite Fragmentations, 15th Edition - NTRS
4 July 2018
Orbital Debris Program Office
Since the 14th edition (information cut-off date of 1 August 2007, published in June 2008) there have been 41 identified on-orbit breakups and 18 anomalous events (new or discerned), for a historical total of 242 fragmentations and 78 anomalous events.
Satellite breakups
IRS B3
Int'l Code: 1996-017A
NORAD ID: 23827
SATELLITE DATA
TYPE: Payload
OWNER:India
LAUNCH DATE:21 March 1996
DRY MASS (KG):838
MAIN BODY:Cubical box; 1.6 m x 1.6 m by 1.2 m high
MAJOR APPENDAGES:Solar panels
ATTITUDE CONTROL:three-axis stabilized; reaction wheels, torque rods, and monopropellant reaction control system
EVENT DATA
KNOWN EVENTS: 1
FIRST DATE: October 2000
APOGEE 821.9 km
PERIGEE 820.3 km
PERIOD 101.3 min
INCLINATION 98.6 deg
COMMENTS
A single relatively high area-to-mass ratio object has been cataloged. “Event Data” epoch is 30 October 2000. Unless other evidence is uncovered, this event will be classified as an anomalous event. The payload was operational at the of separation and was decommissioned in January 2006.
__________________________
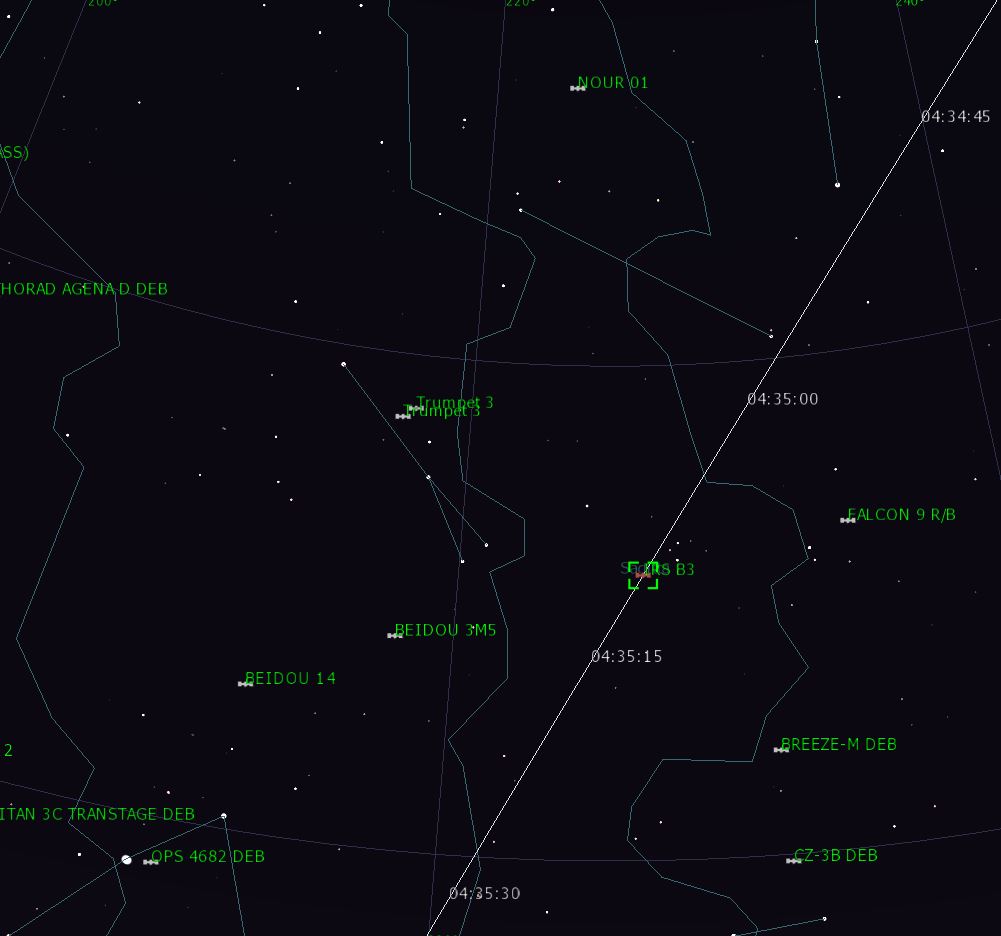
The latest attempt to catch the most elusive Iranian Noor-1 satellite and its mysterious 3rd stage QASED R/B (Arash 24 solid motor) was unsuccessful due to the proximity of the dawn, but the frame has easily captured along the Chinese Shijian-16, a much brighter Indian space zombie, or what is now left of the wreckage of the late
IRS P3 Remote sensing satellite, with a large RCS of 2.718 m2.
Very high noise level of the camera sensor caused by the current record heatwave (38C degrees in the arctic this week or 17C degrees above the average June level).
Two Line Element Set (TLE):
IRS B3
1 23827U 96017A 20175.58883364 -.00000010 00000-0 15577-4 0 9996
2 23827 98.8463 124.5706 0004536 92.7198 267.4498 14.22619133259144
http://archive.vn/ClLQv/1e5a1e39a4c6bd1f3979e9996deed7f1c43d6136.jpg ; https://archive.vn/ClLQv/b0ffe4846fa81e892393ff5447a3a136fe0cc868/scr.png ; http://web.archive.org/web/20200624185544/https://i.imgur.com/uSuoNHw.jpg
▲ 2. IRS P3 predicted pass: Magnitude ~4.9 (v), Altitude ~820 km, Distance ~967 km, Size ~2 m x 3.5 m, Angular size ~00.7''.
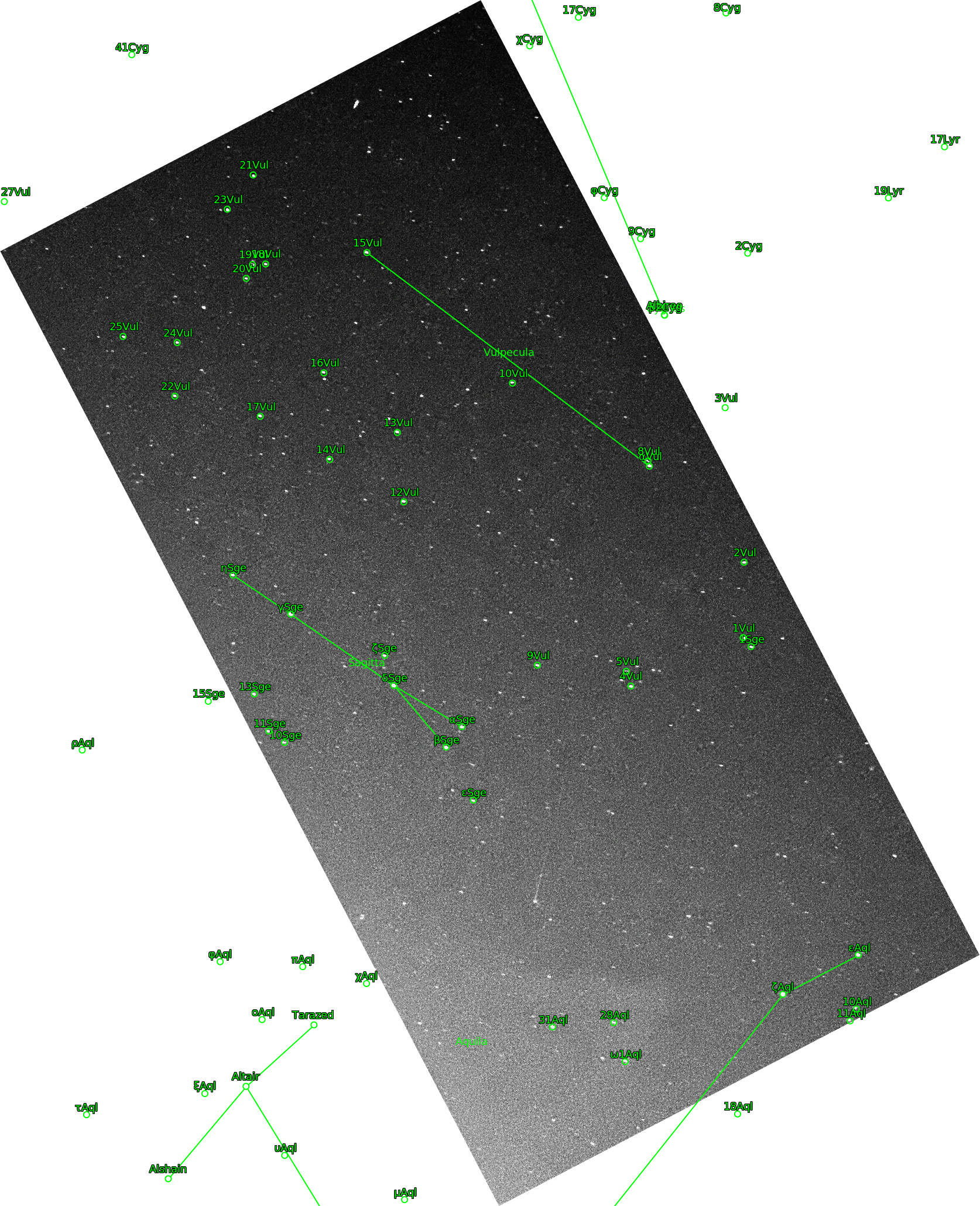
IRS P3 pass caught on camera last night, and calibrated via
astrometry.net:
http://archive.vn/BKjHN/8ad0114a50382eae5a4d12175359cffb4901a289.jpg ; https://archive.vn/BKjHN/42cc2ea205ec3cf8da0f4840e184f447e67dcc40/scr.png ; http://web.archive.org/web/20200624185818/https://i.imgur.com/CDflM5E.jpg ; http://nova.astrometry.net/annotated_full/4336737 ; http://nova.astrometry.net/user_images/3771175#annotated
▲ 3. IRS P3 pass as captured on camera.
TAGS:
BGUSAT, Kwangmyongsong-4, GOSAT-2, Yaogan 25A/25B/25C, FIA-Radar 5, KWANGMYONGSONG R/B, IRS P3

. But I can assure you, us Pakistanis will catch up soon.