Source of major pollutant in China's smog revealed
Source: Xinhua | 2016-12-22 04:06:25 | Editor: huaxia
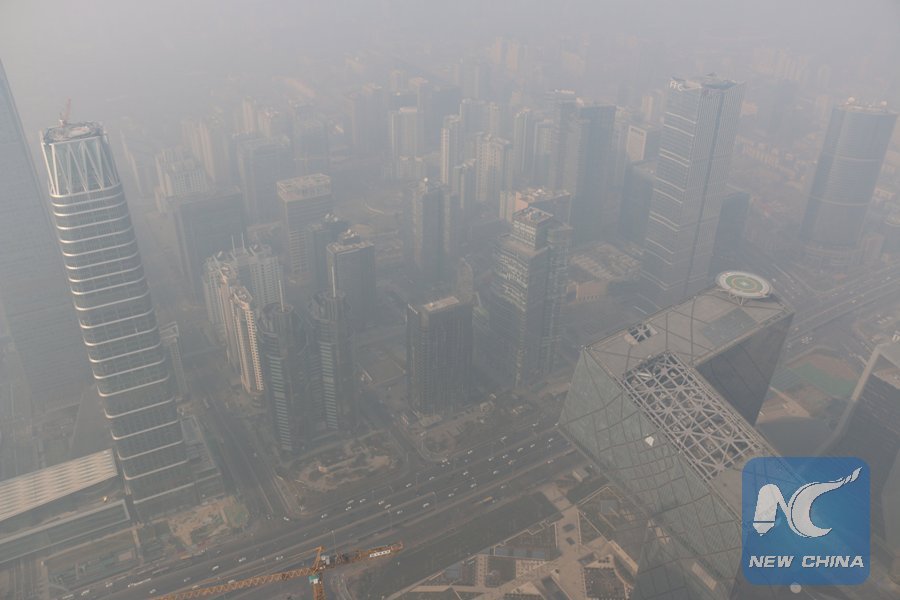
Photo taken on Dec. 17, 2016 shows buildings enveloped in smog in Beijing, capital of China. Beijing activated its first red alert for smog this winter on Friday. (Xinhua/Jin Liangkuai)
WASHINGTON, Dec. 21 (Xinhua) -- Scientists said Wednesday they have solved the perplexing puzzle of how a major smog component, known as sulfate, forms during haze events in northern China, including Beijing.
The study, published in the U.S. journal Science Advances, identified reactive nitrogen chemistry and water particles in the air as the two missing pieces, suggesting that reducing nitrogen oxide (NOx) emission in particular may help curb China's air pollution.
The findings were based on an analysis of the January 2013 winter haze event in Beijing, one of the worst atmospheric pollution events ever recorded in China, which saw the daily concentration of fine particle called PM2.5 exceed the World Health Organization guideline value by 16 times.
At that time, researchers performed aerosol measurements on the roof of a Tsinghua University building in Beijing and analyzed data throughout the surrounding regions.
They identified a reaction pathway that could account for the missing source of sulfate, discovering that fine water particles in the air acted as an reactor, trapping sulfur dioxide (SO2) molecules and interacting with nitrogen dioxide (NO2) to form sulfate.
The reaction rate was further facilitated by stagnant weather in the 2013 haze event, which trapped NO2 near the Earth's surface, resulting in NO2 concentrations that were three fold higher than clean conditions.
This process, according to the researchers, was "self-amplifying," as increasing aerosol mass concentrations led to higher aerosol water content -- accelerating the accumulation of sulfate and causing more severe haze pollution.
"This study unfolds the unique sulfate formation mechanism in NCP (North China Plain) haze events, which differs from traditional scenarios," study author Guangjie Zheng of Tsinghua University said in an email to Xinhua.
"In cleaner environments such as the U.S. or Europe, sulfate is mainly formed through the traditional OH (hydroxide) reaction pathways in atmospheric gas phase, or the H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide) and O3 (Ozon) reaction pathways in cloud chemistry. In NCP haze events, however, the dominant sulfate formation pathway shifts into the NO2 reaction pathway in aerosol water."
Zheng said results in this research reveal "the complex nature" of haze pollution events in China.
"The SO2 comes mainly from power plants, NOx is from power plants and mobile vehicles, while the NH3 (ammonia) and mineral dusts, which serve as the neutralizing substances, are from both natural and anthropogenic emissions such as industry and fugitive dusts," she said.
"These pollutants from various sources were emitted in high intensity at the same time, resulting in the unique heavy haze conditions, and thus the shifting in the dominant sulfate formation pathway. The complexity of haze pollutions in NCP further illustrated the importance of scientific emission-reduction strategies."
For example, reductions of NO2 and nitric oxide, which can react in the air to become NO2, are expected to lower sulfate pollution levels much more than anticipated by traditional air quality models.
These results "will need to be considered in future air quality and pollutant emission control strategies in northern China, and perhaps also in other regions," the reseachers concluded in their paper.
Paper:
Yafang Cheng, Guangjie Zheng, Chao Wei, Qing Mu, Bo Zheng, Zhibin Wang, Meng Gao, Qiang Zhang, Kebin He, Gregory Carmichael, Ulrich Pöschl and Hang Su. "Reactive nitrogen chemistry in aerosol water as a source of sulfate during haze events in China",
Science Advances 21 Dec 2016; DOI:
10.1126/sciadv.1601530
Abstract
Fine-particle pollution associated with winter haze threatens the health of more than 400 million people in the North China Plain. Sulfate is a major component of fine haze particles. Record sulfate concentrations of up to ~300 μg m−3 were observed during the January 2013 winter haze event in Beijing. State-of-the-art air quality models that rely on sulfate production mechanisms requiring photochemical oxidants cannot predict these high levels because of the weak photochemistry activity during haze events. We find that the missing source of sulfate and particulate matter can be explained by reactive nitrogen chemistry in aerosol water. The aerosol water serves as a reactor, where the alkaline aerosol components trap SO2, which is oxidized by NO2 to form sulfate, whereby high reaction rates are sustained by the high neutralizing capacity of the atmosphere in northern China. This mechanism is self-amplifying because higher aerosol mass concentration corresponds to higher aerosol water content, leading to faster sulfate production and more severe haze pollution.











 。该产品的问世,彻底打破国内万瓦级光纤激光器依赖进口的局面,使得国产万瓦光纤激光器水平再上新台阶。
。该产品的问世,彻底打破国内万瓦级光纤激光器依赖进口的局面,使得国产万瓦光纤激光器水平再上新台阶。









