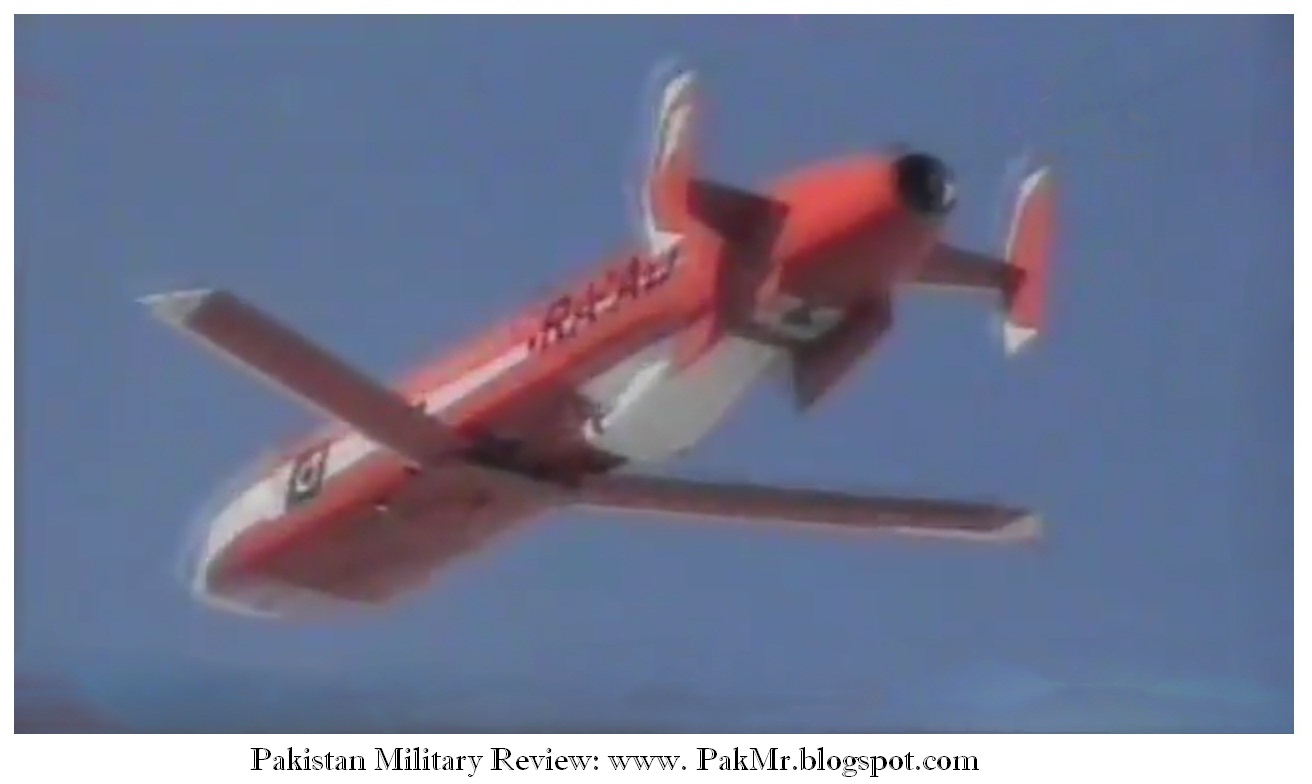
Cruise Missile Hatf-VIII (RAAD) and Torgos
Torgos Cruise Missile
Description:
Torgos is a long-range, precision-guided strike missile, designed to neutralise enemy targets such as hardened aircraft shelters, bunkers and command-and-control centres at extended stand-off ranges. Pinpoint accuracy is achieved by using advanced navigation and autonomous terminal-guidance technology. It will use GPS-INS midcourse guidance, but also has thermal imaging terminal seeker that can operate autonomously, or allow remote control over a data link.
The weapon was derived from the MUPSOW programme. It is not known if Mupsow has entered SAAF service.
The Ra'ad
The Ra'ad (Arabic: رعد‎

(English: Thunder) is an air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) developed by Pakistan and operational with the Pakistan Air Force (PAF). Though initially launched from a PAF Dassault Mirage III ROSE combat aircraft during testing, the missile is planned to be integrated with and launched from other PAF platforms such as the JF-17 combat aircraft. The Ra'ad's current range is stated to be 350 km.[1]
The Ra'ad's airframe is designed with stealth capability,[4][5] provided by the shape of the airframe and the materials used in its construction, to give the missile a low detection probability and allow it to penetrate enemy air defence systems.[1] Designed to carry conventional or nuclear warheads, the missile would most likely be used for precision air strikes on enemy command centres, radars, surface to air missile launchers, ballistic missile launchers and stationary warships.[6]
discussed earlier--
AGM-158 JASSM
Storm Shadow
KEPD 350














 (English: Thunder) is an air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) developed by Pakistan and operational with the Pakistan Air Force (PAF). Though initially launched from a PAF Dassault Mirage III ROSE combat aircraft during testing, the missile is planned to be integrated with and launched from other PAF platforms such as the JF-17 combat aircraft. The Ra'ad's current range is stated to be 350 km.[1]
(English: Thunder) is an air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) developed by Pakistan and operational with the Pakistan Air Force (PAF). Though initially launched from a PAF Dassault Mirage III ROSE combat aircraft during testing, the missile is planned to be integrated with and launched from other PAF platforms such as the JF-17 combat aircraft. The Ra'ad's current range is stated to be 350 km.[1]







