Hindustani78
BANNED

- Joined
- Apr 8, 2014
- Messages
- 40,471
- Reaction score
- -47
- Country
- Location
19:26 Nov. 1, 2016
Russia hastily revamps Soviet missile and radar bases in Crimea – Reuters (photo)
Reuters published an important investigation titled "Putin's Russia: In Crimea, Russia signals military resolve with new and revamped bases"
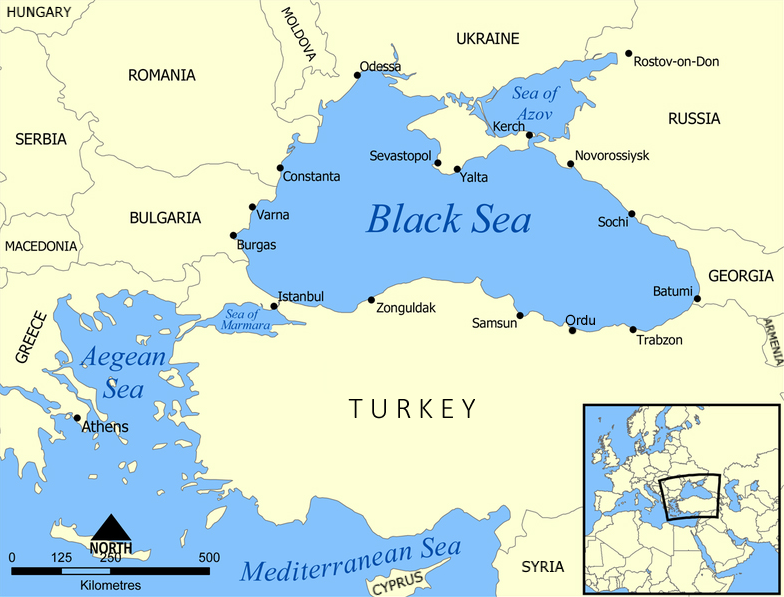
SIMFEROPOL, Crimea – The missile bunkers that dot the verdant hills along Crimea's southern coast are known locally as Object 100. Until recently, tourists paid USD 50 to visit the crumbling and abandoned former Soviet sites, which served during the Cold War as a defence against naval attack from the Black Sea.
Now the bunkers are coming back online. After Russia took control of Crimea from Ukraine in 2014, signs went up in the woods around the sites warning visitors against entering a "forbidden zone of the Russian Ministry of Defence." A resident of a nearby village who said he was employed at the base last year said Russian soldiers had re-occupied the sites and blocked roads leading into the area. He was unable to say when the Russian soldiers arrived.
"It is a functioning military base with an anti-ship missile system," the villager told a Reuters reporter who visited the area in July.
ON THE LOOKOUT: A Russian radar installation near an airfield in the village of Novofedorovka, Crimea, July 6, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

The bunkers are just one small part of a new Russian programme to militarize the Crimean peninsula. Based on recent site observations by Reuters, accounts from locals, media reports and official Russian data, Moscow has reanimated multiple Soviet-built facilities in the region, built new bases and stationed soldiers there.
Crimea sits at the southern end of a line of new and refurbished Russian military facilities that stretches north in an arc through western Russia and ends in the country's Baltic outpost of Kaliningrad.
The military build-up is echoed in NATO countries such as Poland and the Baltic states, where U.S. forces are beefing up patrols and conducting more frequent exercises.
Spurred on by years of growing mutual distrust and in particular the conflict in Ukraine, both Russia and NATO are boosting their military capabilities across eastern Europe, prompting officials such as Polish President Andrzej Duda and Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev to talk of a return to open hostilities.
"We have, in effect, slid into a new Cold War," Medvedev told a security conference in Munich in February.
BUILDUP: Military vehicles near an airfield in Dzhankoy, Crimea, July 7, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

To be sure, the scale of the military confrontation is not the same. Disarmament deals in the past three decades have lowered the temperature of the nuclear confrontation. Absent too are the hundreds of thousands of troops who were stationed on either side of the Iron Curtain in eastern Europe during the Cold War. But elements of the conventional military standoff are now returning.
Crimea is one of the starkest examples. In a week touring the region, a Reuters reporter saw 18 sites, including naval bases, radar stations and airfields. Some were entirely new, some were old military sites that had been refurbished, and others were in the process of being refurbished.
Moscow has made no secret of its build-up in Crimea. But Reuters' observations, combined with the other information, shed light on its scale.
Britain's Defence Minister Michael Fallon said in September that London was concerned about military build-up in Crimea "and indeed the militarisation of the Black Sea region generally. Both Bulgaria and Romania feel very threatened."
INCREASED PRESENCE: Servicemen at a Russian military base in the village of Perevalne, Crimea, July 4, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

Crimea is now the closest Russian-controlled territory to NATO member Romania, which since May has hosted part of a U.S.-controlled international missile shield. The project is scheduled to become operational in late 2018, when work on a radar installation in Poland – the other main land-based component in the shield – is completed.
Washington says the shield is designed as a defence against Iranian missile strikes. But Russian President Vladimir Putin says the system and NATO are both threats to Russia's security, and has promised to retaliate.
Russia's defence ministry did not respond to a request for comment about its activities in Crimea. Nor did the regional government in Crimea.
UNDER CONSTRUCTION: A new building near a Russian military facility in the village of Perevalnoye, Crimea, July 4, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

RING OF RADARS
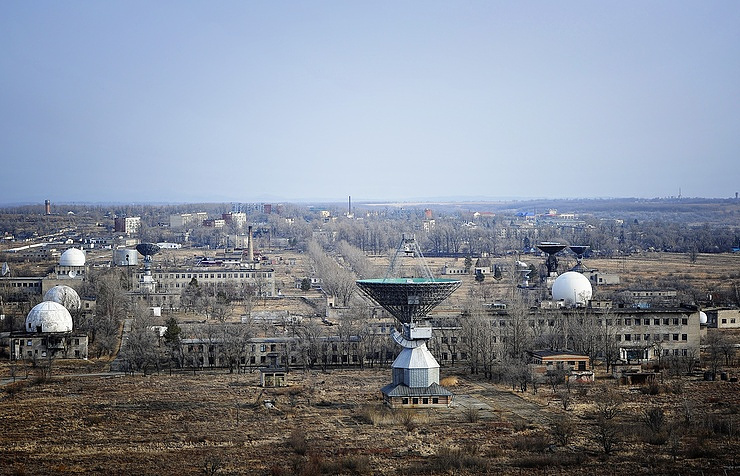
One part of Russia's expansion programme appears to be an attempt to re-create a chain of radar stations on rocky hilltops around Crimea. These stations offer an ideal vantage point for monitoring the Black Sea, and nearby NATO members Turkey, Bulgaria and Romania.
One of the stations – a facility with four revolving radars each encased in a large white dome – sits halfway up a mountain near the Crimean seaside town of Feodosiya. Built in Soviet times, the station had been abandoned by the Ukrainian military.
Now the Russian armed forces have moved in. In July, two green Russian military vehicles with tall antennas were parked beneath the radars. "There is a military base here, air defence system and missiles," said a man who lives in a village about 300 metres from the base. "There are air defence systems on every cape here."
Further around the coast, on the outskirts of the port city of Sevastopol, sits another radar station, called "Dnepr." Built by Soviet engineers, the station was out of order for years before the Russian annexation. A Reuters reporter saw dozens of soldiers in Russian military uniforms inside the base and guarding the perimeter.
TENTS: A Russian military base in Sevastopol, Crimea, July 5, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

Behind three lines of perimeter fencing were two structures, each around 300 meters long, with sloping sides partially covered by black metal sheets. The structures match archive images showing the Dnepr radar system. A Russian flag flew from the roof of a building near the two radar structures.
A sentry said that a nearby lighthouse that used to be a tourist attraction was now part of a military base and off limits to the public.
Russian newspaper ‘Izvestiya' quoted a military source in May as saying Moscow will restore the Dnepr station so it can "detect launches of ballistic, cruise and hypersonic missiles from the Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea area."
The Russian defence ministry did not respond to questions about the radar station.
NEW SCHOOLS AND SWIMMING POOLS
The Russian military build-up seen by Reuters goes beyond what existed in Crimea when it was under the control of Kiev, according to soldiers in Crimea, local residents and Ukrainian accounts of deployments before the annexation.
At Perevalne, a small village at the foot of a mountain not far from Simferopol in the centre of the peninsula, Russia is transforming an abandoned Ukrainian military facility into two new bases.
Inside the fenced perimeter of one in August, stood two 500-metre-long green hangars into which military vehicles drove. Nearby, trucks rumbled between a huge concrete plant and a construction site that will become a second base.
NEW USE: A Russian airforce plane parked at Belbek airport, formerly a civlian facility, near Sevastopol, Crimea, July 5, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

According to documents lodged by the defence ministry on the official website for public procurement tenders, one of the two bases will be for coast guards and the other for artillery units.
The ministry documents, which were lodged from October 2014, indicate the combined projects will include dormitories for more than 1,000 soldiers, residential buildings with more than 300 apartments, an ammunition depot, hangars for more than 500 military vehicles, an artillery range and dining facilities.
A new school and a kindergarten with a pool, as well as barracks for a military orchestra, are also planned, the documents show.
The ministry did not respond to questions about the Perevalne base.
BASES EXPANDING
Before Russia annexed Crimea, Moscow leased facilities from the Ukrainian state to house its Black Sea fleet, which has been based in Crimea for more than two centuries. Those facilities, mainly around Sevastopol, are now being expanded.
In one bay on the outskirts of the city, according to procurement documents, the Russian military is building a training centre for naval divers. There will also be a mooring area and an aircraft runway that has been unused for 20 years will be brought back into service.
From the perimeter fence, a Reuters reporter saw concrete taxiways, large cranes, and work underway to reinforce the shoreline.
The ministry did not reply to questions about the plans for that site.
MONITORING: Radar domes at a Russian military facility near Feodosia, Crimea, July 7, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

Most of the expansion in Crimea is being carried out by the Russian navy and ground forces. But air capabilities are also being beefed up.
The former Belbek civilian airport has been turned into a military air base, according to a Reuters reporter who went to the base. The terminal building has been shut and the entrance to the base is now guarded by a Russian marine.
An Il-76 heavy military transport plane, with the insignia of the Russian air force, was parked on the airfield when Reuters visited.
Two other military airfields that were abandoned by the Ukrainians are also now in use again by the Russian military. At the Novofedorivka airfield, in a coastal village to the north of Sevastopol, a Reuters reporter saw half a dozen dark-grey SU-30 fighter jets and light-grey SU-24 frontline bombers.
At the other recommissioned air base, in Dzhankoy, 40 km south of the de facto border separating Crimea from Ukrainian-controlled territory, Russian servicemen in blue uniform came and went throughout the day. Seven MI-24 attack helicopters were parked on the airfield.
"There were just two airplanes here when Ukraine ruled. And look at this place now, you can see much more here," a young soldier told Reuters at the checkpoint.
The defence ministry did not respond to questions about the air bases.

Russia hastily revamps Soviet missile and radar bases in Crimea – Reuters (photo)
Reuters published an important investigation titled "Putin's Russia: In Crimea, Russia signals military resolve with new and revamped bases"
SIMFEROPOL, Crimea – The missile bunkers that dot the verdant hills along Crimea's southern coast are known locally as Object 100. Until recently, tourists paid USD 50 to visit the crumbling and abandoned former Soviet sites, which served during the Cold War as a defence against naval attack from the Black Sea.
Now the bunkers are coming back online. After Russia took control of Crimea from Ukraine in 2014, signs went up in the woods around the sites warning visitors against entering a "forbidden zone of the Russian Ministry of Defence." A resident of a nearby village who said he was employed at the base last year said Russian soldiers had re-occupied the sites and blocked roads leading into the area. He was unable to say when the Russian soldiers arrived.
"It is a functioning military base with an anti-ship missile system," the villager told a Reuters reporter who visited the area in July.
ON THE LOOKOUT: A Russian radar installation near an airfield in the village of Novofedorovka, Crimea, July 6, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

The bunkers are just one small part of a new Russian programme to militarize the Crimean peninsula. Based on recent site observations by Reuters, accounts from locals, media reports and official Russian data, Moscow has reanimated multiple Soviet-built facilities in the region, built new bases and stationed soldiers there.
Crimea sits at the southern end of a line of new and refurbished Russian military facilities that stretches north in an arc through western Russia and ends in the country's Baltic outpost of Kaliningrad.
The military build-up is echoed in NATO countries such as Poland and the Baltic states, where U.S. forces are beefing up patrols and conducting more frequent exercises.
Spurred on by years of growing mutual distrust and in particular the conflict in Ukraine, both Russia and NATO are boosting their military capabilities across eastern Europe, prompting officials such as Polish President Andrzej Duda and Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Medvedev to talk of a return to open hostilities.
"We have, in effect, slid into a new Cold War," Medvedev told a security conference in Munich in February.
BUILDUP: Military vehicles near an airfield in Dzhankoy, Crimea, July 7, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

To be sure, the scale of the military confrontation is not the same. Disarmament deals in the past three decades have lowered the temperature of the nuclear confrontation. Absent too are the hundreds of thousands of troops who were stationed on either side of the Iron Curtain in eastern Europe during the Cold War. But elements of the conventional military standoff are now returning.
Crimea is one of the starkest examples. In a week touring the region, a Reuters reporter saw 18 sites, including naval bases, radar stations and airfields. Some were entirely new, some were old military sites that had been refurbished, and others were in the process of being refurbished.
Moscow has made no secret of its build-up in Crimea. But Reuters' observations, combined with the other information, shed light on its scale.
Britain's Defence Minister Michael Fallon said in September that London was concerned about military build-up in Crimea "and indeed the militarisation of the Black Sea region generally. Both Bulgaria and Romania feel very threatened."
INCREASED PRESENCE: Servicemen at a Russian military base in the village of Perevalne, Crimea, July 4, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

Crimea is now the closest Russian-controlled territory to NATO member Romania, which since May has hosted part of a U.S.-controlled international missile shield. The project is scheduled to become operational in late 2018, when work on a radar installation in Poland – the other main land-based component in the shield – is completed.
Washington says the shield is designed as a defence against Iranian missile strikes. But Russian President Vladimir Putin says the system and NATO are both threats to Russia's security, and has promised to retaliate.
Russia's defence ministry did not respond to a request for comment about its activities in Crimea. Nor did the regional government in Crimea.
UNDER CONSTRUCTION: A new building near a Russian military facility in the village of Perevalnoye, Crimea, July 4, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

RING OF RADARS
One part of Russia's expansion programme appears to be an attempt to re-create a chain of radar stations on rocky hilltops around Crimea. These stations offer an ideal vantage point for monitoring the Black Sea, and nearby NATO members Turkey, Bulgaria and Romania.
One of the stations – a facility with four revolving radars each encased in a large white dome – sits halfway up a mountain near the Crimean seaside town of Feodosiya. Built in Soviet times, the station had been abandoned by the Ukrainian military.
Now the Russian armed forces have moved in. In July, two green Russian military vehicles with tall antennas were parked beneath the radars. "There is a military base here, air defence system and missiles," said a man who lives in a village about 300 metres from the base. "There are air defence systems on every cape here."
Further around the coast, on the outskirts of the port city of Sevastopol, sits another radar station, called "Dnepr." Built by Soviet engineers, the station was out of order for years before the Russian annexation. A Reuters reporter saw dozens of soldiers in Russian military uniforms inside the base and guarding the perimeter.
TENTS: A Russian military base in Sevastopol, Crimea, July 5, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

Behind three lines of perimeter fencing were two structures, each around 300 meters long, with sloping sides partially covered by black metal sheets. The structures match archive images showing the Dnepr radar system. A Russian flag flew from the roof of a building near the two radar structures.
A sentry said that a nearby lighthouse that used to be a tourist attraction was now part of a military base and off limits to the public.
Russian newspaper ‘Izvestiya' quoted a military source in May as saying Moscow will restore the Dnepr station so it can "detect launches of ballistic, cruise and hypersonic missiles from the Black Sea and Mediterranean Sea area."
The Russian defence ministry did not respond to questions about the radar station.
NEW SCHOOLS AND SWIMMING POOLS
The Russian military build-up seen by Reuters goes beyond what existed in Crimea when it was under the control of Kiev, according to soldiers in Crimea, local residents and Ukrainian accounts of deployments before the annexation.
At Perevalne, a small village at the foot of a mountain not far from Simferopol in the centre of the peninsula, Russia is transforming an abandoned Ukrainian military facility into two new bases.
Inside the fenced perimeter of one in August, stood two 500-metre-long green hangars into which military vehicles drove. Nearby, trucks rumbled between a huge concrete plant and a construction site that will become a second base.
NEW USE: A Russian airforce plane parked at Belbek airport, formerly a civlian facility, near Sevastopol, Crimea, July 5, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

According to documents lodged by the defence ministry on the official website for public procurement tenders, one of the two bases will be for coast guards and the other for artillery units.
The ministry documents, which were lodged from October 2014, indicate the combined projects will include dormitories for more than 1,000 soldiers, residential buildings with more than 300 apartments, an ammunition depot, hangars for more than 500 military vehicles, an artillery range and dining facilities.
A new school and a kindergarten with a pool, as well as barracks for a military orchestra, are also planned, the documents show.
The ministry did not respond to questions about the Perevalne base.
BASES EXPANDING
Before Russia annexed Crimea, Moscow leased facilities from the Ukrainian state to house its Black Sea fleet, which has been based in Crimea for more than two centuries. Those facilities, mainly around Sevastopol, are now being expanded.
In one bay on the outskirts of the city, according to procurement documents, the Russian military is building a training centre for naval divers. There will also be a mooring area and an aircraft runway that has been unused for 20 years will be brought back into service.
From the perimeter fence, a Reuters reporter saw concrete taxiways, large cranes, and work underway to reinforce the shoreline.
The ministry did not reply to questions about the plans for that site.
MONITORING: Radar domes at a Russian military facility near Feodosia, Crimea, July 7, 2016. REUTERS/Stringer

Most of the expansion in Crimea is being carried out by the Russian navy and ground forces. But air capabilities are also being beefed up.
The former Belbek civilian airport has been turned into a military air base, according to a Reuters reporter who went to the base. The terminal building has been shut and the entrance to the base is now guarded by a Russian marine.
An Il-76 heavy military transport plane, with the insignia of the Russian air force, was parked on the airfield when Reuters visited.
Two other military airfields that were abandoned by the Ukrainians are also now in use again by the Russian military. At the Novofedorivka airfield, in a coastal village to the north of Sevastopol, a Reuters reporter saw half a dozen dark-grey SU-30 fighter jets and light-grey SU-24 frontline bombers.
At the other recommissioned air base, in Dzhankoy, 40 km south of the de facto border separating Crimea from Ukrainian-controlled territory, Russian servicemen in blue uniform came and went throughout the day. Seven MI-24 attack helicopters were parked on the airfield.
"There were just two airplanes here when Ukraine ruled. And look at this place now, you can see much more here," a young soldier told Reuters at the checkpoint.
The defence ministry did not respond to questions about the air bases.