Both China and India can buy from Russia as india buying not only keeping in view of Pakistan but also for China than i dont think any problem for Pakistan to buy from Russia as our relations with Russian improving and only concern is do we have funds to pay.
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Information Pool & Analysis on Pakistan's AF Aspiration for Su-35 / Su-35S - FLANKER-E
- Thread starter omegalamba7XL9
- Start date
Lil Mathew
BANNED

- Joined
- Aug 19, 2013
- Messages
- 1,151
- Reaction score
- -5
- Country
- Location
Underground economy or black economy is the economy that is unrecorded and untaxed by its government.. Illegal activities live smuggling, local arms markets, kidnapping etc comprises illegal black market activities & businesses without records and taxation comprises legal black market activities.For a nation who just spent over US$ 4b on sacrificial animals in two days ....... I'd say ...... AFFORDABLE. LOLZ.
Ever heard of undocumented economy. Google it with Pakistan and be enlightened.
Please explain how your government can access this money?? If they can access it, it automatically becames legal white money..
Trumpcard
FULL MEMBER
- Joined
- Sep 28, 2015
- Messages
- 344
- Reaction score
- -3
- Country
- Location
Let them brag brother, they have their own logics! Indian housewives hold approx 11% of the worlds gold reserves but then we are always poorer than our neighbours who sacrifice animals worth billions of $.Underground economy or black economy is the economy that is unrecorded and untaxed by its government.. Illegal activities live smuggling, local arms markets, kidnapping etc comprises illegal black market activities & businesses without records and taxation comprises legal black market activities.
Please explain how your government can access this money?? If they can access it, it automatically becames legal white money..
You can always google and cross check about this figure.
Basel
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Oct 31, 2013
- Messages
- 9,503
- Reaction score
- 2
- Country
- Location
not only Canards , because the design infused in Su30MKI is from SU 37 TD and MKK designed infused from SU-35 Design. Even SU-35MKK have more bigger body then SU30 MKI for extra fuel.
Many changes in Airframe.
If MKI have design from Su-37 then why it had heavier nose? Because Su-35/37 are much lighter airframes and even with heavier radar they don't need canards for extra lift. MKI may got input from Su-37 design but it's not completely based on Su-37 airframe.
Alpha Fighter
FULL MEMBER

- Joined
- Jan 26, 2016
- Messages
- 367
- Reaction score
- -1
- Country
- Location
A) Well to make it more manoeuvrable and because of heavy radar on the noise alter the gravity.If MKI have design from Su-37 then why it had heavier nose? Because Su-35/37 are much lighter airframes and even with heavier radar they don't need canards for extra lift. MKI may got input from Su-37 design but it's not completely based on Su-37 airframe.
B) use of less Titanium based Allow to keep the cost at optimum, now u will see Super SU30MKI can carry more load but the weight of the plane will remain same.
Yes it got Technology / Design inputs from SU-37 that's why Russian also order SU-30MKI based planes for its own Airforce.
Muhammad Omar
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Feb 3, 2014
- Messages
- 13,557
- Reaction score
- 15
- Country
- Location
Na Su-35 aana hai na hi EFT chup Chaap J-11D lelo bhai China se...


Knight Rider
FULL MEMBER

- Joined
- Sep 14, 2014
- Messages
- 1,359
- Reaction score
- 1
- Country
- Location
PAF Loves SU-35 maneuverability  but its also an expensive horse to keep.
but its also an expensive horse to keep.
PAF has no more than two other options left because India is also buying New F\A-18s from US. PAF also needs to counter that threat.
One Option is Rafale. PAF has a lot of experience in maintaining French fighters.
Other Option is the Expensive Warhorse SU-35. Yes it is expensive but its pack a serious punch and great boost.
and great boost.
Whether it is SU-35 or Rafale both Aircrafts must be utilize for maritime patrol and to counter Indian aircraft carrier threat.
 but its also an expensive horse to keep.
but its also an expensive horse to keep.
PAF has no more than two other options left because India is also buying New F\A-18s from US. PAF also needs to counter that threat.
One Option is Rafale. PAF has a lot of experience in maintaining French fighters.
Other Option is the Expensive Warhorse SU-35. Yes it is expensive but its pack a serious punch
 and great boost.
and great boost.Whether it is SU-35 or Rafale both Aircrafts must be utilize for maritime patrol and to counter Indian aircraft carrier threat.
abdulbarijan
PDF THINK TANK: ANALYST

- Joined
- May 15, 2010
- Messages
- 1,251
- Reaction score
- 31
PAF Loves SU-35 maneuverabilitybut its also an expensive horse to keep.
PAF has no more than two other options left because India is also buying New F\A-18s from US. PAF also needs to counter that threat.
One Option is Rafale. PAF has a lot of experience in maintaining French fighters.
Other Option is the Expensive Warhorse SU-35. Yes it is expensive but its pack a serious punchand great boost.
Whether it is SU-35 or Rafale both Aircrafts must be utilize for maritime patrol and to counter Indian aircraft carrier threat.
Add in this beast to the wish list

MastanKhan
PDF VETERAN

- Joined
- Dec 26, 2005
- Messages
- 21,264
- Reaction score
- 165
- Country
- Location
P
Whether it is SU-35 or Rafale both Aircrafts must be utilize for maritime patrol and to counter Indian aircraft carrier threat.
Hi,
For that role---the JH7B is the best aircraft---.
_NOBODY_
SENIOR MEMBER

- Joined
- Jan 6, 2016
- Messages
- 3,314
- Reaction score
- 4
- Country
- Location
In terms of cost effectiveness JH7B is the best, and its capabilities are same as Flankers in this role.Hi,
For that role---the JH7B is the best aircraft---.
14 with SUs, may be. But more probable to get JFs. Bandits are more likely for SUs.A small briefing on the SU-35 for the PAF - Created by my friend Strike Sim.
Is it likely that the aircraft will go to No.14 sq if the deal ever materializes.
Michael Corleone
BANNED

- Joined
- Oct 27, 2014
- Messages
- 10,313
- Reaction score
- -5
- Country
- Location
I got a terrible headache now.Shouldve listened to your warning :-(
Major Shaitan Singh
SENIOR MEMBER

- Joined
- Dec 7, 2010
- Messages
- 3,550
- Reaction score
- 43
- Country
- Location
Multi-purpose fighter. A OKB im.P.O.Suhogo as the development of the Su-27 FLANKER. The general management of the establishment of the aircraft carried out by General Designer OKB Mikhail Simonov , head of the threads of the Su-27M was the chief designer (and the head of the theme of the Su-27) A.I.Knyshev and then - Nikolai Fedorovich Nikitin, hereinafter - the chief designer. In 1996, after the transition to work in N.F.Nikitina AMIC "Sukhoi", chief designer and head of the threads of the Su-27M and its modifications appointed Vladimir S. Konoha.
Development of multipurpose modifying the T-10M / Su-27M launched in early 1980 's,. In addition to optimizing for conducting highly maneuverable air combat aircraft also had the opportunity to engage ground targets with guided missiles. Formally, the plane belongs to the 4 ++ generation jet fighter aircraft, but according to some experts may be considered 5th generation aircraft. The Su-35 is the second generation in the early 2000s while wearing the name of Su-35BM ( "Great Upgrade"), which later ceased to be used. The term "T-10BM", most likely is not an official.
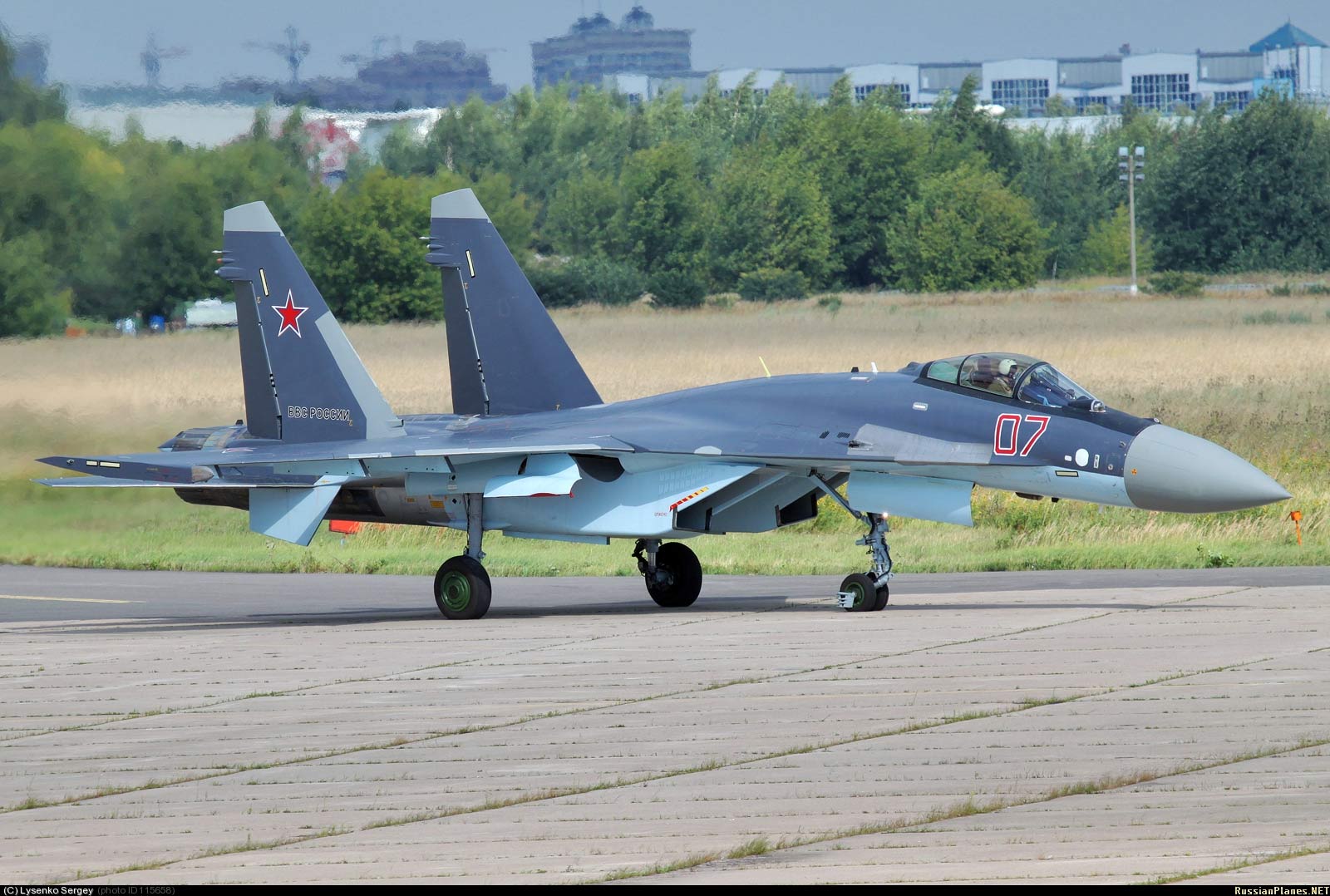

Su-35C aboard №07 Red Ramenskoye, July 2013 (photo - Sergei Lysenko, http://russianplanes.net/id115658 ).
Prehistory of the project . In 1982, it discontinued development of the radar with a slotted array antenna and the electronic beam scanning in the vertical plane of the "Sword", which was created in opposition to the radar AN / APG-63 F-15 aircraft. On the production Su-27 radar installed N001 with antenna Kassegreyna, which had no obvious advantages over the AN / APG-63 radar. At the same time, since 1983 the standard-fighter F-15C installed an improved version of AN / APG-63 with programmable signal processor and more advanced radar data processor and work began on the new AN / APG-70 radar with even higher performance for "dual-purpose" a fighter F-15E (1987 APG-70 station installed on F-15C). In contrast to these radar modified Su-27M was to be equipped with new radar with increased range and better noise immunity and the additional operating mode "air-surface". The development of radar, using the experience gained with the establishment of the radar "Sword", entrusted NIIP im.Tihomirova. The intended use of the latest achievements of digital computers.
In addition, in 1984 the United States began testing a new "air-to-air" guided missile medium-range AMRAAM (Advanced Medium Range Air-to -Air Missile)with a corrected inertial control system and active radar GOS. In 1989, a rocket called AIM-120A entered service Fighter F-15C / E, F- 16C, F-18C and F-14D. After analysis GosNIIAS MAP USSR American fighter capabilities with AIM-120C missiles compared to the Su-27 and MiG-29 to R-27 missiles became clear the need to create a national missile ARS. The absence of such missiles led to the fact that the Su-27 and MiG-29 is significantly inferior to the far missile combat American fighters F-15 and F-16, armed with missiles AIM-120A. On the basis of this decision on the establishment of the missile "air-air" medium-range with a new generation of ARS and ISU - the R-77 RVV-AE. The new missile was to join the arms modified fighter 4th generation Su-27M and MiG-29M, and then the other aircraft, including and promising fighter of the 5th generation.
Design . Thus by 1984 we defined the requirements for the modified Su-27M - ensuring excellence over the last version of the American F-15 and F-16 and make it multifunctional qualities. The basis of the solution of these problems has been equipping the aircraft new radar control system RCS-27, promising missiles "air-to-air" medium-range weapons with the ARS and to effectively engage ground targets. also planned to equip fighter avionics defense complex (the Su-27 were only the elements of the complex) and an upgraded navigation equipment. Upgrades also supposed to be subjected to display facilities - most of the sighting and flight-planned navigation information displayed on widescreen multifunctional displays on cathode ray tubes and advanced head-up displays on the windshield. December 29, 1983 decision of the USSR military industrial complex on the establishment of the Su -27M. In accordance with this decision OKB. Sukhoi has begun to develop conceptual fighter project. The work was done in the brigade fighters department EDO projects led M.A.Pogosyanom .
The general management of the program carried out by General Designer Mikhail Simonov . By plane, it was decided to implement a number of structural improvements, which took place in the mid-1980s on the flying laboratory testing of the Su-27 and Su-27UB. First of all, it concerns the use of canards (PGO), tested on the T-10-24, a modified remote control system and refueling in flight tested on T-10U-2. As the Su-27M was supposed to apply the modification of the AL-31F engines with increased thrust of up to 13,000 kg, and to further increase the flight range to ensure the use of drop tanks with a capacity of 2000 liters. In 1985 prepared preliminary design of the Su-27M. The composition of avionics entered radar control system RCS-27 electro-optical sighting and navigation system, electronic countermeasures set of complex communications equipment, instrumentation equipment guidance, remote control system, IFF transponder control, registration, alarm, etc. All the complexes envisaged widespread use of digital calculators.
Tests . The assembly of the first prototype of the T-10M-1 started at the pilot plant OKB. Sukhoi (Plant №51, MMZ "Pendant") in 1987. The prototype was built on the basis of the Su-27 serial production KnAAPO №16-40 release 1986 first flight of the T-10M-1 board made in №701 LII im.Gromova Ramenskoye June 28, 1988 The plane lifted into the air chief test pilot EDO Oleg G. Choi.

The first prototype of the Su-27M - T-10M-1 board №701 in the Museum of the Air Force in Monino, the beginning of the 1990s (photo - by Christian Waser,http://www.airwar.ru ).
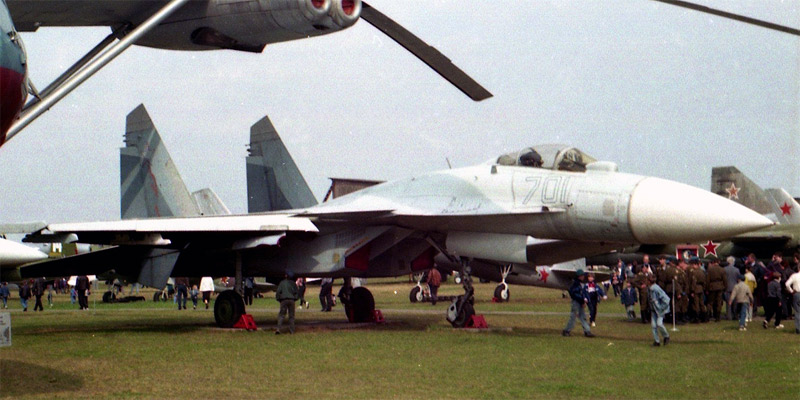

The first prototype of the Su-27M - T 10M-1 aboard the # 701 in the Air Force Museum in Monino, May 9, 1996 (photo - Valery Saveliev,http://russianplanes.net ).

The prototype of the T-10M-1 board # 701, Muzev Air Force in Monino, no later than 2004 g ( http://www.aviation.ru ).
January 18, 1989, to join the second testing experimental machine (T-10M-2 board №702). The second plane was also converted from serial Su-27. At the plant in Komsomolsk-on-Amur, preparations began for the release of the initial batch of modified fighter. the first production of the T-10M KnAAPO flew on 1 April 1992 (T-10M-3). Later, at the pilot plant retooled and T-10M-6 where a new FBWCS was installed. T-10M pilot production assembly had Unicycle front rack chassis -. Similar to the Su-27
total in 1989-1994 GG It produced 12 prototypes. May 29, 1992 approved the technical appearance of the Su-35 / Su-27M export type for demonstrations at international exhibitions and air shows. In 1995 he started serial production of Su-35 of KnAAPO (Komsomolsk-on-Amur), released 3 aircraft. Due to lack of demand both in Russia and abroad August 1, 1997 program to create the T-10M / Su-35 is closed in favor of the Su-37 engines with thrust vector control.Later Su-37 program also has been closed. Deliverables under the program T-10M used in the design of the Su-30MKK and Su-30MKI.
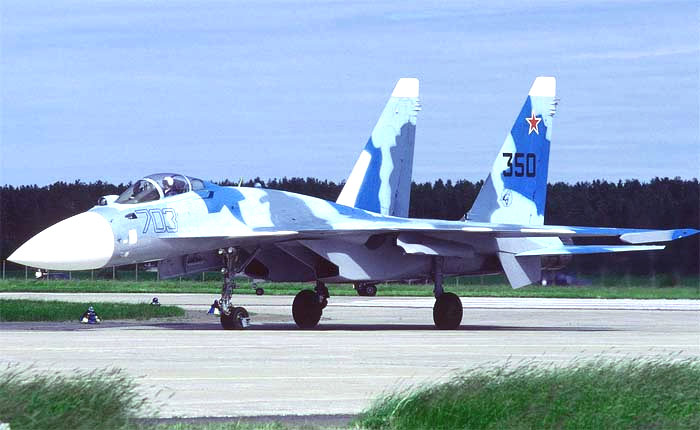


The first prototype of the original assembly KnAAPO - T-10M-3 / Su-35 board №703 (photo - Paul Nann and Huppunen Jukka, http://www.airwar.ru ).
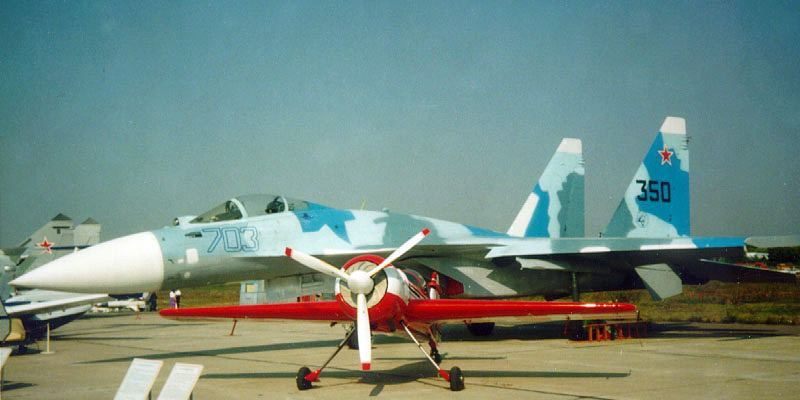

The first prototype of the original assembly KnAAPO - T-10M-3 / Su-35 board №703 on airshow MAKS-1995 Ramenskoye, August 1995 (photo - Maxim Bryansk, http://www.foxbat.ru/ ).
The second-generation Su-35 . In 2005, it decided to resume the development of the Su-35. In a series of aircraft will be known as the Su-35S. Mounting series production started on KnAAPO (Komsomolsk-on-Amur) in 2006. The assembly of the first prototype of the second-generation Su-35 - T-10BM board №901 completed in the summer of 2007 and the aircraft started ground tests. The first flight took place in im.Gromova LII airfield Ramenskoye February 19, 2008, the pilot - Sergey Bogdan. In early July 2008, it has already conducted KnAAPO assembly of the second and third Su-35 prototypes. The first prototype of the Su-35 №901 board made the first public demonstration flight in Ramenskoye 07.07.2008 In July 2008, announced as the start of serial production of Su-35 in 2011 - ostensibly to 2020 is planned to produce for different customers 160 aircraft of this brand (S.Korotkova statement, "dry"). The second flying prototype of the Su-35 flew on Dzemgi airfield in Komsomolsk-on-Amur, October 2, 2008 In February 2009, stated that the tests will soon be joining the third pre-series aircraft. As of March 23, 2009 Su-35BM aircraft carried out a total of 100 flights. The third flight prototype of the Su-35BM has been equipped with radar, in contrast to the first prototypes and other avionics, but the April 26, 2009 Su-35BM №904 board crashed at high speed on the jog Dzemgi airfield in Komsomolsk-on-Amur, due to a system failure motor control.
Development of multipurpose modifying the T-10M / Su-27M launched in early 1980 's,. In addition to optimizing for conducting highly maneuverable air combat aircraft also had the opportunity to engage ground targets with guided missiles. Formally, the plane belongs to the 4 ++ generation jet fighter aircraft, but according to some experts may be considered 5th generation aircraft. The Su-35 is the second generation in the early 2000s while wearing the name of Su-35BM ( "Great Upgrade"), which later ceased to be used. The term "T-10BM", most likely is not an official.

Su-35C aboard №07 Red Ramenskoye, July 2013 (photo - Sergei Lysenko, http://russianplanes.net/id115658 ).
Prehistory of the project . In 1982, it discontinued development of the radar with a slotted array antenna and the electronic beam scanning in the vertical plane of the "Sword", which was created in opposition to the radar AN / APG-63 F-15 aircraft. On the production Su-27 radar installed N001 with antenna Kassegreyna, which had no obvious advantages over the AN / APG-63 radar. At the same time, since 1983 the standard-fighter F-15C installed an improved version of AN / APG-63 with programmable signal processor and more advanced radar data processor and work began on the new AN / APG-70 radar with even higher performance for "dual-purpose" a fighter F-15E (1987 APG-70 station installed on F-15C). In contrast to these radar modified Su-27M was to be equipped with new radar with increased range and better noise immunity and the additional operating mode "air-surface". The development of radar, using the experience gained with the establishment of the radar "Sword", entrusted NIIP im.Tihomirova. The intended use of the latest achievements of digital computers.
In addition, in 1984 the United States began testing a new "air-to-air" guided missile medium-range AMRAAM (Advanced Medium Range Air-to -Air Missile)with a corrected inertial control system and active radar GOS. In 1989, a rocket called AIM-120A entered service Fighter F-15C / E, F- 16C, F-18C and F-14D. After analysis GosNIIAS MAP USSR American fighter capabilities with AIM-120C missiles compared to the Su-27 and MiG-29 to R-27 missiles became clear the need to create a national missile ARS. The absence of such missiles led to the fact that the Su-27 and MiG-29 is significantly inferior to the far missile combat American fighters F-15 and F-16, armed with missiles AIM-120A. On the basis of this decision on the establishment of the missile "air-air" medium-range with a new generation of ARS and ISU - the R-77 RVV-AE. The new missile was to join the arms modified fighter 4th generation Su-27M and MiG-29M, and then the other aircraft, including and promising fighter of the 5th generation.
Design . Thus by 1984 we defined the requirements for the modified Su-27M - ensuring excellence over the last version of the American F-15 and F-16 and make it multifunctional qualities. The basis of the solution of these problems has been equipping the aircraft new radar control system RCS-27, promising missiles "air-to-air" medium-range weapons with the ARS and to effectively engage ground targets. also planned to equip fighter avionics defense complex (the Su-27 were only the elements of the complex) and an upgraded navigation equipment. Upgrades also supposed to be subjected to display facilities - most of the sighting and flight-planned navigation information displayed on widescreen multifunctional displays on cathode ray tubes and advanced head-up displays on the windshield. December 29, 1983 decision of the USSR military industrial complex on the establishment of the Su -27M. In accordance with this decision OKB. Sukhoi has begun to develop conceptual fighter project. The work was done in the brigade fighters department EDO projects led M.A.Pogosyanom .
The general management of the program carried out by General Designer Mikhail Simonov . By plane, it was decided to implement a number of structural improvements, which took place in the mid-1980s on the flying laboratory testing of the Su-27 and Su-27UB. First of all, it concerns the use of canards (PGO), tested on the T-10-24, a modified remote control system and refueling in flight tested on T-10U-2. As the Su-27M was supposed to apply the modification of the AL-31F engines with increased thrust of up to 13,000 kg, and to further increase the flight range to ensure the use of drop tanks with a capacity of 2000 liters. In 1985 prepared preliminary design of the Su-27M. The composition of avionics entered radar control system RCS-27 electro-optical sighting and navigation system, electronic countermeasures set of complex communications equipment, instrumentation equipment guidance, remote control system, IFF transponder control, registration, alarm, etc. All the complexes envisaged widespread use of digital calculators.
Tests . The assembly of the first prototype of the T-10M-1 started at the pilot plant OKB. Sukhoi (Plant №51, MMZ "Pendant") in 1987. The prototype was built on the basis of the Su-27 serial production KnAAPO №16-40 release 1986 first flight of the T-10M-1 board made in №701 LII im.Gromova Ramenskoye June 28, 1988 The plane lifted into the air chief test pilot EDO Oleg G. Choi.

The first prototype of the Su-27M - T-10M-1 board №701 in the Museum of the Air Force in Monino, the beginning of the 1990s (photo - by Christian Waser,http://www.airwar.ru ).

The first prototype of the Su-27M - T 10M-1 aboard the # 701 in the Air Force Museum in Monino, May 9, 1996 (photo - Valery Saveliev,http://russianplanes.net ).

The prototype of the T-10M-1 board # 701, Muzev Air Force in Monino, no later than 2004 g ( http://www.aviation.ru ).
January 18, 1989, to join the second testing experimental machine (T-10M-2 board №702). The second plane was also converted from serial Su-27. At the plant in Komsomolsk-on-Amur, preparations began for the release of the initial batch of modified fighter. the first production of the T-10M KnAAPO flew on 1 April 1992 (T-10M-3). Later, at the pilot plant retooled and T-10M-6 where a new FBWCS was installed. T-10M pilot production assembly had Unicycle front rack chassis -. Similar to the Su-27
total in 1989-1994 GG It produced 12 prototypes. May 29, 1992 approved the technical appearance of the Su-35 / Su-27M export type for demonstrations at international exhibitions and air shows. In 1995 he started serial production of Su-35 of KnAAPO (Komsomolsk-on-Amur), released 3 aircraft. Due to lack of demand both in Russia and abroad August 1, 1997 program to create the T-10M / Su-35 is closed in favor of the Su-37 engines with thrust vector control.Later Su-37 program also has been closed. Deliverables under the program T-10M used in the design of the Su-30MKK and Su-30MKI.


The first prototype of the original assembly KnAAPO - T-10M-3 / Su-35 board №703 (photo - Paul Nann and Huppunen Jukka, http://www.airwar.ru ).

The first prototype of the original assembly KnAAPO - T-10M-3 / Su-35 board №703 on airshow MAKS-1995 Ramenskoye, August 1995 (photo - Maxim Bryansk, http://www.foxbat.ru/ ).
The second-generation Su-35 . In 2005, it decided to resume the development of the Su-35. In a series of aircraft will be known as the Su-35S. Mounting series production started on KnAAPO (Komsomolsk-on-Amur) in 2006. The assembly of the first prototype of the second-generation Su-35 - T-10BM board №901 completed in the summer of 2007 and the aircraft started ground tests. The first flight took place in im.Gromova LII airfield Ramenskoye February 19, 2008, the pilot - Sergey Bogdan. In early July 2008, it has already conducted KnAAPO assembly of the second and third Su-35 prototypes. The first prototype of the Su-35 №901 board made the first public demonstration flight in Ramenskoye 07.07.2008 In July 2008, announced as the start of serial production of Su-35 in 2011 - ostensibly to 2020 is planned to produce for different customers 160 aircraft of this brand (S.Korotkova statement, "dry"). The second flying prototype of the Su-35 flew on Dzemgi airfield in Komsomolsk-on-Amur, October 2, 2008 In February 2009, stated that the tests will soon be joining the third pre-series aircraft. As of March 23, 2009 Su-35BM aircraft carried out a total of 100 flights. The third flight prototype of the Su-35BM has been equipped with radar, in contrast to the first prototypes and other avionics, but the April 26, 2009 Su-35BM №904 board crashed at high speed on the jog Dzemgi airfield in Komsomolsk-on-Amur, due to a system failure motor control.
Major Shaitan Singh
SENIOR MEMBER

- Joined
- Dec 7, 2010
- Messages
- 3,550
- Reaction score
- 43
- Country
- Location
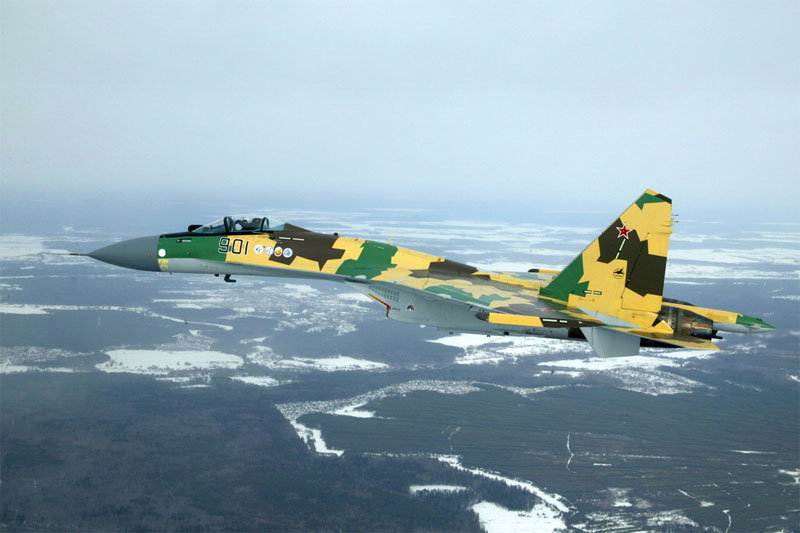
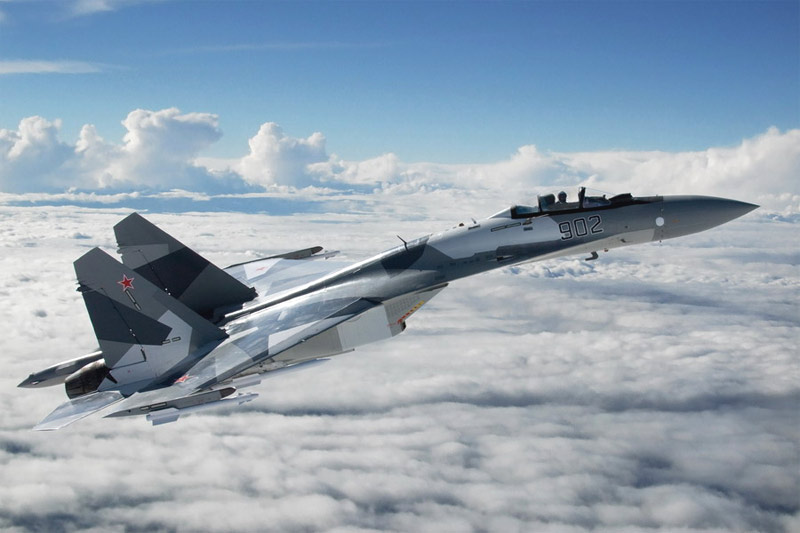


Su-35BM board №901 (16 and 19.02.2008) and board №902 (01.04.2009 g) ( http://www.knaapo.ru ).
State tests and serial production . During MAKS-2009 (opening 18.08.2009,) signed a contract for the supply of 48 Russian air force Su-35S in the period from 2012 to 2015 A similar agreement is expected to be signed in the 2015-2020 GG In mid-November 2009, KnAAPO started execution of the contract for the supply of Su-35S for the Russian Air Force.
In July 2010, announced the completion of the preliminary tests of the Su-35BM. State aircraft test program scheduled to begin in September-October 2010. In the future, in the state tests predpolaetsya part 6 aircraft. The first production Su-35S production KnAAPO made its maiden flight on 03.05.2011 Dzemgi airport (Komsomolsk-on-Amur) - the first aircraft project, a fully stocked avionics.
August 15, 2011 the first two pre-production Su-35BM ( board №№901 and 902) and the first production Su-35s started the program state joint tests in the 929 th state flight test center (glycyl) Air Force. The Su-35BM (901 and 902) are pre-flight tests, during which were fully confirmed by the major established performance characteristics of the complex avionics and super maneuverability characteristics, verified stability and controllability characteristics, the characteristics of the power plant, the work of the navigation system. In March 2012, to participate in the joint state tests of Su-35S transferred №4.
By default, the Su-35 first generation (1988).
The design of the aircraft Su-27 is similar with some differences. Normal aerodynamic configuration with canards and two keels. Horizontal tail and all-moving canards. Strength and design resource is higher than that of the basic Su-27. First-generation fighter aircraft equipped with vertical keels, excellent shape and the height from the classic to the Su-27 (except part of prototypes, built on the basis of serial Su-27). Container drogue keyboard type. In svzya with the installation of the radar of new types of modified contours of the nose cone, and radio transparent central tail boom. Brake aerodynamic shield area of 2.6 m is located on top of the fuselage behind the cockpit. The angle of the flap deflection - 54 degrees, the release is carried out with the air speed of up to 1000 km / h. In the process of construction of the aircraft structure changed to increase the volume of fuel tanks (to increase the flight range of the aircraft). Integral fuel tanks are placed including Aircraft in the keels. The mass of fuel in the keels - 300 kg Fuel Weight additionally placed in the wing - 500 kg Chassis tricycle with controlled front desk, strengthened compared to the baseline Su-27.
The front landing gear with a rack polurychazhnogo type instead of a wheel size of 680x260 mm was equipped with two-wheel non brake related dimensions of 620x180 mm. Air intakes supersonic mechanization. Movable panel adjustable wedge and feeding shutters are located on the bottom surface. Adjustable three-step wedge intake consists of interconnected front and rear movable panels. The front panel is a second and third stage of braking wedge intake, the rear moving panel forms a movable wall of the upper air passage zagorlovogo diffuser. Protective guard is in the retracted position on the bottom surface of the inlet channel. Release of the grid is performed against the current, the axis of rotation is located in the throat of the diffuser channel. Drains Shutters arranged on the outside bottom surface of the inlet zone in placing a protective grid. Shutters are made to "float", ie opening and closing due to pressure difference. They may be opened at both grid harvested, and when released. Optimal braking supersonic flow in the diffuser intake by installing its adjustable components in the calculated position of the automatic control system air intake such as ARV 40A. On the side surface air intakes mounted antenna radar warning receiver.
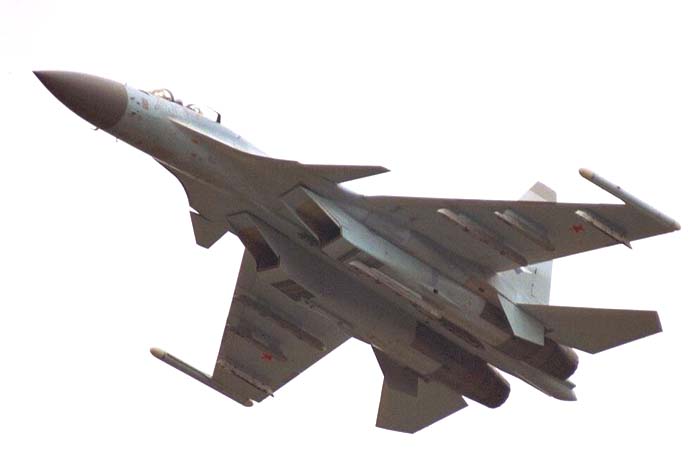

Su-35 / T-10M-9 board №709 in flight (photo - by Paul Dopson, http://www.airwar.ru ).
Su-35C / T-10BM - Aircraft design completely redesigned using the software design of the complex. Significantly increased resources airframe modified cutting fuselage and airframe parts reshaped keels (shape closer to the shape of the keel of the Su-27), CHR and brake flap behind the cab piloga absent.Airbrake functions perform rudders - in synchronous deviation outside.
The service life - up to 30 years
of glider Resource - 6000 hours ( I.Demin, OKB "Dry" to Lenta.Ru )
TBO - 1500 hours ( Fomin )
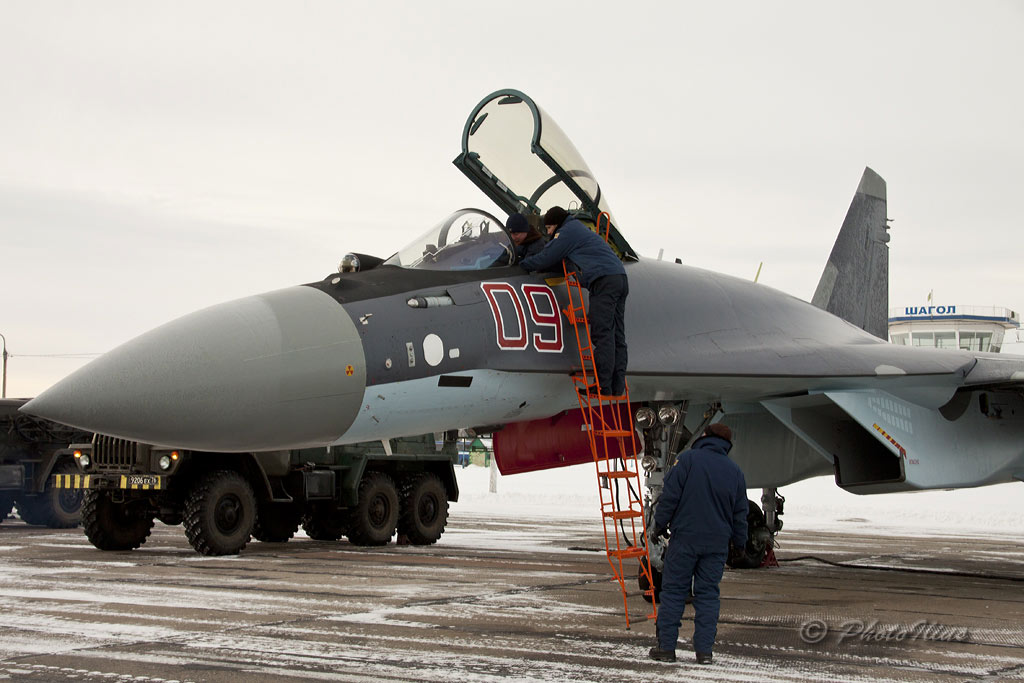

The Su-35S SDO 2012 bort№09 red airbase Shagol / Chelyabinsk during playout with KnAAPO February 8, 2013 (photo - Ilius,http://forum.keypublishing.com ).
Engines :
1) T-10M - 2 x AL-31FM thrust of 12,800 kg in afterburner.
2) of the Su-35 / T-10BM / Su-35S - 2 x turbofans with UHT AL-41F1S / product 117C NGO development "Saturn" plasma ignition system and the electro-mechanical control system. They are to be installed on the aircraft after the release of development engine AL-41F1 / 117 product. flight test engines started on the plane T-10M-10 in March 2004, the first two of the engine for the first flight of the prototype delivered on KnAAPO in early 2007 Engine tests are completed 07.02.2008 It is planned to install the engines' product on the Su-35S 117 ". Production of engines AL-41F1S planned on an equal footing "50 to 50" NPO "Saturn" and Ufa motorostroitlnym software (Ufa).
The engine thrust:
- Maximal without afterburner - at 8800 kg
- full afterburner - at 14000 kg
- Maximal Fast and the Furious / special treatment - for 14,500 kg
fan diameter - 932 mm
engine weight - 1520 kg
angles of deviation of the thrust vector - + -20 degrees. plane
deviation of the velocity vector of thrust - 60 deg / s
Resource - about 4,000 hours
resource to 1st overhaul - 1500 hours ( Fomin )
TBO - 1000 hours ( Fomin )
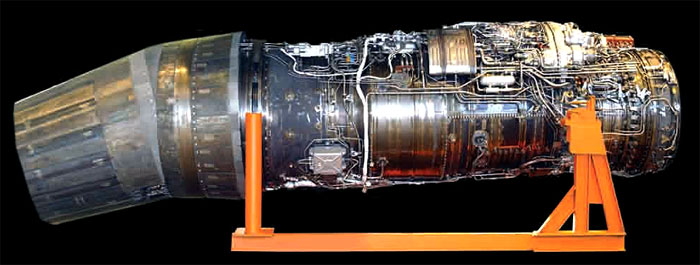
Engine AL-41F1S / product 117C ( http://www.knaapo.ru ).
On the Su-35BM used auxiliary gas turbine engine-generator set VGTD TA14-130-35 capacity of 105 kW. VGTD provides air-conditioning and cabin aircraft compartments, as well as alternating current power supply with a voltage of 115/200 volts up to 30 kVA.

Auxiliary power unit TA14-130-35 ( http://www.knaapo.ru ).
Similar threads
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 742
- Replies
- 55
- Views
- 7K
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 999
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 1K


