The Ronin
SENIOR MEMBER

- Joined
- Mar 24, 2017
- Messages
- 3,386
- Reaction score
- 0
- Country
- Location
By Lt Col Mohammad Baker, afwc, psc, Sigs
Introduction
Future war is likely to be short and intense and thoroughly dependent on technology. As such, technological advancement is likely to play a critical role to dictate the situations of the war. With the initiation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) new conceptual dimension to warfare popularly termed as Network Centric Warfare (NCW), Cyber Warfare, etc. are introduced.
In order to achieve dominance, today’s fragmented command, control, decision making actions and all activities related to warfare should be more focused, efficient and effective to ascertain the common goal. Most of the modern armies in present world are increasingly becoming dependent on technological advancement. The trend in modern warfare is towards the increased use of smart weapons and the integration of Command, Control, Computers, Communications and Intelligence (C4I) system with Surveillance and Reconnaissance (known as C4ISR) to maximize combat effectiveness (1).
For achieving technological superiority integrated C4ISR is required which will offer a commander to make and communicate decision faster to a wide array of forces (2). Therefore, transforming towards ICT based C4ISR system will facilitate to fulfill the operational need of the future war.
It connects the strategic level with tactical level in real time. Modern armies have digitalized their command and control (C2) infrastructure by exploiting the technological advancements to a greater extend. To remain vigilant and effective for any unforeseen transforming to C4ISR is a non-negotiable urgency. Bangladesh Army also needs to plan and incorporate such technological advancements to fulfill requirement of future warfare.
The essay begins with an overview of the future warfare trends and preparation of Bangladesh Army. Subsequently technological advancement adopted by the modern armies and preferred technological advancement for Bangladesh Army were highlighted. Probable C4ISR structure including challenges of implementation was discussed under preferred technological outlook.
TRENDS OF FUTURE WARFARE
General: In future the typical linear battlefield is likely to be replaced by a combat situation with a 360 degree threat, potential for new high-tech weapons and non-traditional forces. It is observed that advancements in technology have led to faster airplanes, laser-guided weapons, unmanned bomb-carrying vehicles and all are under same network (3).
Modern War Fighting Trends: According to Carl von Clausewitz “War is like a chameleon, always changing as per its environment”. Over the centuries rapid development of technology has made an enduring impact on war-fighting concepts. Technology has always been the major determinant of warfare and always shaped its concept. Today’s soldiers will have to perform as a soldier, a technocrat, a cyber-warrior and many other roles. The concepts of modern day war fighting are changing and will undergo more dramatic changes in future.
Dimension of Future Warfare: Martin Van Creveld (4) , in his ‘On Future War’ stated “in the future, war will not be waged by armies but by groups whom we today call terrorists, guerrilla, bandits and robbers”. As the information age matures, a determined adversary will be able to sabotage, disrupt or contaminate the information highway. General Gordon R Sulivan and Colonel James of Dubik of United States in a research suggested five trends of future warfare where ‘increased integration of technologies’ is one (5) . In future conflicts, even soldiers at the lowest echelons of command will have smart devices that connect them to Brigade level network (6).
Effect of ICT on Future Warfare: The rapid development in technology has made a permanent impact on war-fighting concepts. ICT based military platform will definitely ensure a paradigm shift in planning, weaponry, accuracy and lethality in terms of achieving synergic effect in battle space. The likely effects are discussed below:
a. War Fighting Concepts. The concept of modern day war fighting is now hinge around countering both the conventional and unconventional threat. Warfare today is based on information dominance. Satellites provide a steady flow of real time information that makes the battle space virtually transparent (7).
b. Networked Battle Space. Information warfare and its concept of NCW have reshaped warfare. A networked battle space integrates all elements together and synergizes their firepower and information flow. Battle space Management System (BMS) comprises of computer integrated together to link each soldier, fire and supporting elements, logistics and other elements. ICT enhanced logistic system will ensure getting the right supplies to the right place at the right moment
c. Information Warfare (IW). In the ICT based IW will deny, exploit, corrupt or destroy an adversary's information, information systems and computer-based networks while protecting one's own. Such actions are predominant by ICT based systems and designed to achieve advantages over military adversaries.
d. Cyber War. The increased dependency on information spectrum forces across the world are gearing up for the battle of fifth dimension i.e. cyber space. Cyber war is waged insidiously and covertly years and month before the actual conflict to corrupt and disable enemy networks. It would cause ten times destructive effect without firing a shot.
Influence of ICT over C2 Environment: The influence of ICT aims to pursue for information superiority. Information advantage is to be transformed into decision superiority for command as described in the OODA loop (8). The C2 influenced the tenants of army operations in respect to initiative, tenacity, non-linear engagement and battlefield imperatives with connections to many principles of war.
PREPARATION OF BANGLADESH ARMY ON FUTURE WARFARE
General: The development of Bangladesh Army has been ongoing since independence. It is undergoing major modernization and upgradation of existing systems. Over the last few years Bangladesh Army has taken many initiatives to modernize its ICT sector.
Increasing Fighting Capabilities: At present Bangladesh Army is a wellequipped force with modern war fighting gadgets. It has adopted a Forces Goal-2030 to transform into a modern, efficient and time-befitting force. Accordingly, mobility of infantry and fire power of Armoured and Artillery including Air Defence has been increased. Infantry soldiers are equipping with ultra-modern equipment like Night Vision Goggles (NVG), Ballistic helmet, protective eye gear, bulletproof vest, hand to hand communicator, palmtop GPS device.
Army Aviation has been modernized with new helicopters. Infantry Reconnaissance Vehicle (IRV), Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) to increase the surveillance capability. A remarkable technological advancement took place by the establishment of Electronic Warfare element, Army IT Support Organization (AITSO) and a tier-III (9) Army Data Center, Army War Game Centre, etc.
Development in ICT Sector: Vision of IT policy of Bangladesh Army is to expand and diversify the use of ICT in all walks of military life by creating a functional and secure IT platform. The Wide Area Network of Bangladesh Army is connecting all the formations and garrisons with AHQ. As per the plan all members of Bangladesh Army will be an IT literate. Basic IT training will be provided to qualify as IT capable in an e-military environment (10).
TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENT OF MODERN ARMIES
General: Maximum modern armies are increasingly becoming dependent on technological advancement as the key to victory in future wars. National Defence of USA identifies few key technologies that U.S. forces will need to fight future wars, where maximum emphasis was on information based technology. According to their opinion, success in future conflict will require technologies that can perform persistent surveillance and reconnaissance (11).
Establishing C4I Structure: The concept of integrated C4ISR is capable of integrating war fighting entities, efficient and effective complete system to manage decision making. Therefore, Countries like USA, UK, Germany, China, India, etc. have established C4ISR structure. USA has established C4ISR architecture at every tiers of command in static and mobile form. Individual command, services and agencies in department of defense of USA traditionally developed their C4ISR architectures using techniques and presentation schemes that suited their unique needs and purposes (12).
China terms it as C4KISR (Command, Control, Communication, Computer, Killing, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance). The digitized C4KISR system is capable of assisting the commander to command troops and control its weapons by means of supporting efficient seamless communication network (13).
India terms it as C4I2 (Command, Control, Communication, Computer, Information and Intelligence). Indian Army has launched an ambitious programme for transforming C4I2 into the NCW paradigm. Indian Army has evolved doctrine for integrating various components of C4I2 together with an IW doctrine (14). Modern armies are also using Soldier’s C4ISR system may comprises portable equipment which can be dismounted and assembled fast.
Benefits of C4ISR at Various Decision Making Tires: The benefits of C4ISR at various decision making tires are discussed below (15):
a. Greater Integration. The integration in C4ISR will occur over time, space, function and echelon. It will benefit at various levels and decision making tires i.e. data, information, knowledge, better integrated approach, etc. C4ISR process will be transformed, which will have massive implications in concept, doctrine, organization and training. By connecting UAV to the system, it will provide more precise location and guide a stand-off weapon to the target.
b. Rapid and Effective Decision Making Process. As C4ISR system collects, collates and process data simultaneously within very short time, decision making will be swift, effective and rapid. In future the computational power and better network will be dominant factor for initial planning, comfortable battle space awareness, more rapid and effective decision making process.
c. Self-reporting by Major Platforms. Key platforms through their own system architecture can also provide with self-reporting. This will primarily assist battle space management by linking current operations to logistics and sustainment functions.
d. Information Sharing or Distribution. C4ISR system will allow ‘Push Service Based’ information sharing depending on various command echelons by means of integrated network. For example a GSM based mobile network can update enemy situation regularly through text messages.
PREFERRED TECHNOLOGICAL OUTLOOK FOR BANGLADESH ARMY
General. Apprehending the future war's demand, most of the contemporary armies have already incorporated technological advancement process and established C4I system. From the study it can be assumed that integration of C4ISR system would be the appropriate option for Bangladesh Army to meet the demand of future warfare.
Preferred Outlook for Bangladesh Army. To remain vigilant and effective for any unforeseen, transforming to C4ISR system is a non-negotiable urgency. The future warfare will depend largely on digital data and voice and video communication. Table 1 shows rate of data transfer during various wars (16).
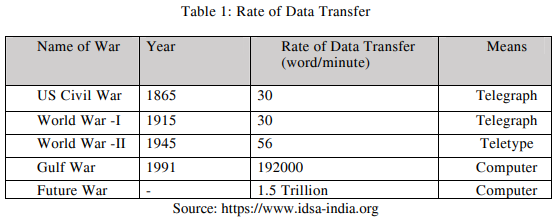
From the above table it can be envisaged that in future war huge data transfer will take place and that can be performed by a strong C4ISR structure. It is also essential for Bangladesh Army to adopt technologies which will focus on key battle winning aspects like, maneuver, surveillance, concentrated fire power, focused logistics and situational awareness. All these will be possible by digitizing the battlefield i.e. by establishing integrated C4ISR structure.
Probable C4ISR Structure of Bangladesh Army
Prerequisite of C4ISR System. An effective C4ISR system demands a strong and reliable communication network, an accurate data processing system, digitalization of equipment and a superior C2 system. C4ISR system will require data warehouse and Army Data Center may be used for that.
Integration of Various Elements. Various gadgets may be integrated with digital maps and symbols which can work as input source for the network. Armoured and Infantry to be integrated with required equipment. Modern Artillery acts as eyes and ear, same way performs the task of shooters. Therefore, both Field and AD Artillery are to be integrated with C4ISR system. Own EW capability will be enhanced by integrating with C4ISR system. Incorporating and integrating a welldefined logistic support with networked vehicle tracking will ease up in speedy decision making.
Communication Infrastructure for C4ISR System. For C4ISR system Tactical Communication System (TCS) of Bangladesh Army has to be modernized first. Seamless communication system to be introduced to support military operations (17). For C4ISR system interfaces are to be designed to integrate both terrestrial and satellite communication backbones to enable connectivity from the highest HQ down to frontline troops. National fiber augmented by microwave backbone will be used as core backbone for field communication. Redundancy of backbone will be created by Radio Relay, radio with higher data capacity and VSAT as emergency or alternative communication backbone.
Probable C4ISR Outfits. C4ISR centers will be both fixed and mobile type having option for deployed to the field in case of requirement. Various command posts will be positioned in this center as per the requirements of respective HQs. Communication backbone like, national fiber optic and Short Range (SR) High Capacity Line of Sight Radio (HCLOS), Long Range (LR) HCLOS and VSAT will be established. C4ISR system of higher HQ will be connected to C4ISR system of lower HQ. Each soldier will be connected to respective C4ISR system through Integrated Digital Soldier System (IDSS) (18).
Likely Challenges of Implementation and Measures
Considering all requirements likely challenges for implementation of C4ISR system in Bangladesh Army and apposite measures are discussed as under:
a. Mind Setup. Transformation from analogical environment to digital world is a huge challenge. Due to the techno phobia soldiers may not take this change positively. Conduct of training and awareness program for all ranks on C4ISR and motivation may solve this problem.
b. Dependency on Network and Hardware/Software. C4ISR system will be software based network with combination of resources of Army and nationwide backbone. It requires integrating multi standard equipment and platforms. As such, the system will totally depend on network and hardware/software, which will be a great constrain. However, with proper integration and awareness, the problem can be overcome.
c. Standardization of Training. Understanding of C4ISR and use of modernized ICT platforms and equipment will require expert handling. The officers and men of Bangladesh Army are not adequately trained on those gadgets. This can be overcome by planned training, proper understanding of operating procedure and other related issues.
d. Budgetary Constrain. Budgetary constraint would be the major barrier for an effective C4ISR structure. Most of the equipment and platforms need to be procured from foreign countries, which involve huge amount of budget. A phase wise switching to a standard platform vis-à-vis developing the core network will integrate through a time plan.
e. Organizational Set Up. At present there is no dedicated organization in Bangladesh Army for C4ISR system. But for smooth functioning of the system an organizational structure of C4ISR is required.
f. Security Issues. For communication with C4ISR center additional layered of security arrangement to be ensured. Another important aspect is that all soldiers will have the access to real time information. Data communication shall maintain confidentiality in respect of all information provided by the subscriber.
g. Challenges Faced by User Countries. Modern countries like USA, UK, etc. sometimes suffer heavy casualties in the battle field, despite having C4ISR system. Bangladesh Army also likely to face the same difficulties. Therefore, before implementing such a vast project, detail study and analysis of C4ISR system of contemporary armies are essential.
Recommendations
Basing on the discussions following are recommended:
a. AHQ, GS Branch may formulate a board of officers to study C4ISR system of other counties and propose a suitable system for Bangladesh Army. IT Directorate or Signal Directorate may take lead role.
b. A separate organization for C4ISR may be incorporated under AHQ, GS Branch. There may be C4ISR cell in all the formations of Bangladesh Army.
c. AHQ, IT directorate may organize an effective and interactive training module by AITSO to train the men on handling of modern equipment and platforms.
Conclusion
The rapid development of technology has made a permanent impact on warfighting concepts. Battle space is likely to be characterized by highly mechanized forces and increased use of strategic reconnaissance and surveillance. ICT based future warfare will have dominating manoeuvre over adversaries in terms of finding out accurate positioning of forces. Bangladesh Army has started its preparation since long to conform to the future war fighting trends and acquired quite significant technological advancement in the field of ICT.
C4ISR is an automated and systematic C2 system which provides real time situation awareness, battle space information to the commanders. Large scale integration is required for its implementation of C4ISR system, where some of the portion will be military owned and some are nationwide communication backbone. C4ISR system is used by advanced countries for long time including India. C4ISR is a network and hardware based system and customized software has to be developed with appropriate security measures.
Probable C4ISR Architecture of Bangladesh Army demands integration of various elements to the system. As such, integration of Armoured/Infantry, field and AD artillery, EW capability, logistic system to be done with C4ISR system. Nationwide ICT will be used as core backbone to support adequate bandwidth in the field for integrated voice, data and video.
Implementation process of C4ISR will take long time, modern equipment and huge amount of budget. Therefore, many challenges are likely to be faced during implementation phase. Challenges faced by user countries are also to be taken into consideration. For smooth implementation of the system all those hurdles are to be addressed appropriately.
Footnote
1 Tolk, Andreas Tolk, Andreas, 2002, “Using the C4ISR Architecture Framework as a Tool to Facilitate Systems within the Military Application” at page 09.
2 Mandeles D. Mark 2007, The Future of War, Organizations as Weapons, at page 31.
3 Eric Beidel, Sandra Erwin and Stew Magnuson, November 2011, “Technologies That Transformed Warfare”, available at.http://www.livescience.com/41321-military-war-technologies.html, accessed on 14 Oct 2016.
4 Martin Levi van Creveld is an Israeli military historian and theorist. He was a teacher at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He is the author of seventeen books on military history and strategy
5 Ali, Mohammad Abu Sayeed, 2010, December 2010, “Trends of Future Warfare and Options Available,” Bangladesh Army Journal, Volume 2010 Number 48,Other trends are; Increased lethality and dispersion, Increased volume and precision fires, Achievement of greater mass and effect and Reinforcements in invisibility and delectability.
6 Eric Beidel, Sandra Erwin and Stew Magnuson, Op Cit, pp 9.
7 Singh, Ajay 2013, “A Spectrum of Modern Warfare” page 89.
8 The phrase OODA loop refers to the decision cycle of observe, orient, decide, and act, developed by military strategist and United States Air Force Colonel John Boyd.
9 The Uptime Institute, USA categorizes the data centers by four levels: Tier I, II, III and IV. These levels correspond to a certain number of guarantees on the type of hardware deployed in the data center to ensure redundancy. A Tier III data center offers 99.98% availability. With this configuration, it is possible to manage maintenance periods without affecting the continuity of service on the servers.
10 As per the Structured IT Training Plan of IT Dte, AHQ.
11 Eric Beidel, Sandra Erwin and Stew Magnuson, Op Cit, pp 1.
12 AHQ, GS Branch, Signal Directorate.
13 Ibid.
14 Kumar, Davinder, 2014, “An Indian C4ISR System by 2020” available at http://defencesecurityindia.com/indian-c4isr-system-2020-strategic- imperative/
15 86 Independent Signal Brigade, Presentation of Study Period on C4I, Dhaka, April 2013.
16 Vinod Anand, “Impact of Technology on Conduct of Warfare” available at https://www.idsa-india.org
17 Discussion with SM Farhad, Brigadier General, Director, Signals Directorate, AHQ, on 05 July, 2016.
18 IDSS developed by Cobham Defence Communications (CDC) provides a fully integrated Combat Management System (CMS). The system is provided in three basic configurations – a commander system, a soldier system and a tracking system. It has soldier data terminal (SDT) which provides target identification, reporting and messaging.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Books
1. Chief of General Staff 2006, Operations of War (Volume One), GSPT 0032, Bangladesh Army.
2. Creveld, van Martin 1991, On Future War, The Most Radical Reinterpretation of Armed Conflict Since Clausewitz, The Free Press, USA.
3. Department of Defence, USA 2010, Army Modeernization Strategy, Manas Publications, India.
4. Mandeles D. Mark 2007, The Future of War, Organizations as Weapons, Manas Publications, India.
5. Singh, Ajay 2013, A Spectrum of Modern Warfare, Pentagon Press, New Delhi.
Dissertation and Research Papers
6. Azam, Mohammad Shafiul 2013, Challenges and Prospect of Battle Space Surveillance System of Bangladesh Armed Forces, National Defence College, Individual Research Paper submitted as part of Armed Forces War Course 2013, Mirpur, Dhaka.
7. Chowdhury, Rakibul Karim, 2016, Integration of Non-Military and Commercial Facilities Towards Enhanced Communication for Bangladesh Army, National Defence College, Individual Research Paper submitted as part of Armed Forces War Course 2016, Mirpur, Dhaka
8. Rouf, S M Abdur 2014, Information Warfare: Challenges for the Warfighting Concept of Bangladesh Armed Forces and Ways Ahead, National Defence College, Group Research Paper submitted as part of Armed Forces War Course 2014, Mirpur, Dhaka.
Journals and Periodicals
9. Ali, Mohammad Abu Sayeed, 2010, December 2010, “Trends of Future Warfare and Options Available,” Bangladesh Army Journal, Volume 2010 Number 48.
10. Shamsuddin, Sarker Muhammad, 2011, “Towards the Concept of Effect Based Operations to Network Centric Warfare – Validating the Blending Doctrine.” Mirpur Papers, Volume 1023-6325 Number 17.
Presentations
11. C4I Cell, 2015, C4I System for Bangladesh Army, Presentation to Chief of Army Staff, AHQ, Dhaka, 18 March, 2015.
12. 86 Independent Signal Brigade, 2013, A View of Command, Control, Communications, Computer and Intelligence (C4I) Architecture in Bangladesh Army, Presentation of Study Period, Dhaka, April 2013.
Internet Articles
13. AWG (Architectures Working Group), 1997, “C4ISR Architecture Framework Version 2.0,” http://www.afcea.org/education/courses/archfwk2.pdf , accessed on 20 September 2016.
14. Cogan J. Kevin 2007 “Command, Control, Communications and Computer Architectures at the Dawn of Network Centric Warfare,” U.S. Army War College, http://www.researchgate.net/publication/ 235086574, accessed on 10 August 2016.
15. Cobham, “Integrated Digital Soldier System (IDSS)” https://www.cobham.com/media/34974/ idss%20brochure. pdf, accessed on 31 July 2016.
16. Kumar, Davinder, 2014, “An Indian C4ISR System by 2020” http://defencesecurityindia.com/indianc4isr-system-2020-strategic- imperative/ , accessed on 31 July 2016.
17. Tolk, Andreas, 2002, “Using the C4ISR Architecture Framework as a Tool to Facilitate Systems within the Military Application” http://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1011/1011.5656.pdf, accessed on 30 July 2016.
Interview/Discussion
18. Hossain, SM Farhad, Brigadier General, Director Signal, Signal Directorate, AHQ, Discussed on July 05, 2016.
19. Hossain, Monowar, Lieutenant Colonel, Commandant, Army IT Support Organzation, Interviewed on July 30, 2016.
Source- Bangladesh Army Journal 61st Issue, 2017.
Introduction
Future war is likely to be short and intense and thoroughly dependent on technology. As such, technological advancement is likely to play a critical role to dictate the situations of the war. With the initiation of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) new conceptual dimension to warfare popularly termed as Network Centric Warfare (NCW), Cyber Warfare, etc. are introduced.
In order to achieve dominance, today’s fragmented command, control, decision making actions and all activities related to warfare should be more focused, efficient and effective to ascertain the common goal. Most of the modern armies in present world are increasingly becoming dependent on technological advancement. The trend in modern warfare is towards the increased use of smart weapons and the integration of Command, Control, Computers, Communications and Intelligence (C4I) system with Surveillance and Reconnaissance (known as C4ISR) to maximize combat effectiveness (1).
For achieving technological superiority integrated C4ISR is required which will offer a commander to make and communicate decision faster to a wide array of forces (2). Therefore, transforming towards ICT based C4ISR system will facilitate to fulfill the operational need of the future war.
It connects the strategic level with tactical level in real time. Modern armies have digitalized their command and control (C2) infrastructure by exploiting the technological advancements to a greater extend. To remain vigilant and effective for any unforeseen transforming to C4ISR is a non-negotiable urgency. Bangladesh Army also needs to plan and incorporate such technological advancements to fulfill requirement of future warfare.
The essay begins with an overview of the future warfare trends and preparation of Bangladesh Army. Subsequently technological advancement adopted by the modern armies and preferred technological advancement for Bangladesh Army were highlighted. Probable C4ISR structure including challenges of implementation was discussed under preferred technological outlook.
TRENDS OF FUTURE WARFARE
General: In future the typical linear battlefield is likely to be replaced by a combat situation with a 360 degree threat, potential for new high-tech weapons and non-traditional forces. It is observed that advancements in technology have led to faster airplanes, laser-guided weapons, unmanned bomb-carrying vehicles and all are under same network (3).
Modern War Fighting Trends: According to Carl von Clausewitz “War is like a chameleon, always changing as per its environment”. Over the centuries rapid development of technology has made an enduring impact on war-fighting concepts. Technology has always been the major determinant of warfare and always shaped its concept. Today’s soldiers will have to perform as a soldier, a technocrat, a cyber-warrior and many other roles. The concepts of modern day war fighting are changing and will undergo more dramatic changes in future.
Dimension of Future Warfare: Martin Van Creveld (4) , in his ‘On Future War’ stated “in the future, war will not be waged by armies but by groups whom we today call terrorists, guerrilla, bandits and robbers”. As the information age matures, a determined adversary will be able to sabotage, disrupt or contaminate the information highway. General Gordon R Sulivan and Colonel James of Dubik of United States in a research suggested five trends of future warfare where ‘increased integration of technologies’ is one (5) . In future conflicts, even soldiers at the lowest echelons of command will have smart devices that connect them to Brigade level network (6).
Effect of ICT on Future Warfare: The rapid development in technology has made a permanent impact on war-fighting concepts. ICT based military platform will definitely ensure a paradigm shift in planning, weaponry, accuracy and lethality in terms of achieving synergic effect in battle space. The likely effects are discussed below:
a. War Fighting Concepts. The concept of modern day war fighting is now hinge around countering both the conventional and unconventional threat. Warfare today is based on information dominance. Satellites provide a steady flow of real time information that makes the battle space virtually transparent (7).
b. Networked Battle Space. Information warfare and its concept of NCW have reshaped warfare. A networked battle space integrates all elements together and synergizes their firepower and information flow. Battle space Management System (BMS) comprises of computer integrated together to link each soldier, fire and supporting elements, logistics and other elements. ICT enhanced logistic system will ensure getting the right supplies to the right place at the right moment
c. Information Warfare (IW). In the ICT based IW will deny, exploit, corrupt or destroy an adversary's information, information systems and computer-based networks while protecting one's own. Such actions are predominant by ICT based systems and designed to achieve advantages over military adversaries.
d. Cyber War. The increased dependency on information spectrum forces across the world are gearing up for the battle of fifth dimension i.e. cyber space. Cyber war is waged insidiously and covertly years and month before the actual conflict to corrupt and disable enemy networks. It would cause ten times destructive effect without firing a shot.
Influence of ICT over C2 Environment: The influence of ICT aims to pursue for information superiority. Information advantage is to be transformed into decision superiority for command as described in the OODA loop (8). The C2 influenced the tenants of army operations in respect to initiative, tenacity, non-linear engagement and battlefield imperatives with connections to many principles of war.
PREPARATION OF BANGLADESH ARMY ON FUTURE WARFARE
General: The development of Bangladesh Army has been ongoing since independence. It is undergoing major modernization and upgradation of existing systems. Over the last few years Bangladesh Army has taken many initiatives to modernize its ICT sector.
Increasing Fighting Capabilities: At present Bangladesh Army is a wellequipped force with modern war fighting gadgets. It has adopted a Forces Goal-2030 to transform into a modern, efficient and time-befitting force. Accordingly, mobility of infantry and fire power of Armoured and Artillery including Air Defence has been increased. Infantry soldiers are equipping with ultra-modern equipment like Night Vision Goggles (NVG), Ballistic helmet, protective eye gear, bulletproof vest, hand to hand communicator, palmtop GPS device.
Army Aviation has been modernized with new helicopters. Infantry Reconnaissance Vehicle (IRV), Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) to increase the surveillance capability. A remarkable technological advancement took place by the establishment of Electronic Warfare element, Army IT Support Organization (AITSO) and a tier-III (9) Army Data Center, Army War Game Centre, etc.
Development in ICT Sector: Vision of IT policy of Bangladesh Army is to expand and diversify the use of ICT in all walks of military life by creating a functional and secure IT platform. The Wide Area Network of Bangladesh Army is connecting all the formations and garrisons with AHQ. As per the plan all members of Bangladesh Army will be an IT literate. Basic IT training will be provided to qualify as IT capable in an e-military environment (10).
TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCEMENT OF MODERN ARMIES
General: Maximum modern armies are increasingly becoming dependent on technological advancement as the key to victory in future wars. National Defence of USA identifies few key technologies that U.S. forces will need to fight future wars, where maximum emphasis was on information based technology. According to their opinion, success in future conflict will require technologies that can perform persistent surveillance and reconnaissance (11).
Establishing C4I Structure: The concept of integrated C4ISR is capable of integrating war fighting entities, efficient and effective complete system to manage decision making. Therefore, Countries like USA, UK, Germany, China, India, etc. have established C4ISR structure. USA has established C4ISR architecture at every tiers of command in static and mobile form. Individual command, services and agencies in department of defense of USA traditionally developed their C4ISR architectures using techniques and presentation schemes that suited their unique needs and purposes (12).
China terms it as C4KISR (Command, Control, Communication, Computer, Killing, Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance). The digitized C4KISR system is capable of assisting the commander to command troops and control its weapons by means of supporting efficient seamless communication network (13).
India terms it as C4I2 (Command, Control, Communication, Computer, Information and Intelligence). Indian Army has launched an ambitious programme for transforming C4I2 into the NCW paradigm. Indian Army has evolved doctrine for integrating various components of C4I2 together with an IW doctrine (14). Modern armies are also using Soldier’s C4ISR system may comprises portable equipment which can be dismounted and assembled fast.
Benefits of C4ISR at Various Decision Making Tires: The benefits of C4ISR at various decision making tires are discussed below (15):
a. Greater Integration. The integration in C4ISR will occur over time, space, function and echelon. It will benefit at various levels and decision making tires i.e. data, information, knowledge, better integrated approach, etc. C4ISR process will be transformed, which will have massive implications in concept, doctrine, organization and training. By connecting UAV to the system, it will provide more precise location and guide a stand-off weapon to the target.
b. Rapid and Effective Decision Making Process. As C4ISR system collects, collates and process data simultaneously within very short time, decision making will be swift, effective and rapid. In future the computational power and better network will be dominant factor for initial planning, comfortable battle space awareness, more rapid and effective decision making process.
c. Self-reporting by Major Platforms. Key platforms through their own system architecture can also provide with self-reporting. This will primarily assist battle space management by linking current operations to logistics and sustainment functions.
d. Information Sharing or Distribution. C4ISR system will allow ‘Push Service Based’ information sharing depending on various command echelons by means of integrated network. For example a GSM based mobile network can update enemy situation regularly through text messages.
PREFERRED TECHNOLOGICAL OUTLOOK FOR BANGLADESH ARMY
General. Apprehending the future war's demand, most of the contemporary armies have already incorporated technological advancement process and established C4I system. From the study it can be assumed that integration of C4ISR system would be the appropriate option for Bangladesh Army to meet the demand of future warfare.
Preferred Outlook for Bangladesh Army. To remain vigilant and effective for any unforeseen, transforming to C4ISR system is a non-negotiable urgency. The future warfare will depend largely on digital data and voice and video communication. Table 1 shows rate of data transfer during various wars (16).
From the above table it can be envisaged that in future war huge data transfer will take place and that can be performed by a strong C4ISR structure. It is also essential for Bangladesh Army to adopt technologies which will focus on key battle winning aspects like, maneuver, surveillance, concentrated fire power, focused logistics and situational awareness. All these will be possible by digitizing the battlefield i.e. by establishing integrated C4ISR structure.
Probable C4ISR Structure of Bangladesh Army
Prerequisite of C4ISR System. An effective C4ISR system demands a strong and reliable communication network, an accurate data processing system, digitalization of equipment and a superior C2 system. C4ISR system will require data warehouse and Army Data Center may be used for that.
Integration of Various Elements. Various gadgets may be integrated with digital maps and symbols which can work as input source for the network. Armoured and Infantry to be integrated with required equipment. Modern Artillery acts as eyes and ear, same way performs the task of shooters. Therefore, both Field and AD Artillery are to be integrated with C4ISR system. Own EW capability will be enhanced by integrating with C4ISR system. Incorporating and integrating a welldefined logistic support with networked vehicle tracking will ease up in speedy decision making.
Communication Infrastructure for C4ISR System. For C4ISR system Tactical Communication System (TCS) of Bangladesh Army has to be modernized first. Seamless communication system to be introduced to support military operations (17). For C4ISR system interfaces are to be designed to integrate both terrestrial and satellite communication backbones to enable connectivity from the highest HQ down to frontline troops. National fiber augmented by microwave backbone will be used as core backbone for field communication. Redundancy of backbone will be created by Radio Relay, radio with higher data capacity and VSAT as emergency or alternative communication backbone.
Probable C4ISR Outfits. C4ISR centers will be both fixed and mobile type having option for deployed to the field in case of requirement. Various command posts will be positioned in this center as per the requirements of respective HQs. Communication backbone like, national fiber optic and Short Range (SR) High Capacity Line of Sight Radio (HCLOS), Long Range (LR) HCLOS and VSAT will be established. C4ISR system of higher HQ will be connected to C4ISR system of lower HQ. Each soldier will be connected to respective C4ISR system through Integrated Digital Soldier System (IDSS) (18).
Likely Challenges of Implementation and Measures
Considering all requirements likely challenges for implementation of C4ISR system in Bangladesh Army and apposite measures are discussed as under:
a. Mind Setup. Transformation from analogical environment to digital world is a huge challenge. Due to the techno phobia soldiers may not take this change positively. Conduct of training and awareness program for all ranks on C4ISR and motivation may solve this problem.
b. Dependency on Network and Hardware/Software. C4ISR system will be software based network with combination of resources of Army and nationwide backbone. It requires integrating multi standard equipment and platforms. As such, the system will totally depend on network and hardware/software, which will be a great constrain. However, with proper integration and awareness, the problem can be overcome.
c. Standardization of Training. Understanding of C4ISR and use of modernized ICT platforms and equipment will require expert handling. The officers and men of Bangladesh Army are not adequately trained on those gadgets. This can be overcome by planned training, proper understanding of operating procedure and other related issues.
d. Budgetary Constrain. Budgetary constraint would be the major barrier for an effective C4ISR structure. Most of the equipment and platforms need to be procured from foreign countries, which involve huge amount of budget. A phase wise switching to a standard platform vis-à-vis developing the core network will integrate through a time plan.
e. Organizational Set Up. At present there is no dedicated organization in Bangladesh Army for C4ISR system. But for smooth functioning of the system an organizational structure of C4ISR is required.
f. Security Issues. For communication with C4ISR center additional layered of security arrangement to be ensured. Another important aspect is that all soldiers will have the access to real time information. Data communication shall maintain confidentiality in respect of all information provided by the subscriber.
g. Challenges Faced by User Countries. Modern countries like USA, UK, etc. sometimes suffer heavy casualties in the battle field, despite having C4ISR system. Bangladesh Army also likely to face the same difficulties. Therefore, before implementing such a vast project, detail study and analysis of C4ISR system of contemporary armies are essential.
Recommendations
Basing on the discussions following are recommended:
a. AHQ, GS Branch may formulate a board of officers to study C4ISR system of other counties and propose a suitable system for Bangladesh Army. IT Directorate or Signal Directorate may take lead role.
b. A separate organization for C4ISR may be incorporated under AHQ, GS Branch. There may be C4ISR cell in all the formations of Bangladesh Army.
c. AHQ, IT directorate may organize an effective and interactive training module by AITSO to train the men on handling of modern equipment and platforms.
Conclusion
The rapid development of technology has made a permanent impact on warfighting concepts. Battle space is likely to be characterized by highly mechanized forces and increased use of strategic reconnaissance and surveillance. ICT based future warfare will have dominating manoeuvre over adversaries in terms of finding out accurate positioning of forces. Bangladesh Army has started its preparation since long to conform to the future war fighting trends and acquired quite significant technological advancement in the field of ICT.
C4ISR is an automated and systematic C2 system which provides real time situation awareness, battle space information to the commanders. Large scale integration is required for its implementation of C4ISR system, where some of the portion will be military owned and some are nationwide communication backbone. C4ISR system is used by advanced countries for long time including India. C4ISR is a network and hardware based system and customized software has to be developed with appropriate security measures.
Probable C4ISR Architecture of Bangladesh Army demands integration of various elements to the system. As such, integration of Armoured/Infantry, field and AD artillery, EW capability, logistic system to be done with C4ISR system. Nationwide ICT will be used as core backbone to support adequate bandwidth in the field for integrated voice, data and video.
Implementation process of C4ISR will take long time, modern equipment and huge amount of budget. Therefore, many challenges are likely to be faced during implementation phase. Challenges faced by user countries are also to be taken into consideration. For smooth implementation of the system all those hurdles are to be addressed appropriately.
Footnote
1 Tolk, Andreas Tolk, Andreas, 2002, “Using the C4ISR Architecture Framework as a Tool to Facilitate Systems within the Military Application” at page 09.
2 Mandeles D. Mark 2007, The Future of War, Organizations as Weapons, at page 31.
3 Eric Beidel, Sandra Erwin and Stew Magnuson, November 2011, “Technologies That Transformed Warfare”, available at.http://www.livescience.com/41321-military-war-technologies.html, accessed on 14 Oct 2016.
4 Martin Levi van Creveld is an Israeli military historian and theorist. He was a teacher at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem. He is the author of seventeen books on military history and strategy
5 Ali, Mohammad Abu Sayeed, 2010, December 2010, “Trends of Future Warfare and Options Available,” Bangladesh Army Journal, Volume 2010 Number 48,Other trends are; Increased lethality and dispersion, Increased volume and precision fires, Achievement of greater mass and effect and Reinforcements in invisibility and delectability.
6 Eric Beidel, Sandra Erwin and Stew Magnuson, Op Cit, pp 9.
7 Singh, Ajay 2013, “A Spectrum of Modern Warfare” page 89.
8 The phrase OODA loop refers to the decision cycle of observe, orient, decide, and act, developed by military strategist and United States Air Force Colonel John Boyd.
9 The Uptime Institute, USA categorizes the data centers by four levels: Tier I, II, III and IV. These levels correspond to a certain number of guarantees on the type of hardware deployed in the data center to ensure redundancy. A Tier III data center offers 99.98% availability. With this configuration, it is possible to manage maintenance periods without affecting the continuity of service on the servers.
10 As per the Structured IT Training Plan of IT Dte, AHQ.
11 Eric Beidel, Sandra Erwin and Stew Magnuson, Op Cit, pp 1.
12 AHQ, GS Branch, Signal Directorate.
13 Ibid.
14 Kumar, Davinder, 2014, “An Indian C4ISR System by 2020” available at http://defencesecurityindia.com/indian-c4isr-system-2020-strategic- imperative/
15 86 Independent Signal Brigade, Presentation of Study Period on C4I, Dhaka, April 2013.
16 Vinod Anand, “Impact of Technology on Conduct of Warfare” available at https://www.idsa-india.org
17 Discussion with SM Farhad, Brigadier General, Director, Signals Directorate, AHQ, on 05 July, 2016.
18 IDSS developed by Cobham Defence Communications (CDC) provides a fully integrated Combat Management System (CMS). The system is provided in three basic configurations – a commander system, a soldier system and a tracking system. It has soldier data terminal (SDT) which provides target identification, reporting and messaging.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Books
1. Chief of General Staff 2006, Operations of War (Volume One), GSPT 0032, Bangladesh Army.
2. Creveld, van Martin 1991, On Future War, The Most Radical Reinterpretation of Armed Conflict Since Clausewitz, The Free Press, USA.
3. Department of Defence, USA 2010, Army Modeernization Strategy, Manas Publications, India.
4. Mandeles D. Mark 2007, The Future of War, Organizations as Weapons, Manas Publications, India.
5. Singh, Ajay 2013, A Spectrum of Modern Warfare, Pentagon Press, New Delhi.
Dissertation and Research Papers
6. Azam, Mohammad Shafiul 2013, Challenges and Prospect of Battle Space Surveillance System of Bangladesh Armed Forces, National Defence College, Individual Research Paper submitted as part of Armed Forces War Course 2013, Mirpur, Dhaka.
7. Chowdhury, Rakibul Karim, 2016, Integration of Non-Military and Commercial Facilities Towards Enhanced Communication for Bangladesh Army, National Defence College, Individual Research Paper submitted as part of Armed Forces War Course 2016, Mirpur, Dhaka
8. Rouf, S M Abdur 2014, Information Warfare: Challenges for the Warfighting Concept of Bangladesh Armed Forces and Ways Ahead, National Defence College, Group Research Paper submitted as part of Armed Forces War Course 2014, Mirpur, Dhaka.
Journals and Periodicals
9. Ali, Mohammad Abu Sayeed, 2010, December 2010, “Trends of Future Warfare and Options Available,” Bangladesh Army Journal, Volume 2010 Number 48.
10. Shamsuddin, Sarker Muhammad, 2011, “Towards the Concept of Effect Based Operations to Network Centric Warfare – Validating the Blending Doctrine.” Mirpur Papers, Volume 1023-6325 Number 17.
Presentations
11. C4I Cell, 2015, C4I System for Bangladesh Army, Presentation to Chief of Army Staff, AHQ, Dhaka, 18 March, 2015.
12. 86 Independent Signal Brigade, 2013, A View of Command, Control, Communications, Computer and Intelligence (C4I) Architecture in Bangladesh Army, Presentation of Study Period, Dhaka, April 2013.
Internet Articles
13. AWG (Architectures Working Group), 1997, “C4ISR Architecture Framework Version 2.0,” http://www.afcea.org/education/courses/archfwk2.pdf , accessed on 20 September 2016.
14. Cogan J. Kevin 2007 “Command, Control, Communications and Computer Architectures at the Dawn of Network Centric Warfare,” U.S. Army War College, http://www.researchgate.net/publication/ 235086574, accessed on 10 August 2016.
15. Cobham, “Integrated Digital Soldier System (IDSS)” https://www.cobham.com/media/34974/ idss%20brochure. pdf, accessed on 31 July 2016.
16. Kumar, Davinder, 2014, “An Indian C4ISR System by 2020” http://defencesecurityindia.com/indianc4isr-system-2020-strategic- imperative/ , accessed on 31 July 2016.
17. Tolk, Andreas, 2002, “Using the C4ISR Architecture Framework as a Tool to Facilitate Systems within the Military Application” http://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1011/1011.5656.pdf, accessed on 30 July 2016.
Interview/Discussion
18. Hossain, SM Farhad, Brigadier General, Director Signal, Signal Directorate, AHQ, Discussed on July 05, 2016.
19. Hossain, Monowar, Lieutenant Colonel, Commandant, Army IT Support Organzation, Interviewed on July 30, 2016.
Source- Bangladesh Army Journal 61st Issue, 2017.

