Hi, I feel your pain, before I continue, just a quick question: Are you able to use the broadband when you connect a PC or Laptop using an ethernet cable directly to the router? If so I think I know what the problem is and may be able to help you.
STEP 1: ROUTER LOCATION
Router location: Before we being, you have tested a hardwired connection into your router by connecting a desktop pc or laptop directly to your router and you are able to access the internet without any issues, the next step in diagnostics for WLAN connection is router location.
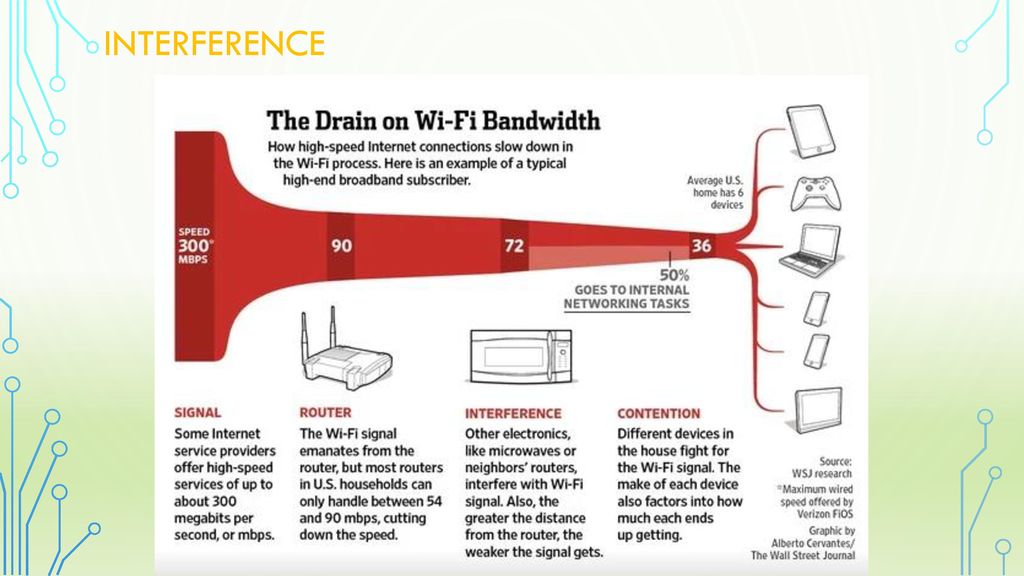
The Wireless router is a weak and fragile create, like most radio waves 802.11 is a delicate flower and doesn't like much interference from its surroundings such as the router being next to the television, microwaves, on top of a fridge, a glass table, in a cupboard, next to a window etc, in tech speak this is known as RIEN: Repetitive Electrical Impulse Noise.
This diagram will help you understand:
Another thing you need to be very careful about with regards to wifi routers is: Never place them next to an extension plug/lead as these are not shielded and leak electrical impulse noise which interferes the signal, the next device you should not have next to your router is a cordless telephone as it runs on the same 802.11 frequency and any AM/FM radio.
So now that you have checked your router location and you are comfrotable that there is no device interfering with the signals from the router and the router is placed in a open, clear space without obstructions, we can move onto the next step.
STEP 2: Wireless Diganotics
1. Find out what router you are using (this is important to continue with troubleshooting)
3. Keep your devices connected to your router wirelessly (do not disconnect them)
4. Now on your pc run Command Prompt as admin (Black DOS Screen)
5. And you will need to type in:
netsh wlan show all
It will run and a lot of text will come up on the screen, don't worry, find your devices on the list, most importantly find your router and check for the following:
It will be something like:
SSID 1: PTCL or DLINK etc
Check which radio type you are on: is it 802.11ac or N? (This is important)
Check what channel it is on i.e: Channel 1/9/11 etc
6. Next in the command prompt (black screen) type in the command:
netsh wlan show networks mode=bssid
This will show you a list of all the wireless routers around you i.e your, your neighbours etc. You are looking to find your router for example SSID 1: PTCL/DLINK etc
View attachment 610881
A. Check the channel your router is on and what signal strength it has
B. Check your neighbours routers are they on the same channel (for example if your router is on channel 1 is your neighbours router also on channel 1?)
Scenario 1: Channel Co/location/ overlapping
If your router and neighbours router are on the same channel you will be experiencing bandwidth congestion, this can be resolved very easily and this is why you need to know your router make/model to access it's admin portal, normally this can be done by typing 192.168.0.1 or a similar IP which should be on the back of your router.
The username is normally admin and the password is also admin but check your user manual, if you don't have the manual, you can visit this website which is a emulator :
https://www.chasms.com/#
Click on network > router emulator > select your router make/model and follow the on screen instructions to change the channel.
For this example I am going to use my router which is a TP LINK as an example for your ease, the IP address to access my router's admin page is 192.168.0.1 in the address bar and you will be met with this screen:
View attachment 610882
To log in to the router you will need the default username and password which is normally admin and admin or admin and password etc, you can find this information online.
View attachment 610883
When you log into your router, you will have a page very similar to this, you need to find the Wireless/WLAN tab and click on it.
View attachment 610885
Changing the channel on your router: You will see that your router's channel will be set on Auto, this is factory default and AUTO select normally makes the router use Channel 1, 6 or 11 and you will see when you run the
netsh wlan show networks mode=bssid command, your neighbours router will also be on the same channel.
Change your router to Channel 9 for starters and press save.
Further diagnostics:
Now go back on your phone and download an app called Wifi Analyzer from the google play store, its free:
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.farproc.wifi.analyzer&hl=en_GB
Make sure your mobile data on your phone is turned off and launch wifi analyzer, this app will allow you to see the wireless signal strength of your router in each room as well as provide a graph to see if your neighbouring routers are called interference/overlapping and also if you have any wireless deadspots in your house.
Here is a basic video on how to use the app:
Scenario 2:
You have tried the above, your mobile phone/tablet is connected to the router and your mobile data is off but you still can't access the internet.
Launch the settings tab on your phone, click on wifi settings, find your wifi connection, click on it, then click on the option to "FORGET". Now restart your mobile phone, and reconnect to the router, this will force the phone to request a new IP from the routers internal IP table and should resolve the issue.
Let me know if this helps...