从八品主簿
FULL MEMBER

- Joined
- May 11, 2019
- Messages
- 309
- Reaction score
- 0
- Country
- Location
Initial public offerings (IPOs) in mainland China hit a record high in 2022. The amount of IPO financing reached 610 billion yuan, which is expected to reach about half of the global total. The return of listed Chinese companies against the background of Sino-US confrontation and the active listing of semiconductor companies in line with national industrial policies. Behind it, you can see the intention to support strategic companies through IPO.
According to data from accounting firm KPMG, global IPO financing will be US$180 billion in 2022, a sharp drop from US$468 billion in 2021. IPOs in the U.S. dwindled rapidly as inflation and rising interest rates rattled financial markets. Funding in the U.S. is more than 90% lower than in 2021. Under such circumstances, it is expected that China's IPO financing will increase by 5% over the previous year, hitting a record high for two consecutive years. In terms of financing amount rankings of various exchanges, Shanghai Stock Exchange ranks first in the world, Shenzhen Stock Exchange ranks second, while New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq fall out of the top five. The number of IPOs in China in 2022 will be 410, down from 503 in 2021, but large IPOs will increase. The background is that under the influence of confrontation with China and the United States, the Chinese government is actively promoting the domestic listing of domestic companies. China Mobile, the largest state-owned telecommunications operator that terminated its listing in the US, and China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC), a state-owned oil giant, have successively completed large-scale IPOs in Shanghai. The amount of financing reached 52 billion yuan and 32.3 billion yuan respectively.
China is actively using emerging markets in order to drive domestic capital flows to key industries in line with national policy. Domestic semiconductor manufacturer Haiguang Information Technology and Shanghai United Imaging Medical Technology, a medical device company, were listed on the "Science and Technology Innovation Board" in Shanghai, a market for high-tech emerging companies. Financing for semiconductors and semiconductor production equipment was 82.8 billion yuan, the most among industries, according to data from Chinese research firm Wind. According to data from PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), among China's domestic IPOs in 2022, the "Science and Technology Innovation Board" and Shenzhen's "GEM" market for emerging companies will account for two-thirds in terms of volume, accounting for 2/3 of the total amount of financing. accounted for nearly 70%. The financing volume of the Beijing Stock Exchange, which will be opened in 2021, is also expected to reach nearly 13 billion yuan
In order to simplify the IPO procedures, China has continuously shifted from a method in which securities regulatory authorities are responsible for reviewing to a registration system in which stock exchanges review listing applications. "The reform of the registration system has become the key to strong IPOs," said Sun Jin of PwC. Regarding the Sci-tech Innovation Board and the ChiNext Board, which have enhanced their presence, they "reflect the intention to support technology and innovation through the capital market." "High inflation, rising interest rates and monetary tightening are not conducive to high-tech companies listing in the US and Hong Kong. The financial environment in mainland China is rarely affected by rising interest rates," said KPMG's Dachang Lau.
Chinese IPOs are also expected to remain strong in 2023. According to KPMG data, there are about 900 IPOs queuing up, and active financing is expected to remain. PricewaterhouseCoopers predicts that in 2023, there will be 400-460 IPOs, and the amount of financing will reach 590 billion-652 billion yuan. The Hong Kong Stock Exchange, whose IPO financing in 2022 will be reduced by 70% compared with the previous year, has also begun to discuss relaxing listing standards in specific areas such as new-generation IT and cutting-edge hardware. In the future, it may become an option for high-tech companies that China values to go public. Zhao Yaoting of Invesco, an American asset management company, said, "There is still a huge demand for Chinese companies to go public in Hong Kong." For China, the expansion of the IPO market has the advantages of not relying on external capital such as the United States and making it easier to cultivate strategic companies. On the other hand, the color of "national policy IPO" that only companies that conform to China's policy guidelines are listed may also be strengthened.
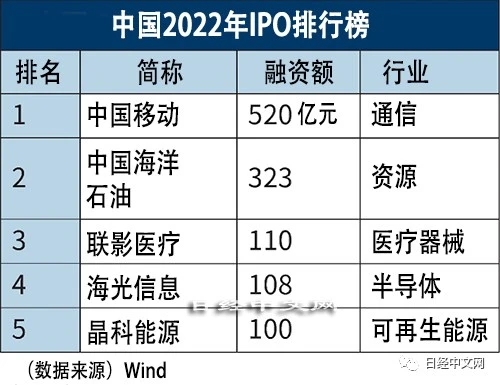
The picture shows the top five IPOs in China
According to data from accounting firm KPMG, global IPO financing will be US$180 billion in 2022, a sharp drop from US$468 billion in 2021. IPOs in the U.S. dwindled rapidly as inflation and rising interest rates rattled financial markets. Funding in the U.S. is more than 90% lower than in 2021. Under such circumstances, it is expected that China's IPO financing will increase by 5% over the previous year, hitting a record high for two consecutive years. In terms of financing amount rankings of various exchanges, Shanghai Stock Exchange ranks first in the world, Shenzhen Stock Exchange ranks second, while New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and Nasdaq fall out of the top five. The number of IPOs in China in 2022 will be 410, down from 503 in 2021, but large IPOs will increase. The background is that under the influence of confrontation with China and the United States, the Chinese government is actively promoting the domestic listing of domestic companies. China Mobile, the largest state-owned telecommunications operator that terminated its listing in the US, and China National Offshore Oil Corporation (CNOOC), a state-owned oil giant, have successively completed large-scale IPOs in Shanghai. The amount of financing reached 52 billion yuan and 32.3 billion yuan respectively.
China is actively using emerging markets in order to drive domestic capital flows to key industries in line with national policy. Domestic semiconductor manufacturer Haiguang Information Technology and Shanghai United Imaging Medical Technology, a medical device company, were listed on the "Science and Technology Innovation Board" in Shanghai, a market for high-tech emerging companies. Financing for semiconductors and semiconductor production equipment was 82.8 billion yuan, the most among industries, according to data from Chinese research firm Wind. According to data from PricewaterhouseCoopers (PwC), among China's domestic IPOs in 2022, the "Science and Technology Innovation Board" and Shenzhen's "GEM" market for emerging companies will account for two-thirds in terms of volume, accounting for 2/3 of the total amount of financing. accounted for nearly 70%. The financing volume of the Beijing Stock Exchange, which will be opened in 2021, is also expected to reach nearly 13 billion yuan
In order to simplify the IPO procedures, China has continuously shifted from a method in which securities regulatory authorities are responsible for reviewing to a registration system in which stock exchanges review listing applications. "The reform of the registration system has become the key to strong IPOs," said Sun Jin of PwC. Regarding the Sci-tech Innovation Board and the ChiNext Board, which have enhanced their presence, they "reflect the intention to support technology and innovation through the capital market." "High inflation, rising interest rates and monetary tightening are not conducive to high-tech companies listing in the US and Hong Kong. The financial environment in mainland China is rarely affected by rising interest rates," said KPMG's Dachang Lau.
Chinese IPOs are also expected to remain strong in 2023. According to KPMG data, there are about 900 IPOs queuing up, and active financing is expected to remain. PricewaterhouseCoopers predicts that in 2023, there will be 400-460 IPOs, and the amount of financing will reach 590 billion-652 billion yuan. The Hong Kong Stock Exchange, whose IPO financing in 2022 will be reduced by 70% compared with the previous year, has also begun to discuss relaxing listing standards in specific areas such as new-generation IT and cutting-edge hardware. In the future, it may become an option for high-tech companies that China values to go public. Zhao Yaoting of Invesco, an American asset management company, said, "There is still a huge demand for Chinese companies to go public in Hong Kong." For China, the expansion of the IPO market has the advantages of not relying on external capital such as the United States and making it easier to cultivate strategic companies. On the other hand, the color of "national policy IPO" that only companies that conform to China's policy guidelines are listed may also be strengthened.
The picture shows the top five IPOs in China
