NG Missile Vessels
FULL MEMBER

- Joined
- Apr 9, 2023
- Messages
- 1,600
- Reaction score
- 0
- Country
- Location
In a groundbreaking move aimed at advancing scientific comprehension in the field of astronomy, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has announced its latest venture, XPoSat (X-ray Polarimeter Satellite). Following the successful launches of the Chandrayaan-3 Moon lander and Aditya-L1 missions, ISRO is now turning its focus towards unlocking the mysteries of bright astronomical X-ray sources under extreme conditions.
XPoSat marks India's inaugural dedicated polarimetry mission, with the mission's core objective being the study of various dynamics within bright astronomical X-ray sources. Positioned in low Earth orbit, the spacecraft will carry two essential scientific payloads designed to collect invaluable data.
The primary payload, known as POLIX (Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays), is tailored to measure the polarimetry parameters, encompassing the degree and angle of polarisation. It will specifically target the medium X-ray energy range of 8-30 keV photons of astronomical origin. Alongside POLIX, the XSPECT (X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing) payload will play a crucial role by offering spectroscopic information in the energy range of 0.8-15 keV.
ISRO emphasises that the emission mechanisms observed in various astronomical sources, including black holes, neutron stars, active galactic nuclei, and pulsar wind nebulae, stem from complex physical processes that challenge our understanding. While spectroscopic and timing data collected from space-based observatories provide significant insights, the precise nature of these emissions remains enigmatic, as acknowledged by ISRO officials.
"The polarimetry measurements add two more dimensions to our understanding, the degree of polarisation and the angle of polarization, and thus is an excellent diagnostic tool to understand the emission processes from astronomical sources," ISRO stated.
The integration of polarimetric observations with spectroscopic measurements is expected to break down the barriers of several theoretical models of astronomical emission processes, ISRO noted. This fusion of data is poised to be the primary avenue of research for the Indian scientific community through the XPoSat mission.
POLIX, the X-ray Polarimeter, operates in the energy band of 8-30 keV and consists of a collimator, a scatterer, and four X-ray proportional counter detectors. The collimator narrows the field of view to 3 degrees by 3 degrees, ensuring that only one bright source is observed at a time during most observations. POLIX's mission will involve observing approximately 40 bright astronomical sources of various categories over the planned five-year lifespan of the XPoSat mission, making it the first payload dedicated to polarimetry measurements in the medium X-ray energy band.
XSPECT, the X-ray Spectroscopy and Timing payload, offers rapid timing measurements and impressive spectroscopic resolution in soft X-rays. Complementing POLIX's long-duration observations for X-ray polarisation measurement, XSPECT will provide extended monitoring of spectral state changes, alterations in line flux and profile, and simultaneous long-term temporal tracking of soft X-ray emissions within the energy range of 0.8-15 keV. XSPECT's target sources encompass X-ray pulsars, black hole binaries, low-magnetic field neutron stars (NS) in low-mass X-ray binaries (LMXBs), active galactic nuclei (AGNs), and Magnetars.
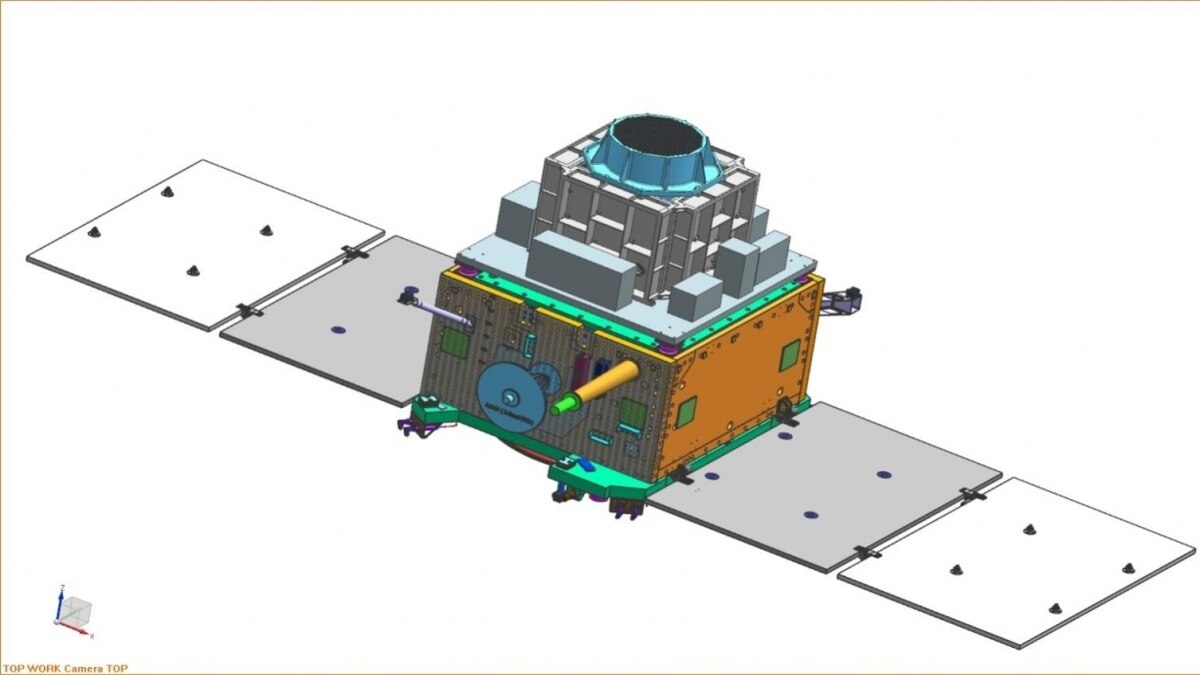
After Moon and Sun, ISRO readies XPoSat mission to enhance understanding in Astronomy
XPoSat marks India's inaugural dedicated polarimetry mission, with the mission's core objective being the study of various dynamics within bright astronomical X-ray sources
