LeGenD
MODERATOR

- Joined
- Aug 28, 2006
- Messages
- 15,813
- Reaction score
- 162
- Country
- Location
The United States (US) has fought many wars and became the most powerful country in the world. This thread provides an overview of American wars and their respective outcomes. This thread also disclose American warfare theories and concepts that were adopted to plan and fight limited-scale wars in post World War II times.
American military publications in following link:
DETAILS of major wars in following link:
http://www.historycentral.com/wars.html
American KIA statistics of major wars from 1775 to 2022 in following link:
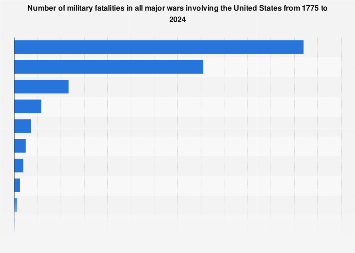
 www.statista.com
www.statista.com
War outcomes in American context:
The US altered political landscape of a particular region = VICTORY = BLUE (Use of force); PURPLE (Other methods)
The opposing side recovered in a particular region or altered political landscape of a particular region = DEFEAT = RED
Victorious Camp in American Civil War = GREEN
Controversy = ORANGE
------ ------ ------
1. REVOLUTIONARY WAR
THE WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE
From [1]: "This treaty, signed on September 3, 1783, between the American colonies and Great Britain, ended the American Revolution and formally recognized the United States as an independent nation."
World Conflict situation
From [1]: "The American War for Independence (1775-1783) was actually a world conflict, involving not only the United States and Great Britain, but also France, Spain, and the Netherlands. The peace process brought a nascent United States into the arena of international diplomacy, playing against the largest and most established powers on earth."
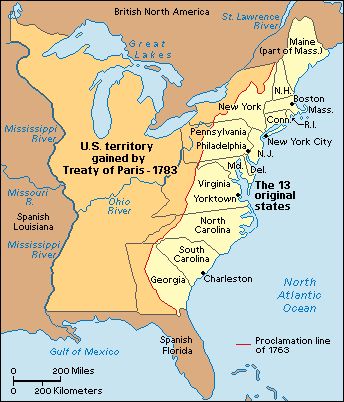
Map of the United States post Treaty of Paris
References
 history.state.gov
history.state.gov

 www.battlefields.org
www.battlefields.org
Comments
1. USA is the only former colony of the mighty British Empire that fought for its independence and accomplished its objective in this manner. American (settlers) were good at fighting on average and decided to formulate a separate nation due to mistreatment from the British.
2. Territorial disputes with the British and Spanish were far from settled yet which led to additional wars in the region:

2. WAR OF 1812
THE WAR FOR EXPANSION OF THE HOMELAND
From [1]: "This "Treaty of Peace and Amity Between the United States and Great Britain" was signed on December 24, 1814. It ended the War of 1812, fought between Great Britain and the United States."
Decisive battle
References
 history.state.gov
history.state.gov

 www.battlefields.org
www.battlefields.org
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/the-10-things-you-didnt-know-about-the-war-of-1812-102320130/
Comments
1. USA actually fought a 4-front war with the British, Canada, Red Indian tribes, and the Spanish to reshape political landscape of the region.
2. This is the only war in history in which an opponent managed to burn the White House (the center of American politics and power).
3. MEXICAN - AMERICAN WAR
THE WAR FOR EXPANSION OF THE HOMELAND
 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com
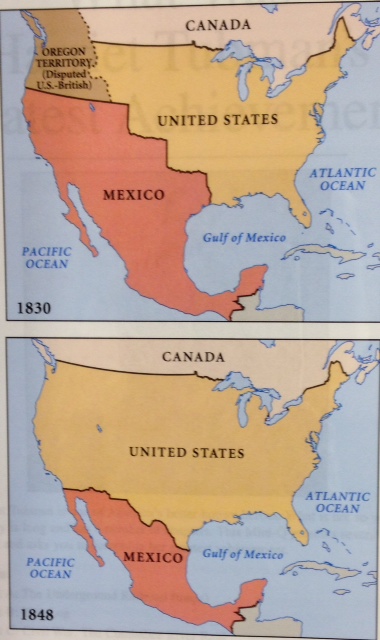
From [1]: "The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, that brought an official end to the Mexican-American War (1846-1848), was signed on February 2, 1848, at Guadalupe Hidalgo, a city north of the capital where the Mexican government had fled with the advance of U.S. forces. By its terms, Mexico ceded 55 percent of its territory, including parts of present-day Arizona, California, New Mexico, Texas, Colorado, Nevada, and Utah, to the United States. Mexico relinquished all claims to Texas, and recognized the Rio Grande as the southern boundary with the United States."
Map of the United States post Treaty of Gualalupe Hidalgo
References
 library.uta.edu
library.uta.edu

Comments
The US - Mexico War (1846 - 1848) is the largest and most significant armed struggle between two nations in the western hemisphere. See references above for more information.
4. CIVIL WAR
DARK TIMES
References

 www.battlefields.org
www.battlefields.org
 westportlibrary.libguides.com
westportlibrary.libguides.com

 www.vox.com
www.vox.com
Comments
1. Americans turned their guns on each other this time (over the issue of legitimacy of slavery) and a brutal civil war ensued:
2. Between 1861 and 1865, 10,000 battles and engagements were fought across the continent, from Vermont to the New Mexico Territory, and beyond. The four-year struggle between north and south made heroes of citizen soldiers, forever changed the role of women in society, and freed more than 3 million slaves. In the end, 620,000 or more Americans were left dead in its wake. See references above for more information.
5. SPANISH - AMERICAN WAR
BECOMING A GREAT POWER
Decisive battle
 www.history.navy.mil
www.history.navy.mil
References
 history.state.gov
history.state.gov
 ohiohistorycentral.org
ohiohistorycentral.org

 dp.la
dp.la
Comments
1. Accident on and subsequent loss of the USS Maine in Havana, Cuba on February 15, 1898 set the stage for this war.
2. USA was able to cement its reputation as a "world power" by liberating several colonies of the Spanish Empire such as Cuba, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. Spanish Empire was one of the greatest in the world for centuries.
6. WORLD WAR I
RESHAPING EUROPE
From [1]: "After four years of devastating fighting, the First World War came to an end in 1919 in Versailles. The treaty, which represented “peace” for some and a “diktat” for others, also sowed the seeds of the Second World War, which would break out twenty years later."
List of battles involving American troops
References
 history.state.gov
history.state.gov
Comments
American intervention in 1917 ensured victory of Allied bloc (Russia; France; British Empire; and satellites) over Axis powers. Over 2 million American troops were deployed on the front-lines to help turn the tide. However, American intervention was restricted to the battlefield across Europe.
7. WORLD WAR II
SAVING THE WORLD
Pacific War (1942 - 1945)
Japanese assault on Pearl Harbor in 1941 set the stage for American intervention in this war.
Major combat operations in the WEST
Operation Torch (1942)
 www.history.navy.mil
www.history.navy.mil
Operation Avalanche (1943)
 www.history.navy.mil
www.history.navy.mil
Operation Overlord (1944)
 www.history.navy.mil
www.history.navy.mil
List of battles involving American troops
US-led forces produced significant battlefield effects and played a key role in downfall of the Axis Powers around the world.
References
Comments
1. American Lend-Lease Act made it possible for the USSR to defeat German forces in the East:
https://historyplex.com/lend-lease-act-1941-facts-summary-significance
2. World War II led to creation of the Global Order in which USA and USSR were respective superpowers. This situation set the stage of Cold War between them (see section 8 below).
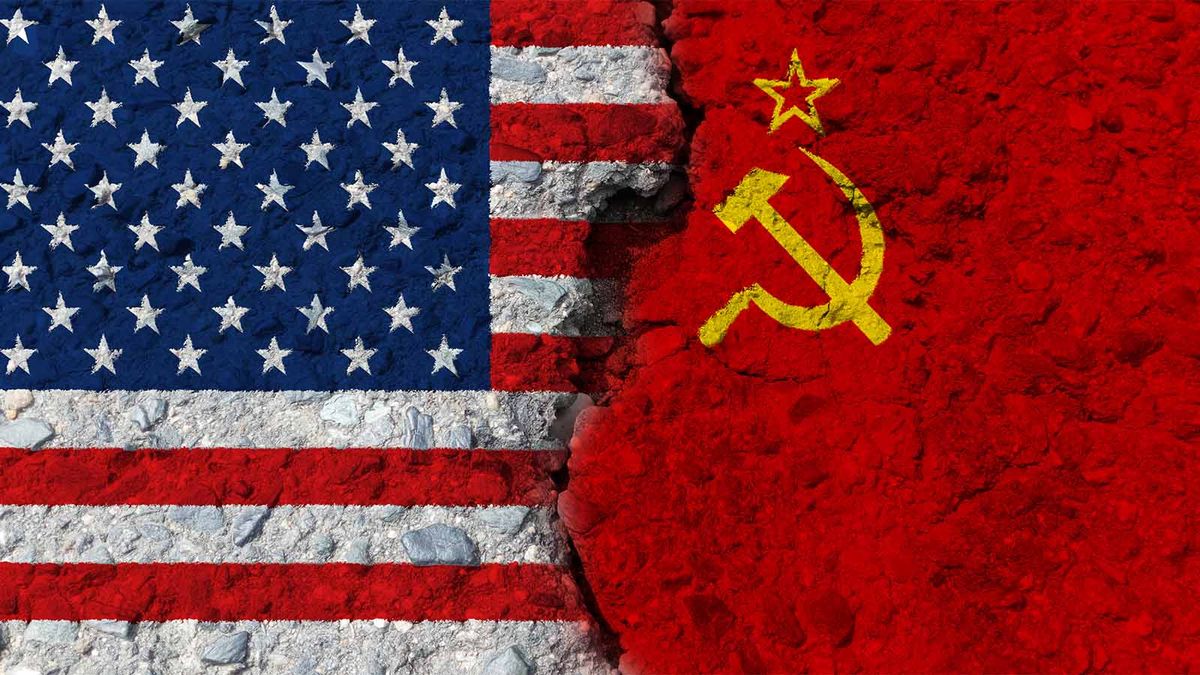
8. COLD WAR
THE CLASH OF CIVILIZATIONS

 history.howstuffworks.com
history.howstuffworks.com

 www.e-ir.info
www.e-ir.info

 tnsr.org
tnsr.org
Associated fronts and/or engagements:-
8.1. North Korea
Main thread

References
Comments
China prevented downfall of North Korea with its military might (Chinese success story), but US-led forces managed to liberate South Korea from communist forces and ensure its independence.
8.2. Cuban Missile Crises
References
 history.state.gov
history.state.gov
Comments
Soviet Union agreed to remove its nuclear umbrella from Cuba in-exchange of assurance from the USA to not invade Cuba and denuclearize Turkey.
8.3. Vietnam
Perspective
My analysis shows that American military was learning from its battlefield experiences and began to produce results in every battle that was fought in Vietnam since 1968. More importantly, a new generation of technologies emerged and could be employed to devastating effect in Operation Linebacker II in 1972 - this operation showed that technological supremacy could help turn the tide of war in Vietnam but domestic pressure on Nixon administration to give up on Vietnam was immense and it followed through.
---
References

 cgsc.contentdm.oclc.org
cgsc.contentdm.oclc.org
Comments
1. Although American military forces were able to win battles in Vietnam, American leaders did not capitalize on such gains (see "My analysis of the Vietnam War" part above).
2. Vietnam War provided valuable lessons for restructuring and re-equipping American military to fight a competent adversary much more effectively at some point in the future. Vietnam War was particularly instructive for re-equipping American military forces and revisiting American battle doctrine in subsequent years.
 merip.org
merip.org
8.4. Afghanistan
US made the war unwinnable for the Soviet Union in Afghanistan by providing massive assistance to the Mujahideen with collaboration of Pakistan.
References
Comments
Some of the Mujahideen banded together to establish Al-Qaeda Network in 1988. This development would set the stage for another war in Afghanistan (see section 11 below).
8.5. Panama
This was the largest and most complex military operation since Vietnam.
Perspective
---

 www.aljazeera.com
www.aljazeera.com
---
---

 www.coffeeordie.com
www.coffeeordie.com
References

 www.rand.org
www.rand.org
 apps.dtic.mil
apps.dtic.mil

 www.rand.org
www.rand.org
 intellibrary.libguides.com
intellibrary.libguides.com
9. Iraq
Perspective
 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com
References

Comments
1. US-led coalition defeated Iraq in the war (and liberated Kuwait by extension) through combination of a well-planned military operation involving a deception plan and tactics and technological supremacy with surprises in the mix.
2. This is the FIRST war in which US applied its AirLand Battle Doctrine to devastating effect.
 apps.dtic.mil
apps.dtic.mil

10. Yugoslavia
Perspective
Yugoslavian A2/AD arrangements were among the finest in Europe shaped by lessons drawn from Operation Desert Storm with a network of radar systems that were collectively optimized to detect Low Observable (LO) aircraft and cruise missiles. Earliest examples of IMAD setups in fact.
"Air Force and NATO aircraft faced significantly more effective air defenses than what they had recently encountered in Iraq, and pilots were initially instructed to stay above 15,000 feet to minimize risk."

But NATO humbled Yugoslavian A2/AD arrangements and lost only two aircraft over Yugoslavia:
"After 65 days of operations, NATO had lost to enemy fire only two aircraft–an F-117 and an F-16–with no casualties."
 www.airandspaceforces.com
www.airandspaceforces.com
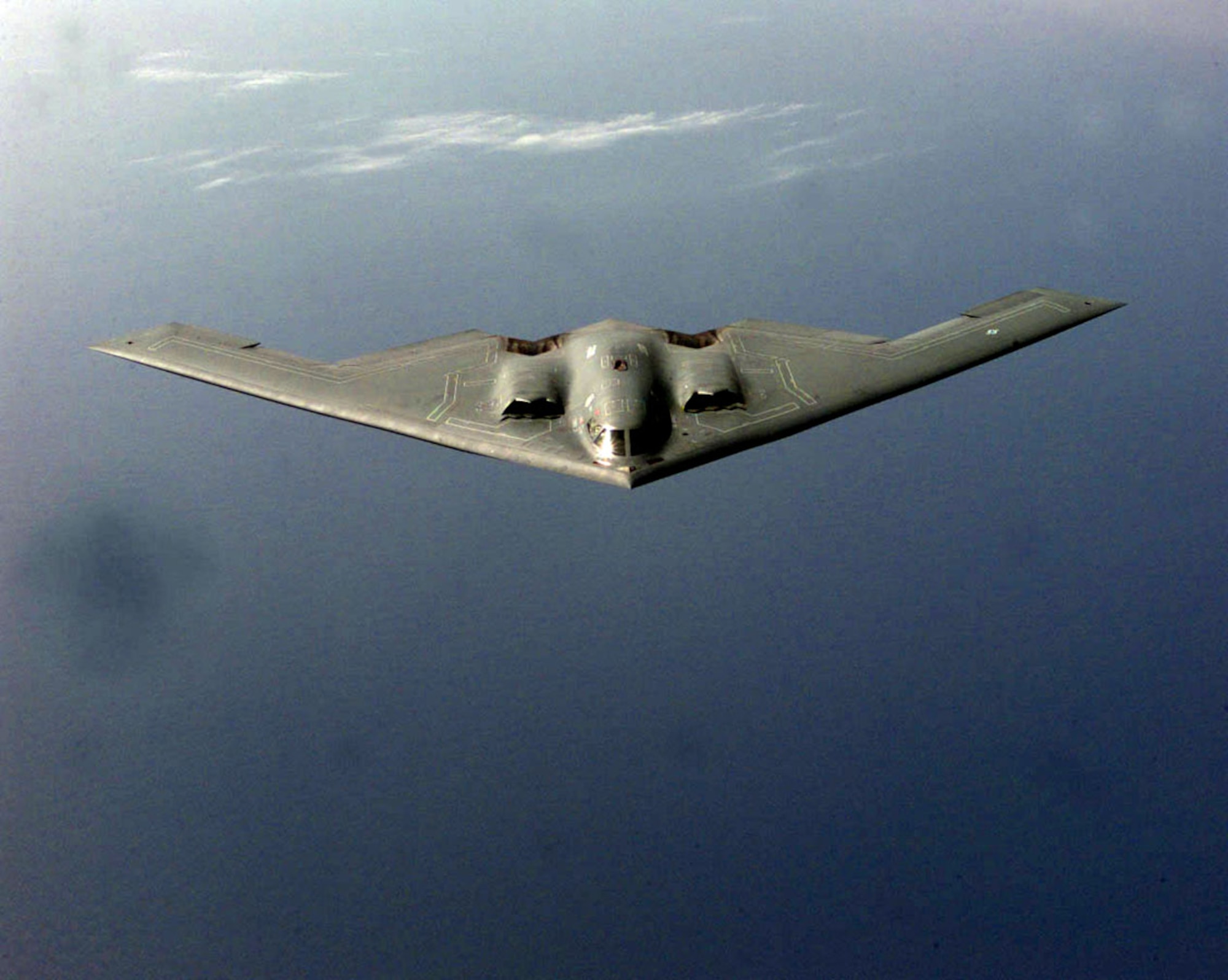
B-2A bomber proved its mettle in Yugoslavia:
"The combat effectiveness of the B-2 was proved in Operation Allied Force, where it was responsible for destroying 33 percent of all Serbian targets in the first eight weeks, by flying nonstop to Kosovo from its home base in Missouri and back."

"In its first combat test, the B-2 bomber defeated not only the Serbian air defense system but also the critics who for years had insisted it would not work as advertised or would never be risked in real war."
 www.airandspaceforces.com
www.airandspaceforces.com
Related Discussion
References

 www.nato.int
www.nato.int
 www.history.navy.mil
www.history.navy.mil


 www.rand.org
www.rand.org
 www.airforcemag.com
www.airforcemag.com
 www.jstor.org
www.jstor.org
11. WAR ON TERROR
GLOBAL WAR ON TERRORISM
*Compromise as a solution to conflict.
Al-Qaeda Network (a multinational terrorist group) was deemed responsible for horrendous acts of terrorism on American soil on September 11, 2001. This event propelled US to launch its War On Terror to degrade or defeat Al-Qaeda Network around the world. US also created the Department of Homeland Security to prevent terror attacks on American soil. But US decided to settle scores with perceived enemies in Iraq and Libya on the side.
Timeline of elimination of the most influential members of the Al-Qaeda Network around the world:
US used drones to assassinate a large number of terrorists in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Somalia, and Yemen respectively:
 www.thebureauinvestigates.com
www.thebureauinvestigates.com
The role of NSA in Drone Warfare:

 theintercept.com
theintercept.com
Killed in action (KIA):

Associated fronts and/or engagements:-
11.1. Afghanistan
Toppling Taliban regime
This mission was accomplished in the (October 2001 - June 2002) period.

 www.rand.org
www.rand.org
US applied its AirLand Battle doctrine to defeat Al-Qaeda Network in Tora Bora Mountains in 2002 (Operation Anaconda).
 apps.dtic.mil
apps.dtic.mil
Notable efforts to dismantle Al-Qaeda Network
Pakistani contribution to this end in times of Musharraf administration is documented in following book:
---
Operation Neptune Spear
This operation is discussed at length in following links:
 usnwc.libguides.com
usnwc.libguides.com
 qr.ae
qr.ae
Wirtz, J. J. (2022). The Abbottabad raid and the theory of special operations. Journal of Strategic Studies, 45(6-7), 972-992.
 dataspace.princeton.edu
dataspace.princeton.edu
This operation set in motion a chain of tragic events in Pakistan:
https://acleddata.com/2017/02/07/the-fallout-of-operation-neptune-spear/
Additional pointers in following links:
1. CIA 3D model of the Abbottabad compound
2. Dr. Shakeel Afridi
3. Dead bodies found in the compound; these people are identified in the Abbottabad Commission Report
4. Documents recovered from the Abbottabad compound
5. General Ehsan ul Haq's account
6. Pakistan showing the preserved part of the crashed helicopter to a Chinese team
7. Osama Bin Laden's family
Seymour Hersh account is disputed and/or refuted in here, here, here, and here.
---

 www.brookings.edu
www.brookings.edu
---
US continues to monitor activity of Al-Qaeda remnants in Afghanistan and assassinated Ayman al-Zawahiri using over-the-horizon strike approach.

 www.washingtoninstitute.org
www.washingtoninstitute.org
Nation Building Failure

 www.project-syndicate.org
www.project-syndicate.org
Afghan Taliban were able to regroup in Pakistan and Iran and plot their return. Pakistan was reluctant to act against Afghan Taliban for various reasons.

 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com
Afghan Taliban demonstrated incredible proficiency in the art of insurgency warfare and continued to assert themselves as a stakeholder in Afghan political affairs. Afghan Taliban and US eventually came to an understanding in US - Taliban agreement.
Perspective

---

 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com
---
References

 www.rand.org
www.rand.org
Comments
1. Afghan Taliban returned to power in Afghanistan with American nod but US has withdrawn its financial assistance to the country. Afghanistan finds itself in a period of significant economic crisis in the present.

 news.un.org
news.un.org

 www.usip.org
www.usip.org
3. Pakistan continues to face security challenges emanating from Afghanistan in spite of fencing Durand Line.

 www.atlanticcouncil.org
www.atlanticcouncil.org

 www.eastasiaforum.org
www.eastasiaforum.org
Pakistan insists on addressing problems of Afghanistan, nevertheless.
11.2. Iraq
Toppling Saddam regime
"The U.S. victory in Iraq makes the German blitzkrieg look positively incompetent by comparison." - Boot (2003)
Urban warfare was central to combat strategy of Saddam regime due to lack of options for its forces in open landscapes in 2003 as noted in here and here. American tanks could survive in Iraqi urban spaces - this dynamic coupled with excellent precision strike capability and good intel was a winning combination. US-led forces toppled Saddam regime in a matter of days in a stunningly effective application of Blitzkrieg in modern times.
"Coalition forces in the second Gulf War were less than half the size of those deployed in the first one. Yet they achieved a much more ambitious goal-occupying all of Iraq, rather than just kicking the Iraqi army out of Kuwait-in almost half the time, with one-third the casualties, and at one-fourth the cost of the first war. Many will argue, in retrospect, that Saddam Hussein's forces were not all that formidable to begin with, and there is no doubt a great deal of truth in this. But they were capable enough when they fought the Iranian army to a draw in the 1980s and put down Kurdish and Shi'ite insurgencies in the 1990s. And, on paper at least, the Baathist regime's military enjoyed a big numerical advantage over U.S. and British forces. Although the Iraqi army was much degraded from its pre-1991 heyday, it still deployed more than 45o,ooo troops, including para-military units, the Republican Guard, and the Special Republican Guard, whose loyalty had been repeatedly demonstrated. Traditionally, war colleges have taught that to be sure of success, an attacking force must have a 3 to 1 advantage-a ratio that goes up to 6 to 1 in difficult terrain such as urban areas. Far from having a 3 to 1 advantage in Iraq, coalition ground forces (which never numbered more than ioo,ooo) faced a 3 to 1 or 4 to 1 disadvantage.
That the United States and its allies won anyway-and won so quickly-must rank as one of the signal achievements in military history. Previously, the gold standard of operational excellence had been the German blitzkrieg through the Low Countries and France in 1940. The Germans managed to conquer France, the Netherlands, and Belgium in just 44 days, at a cost of "only" 27,000 dead soldiers. The United States and Britain took just 26 days to conquer Iraq (a country 80 percent of the size of France), at a cost of 161 dead, making fabled generals such as Erwin Rommel and Heinz Guderian seem positively incompetent by comparison."
Boot, M. (2003). The new American way of war. Foreign Affairs, 41-58.
US applied its AirLand Battle doctrine to topple Saddam regime in 2003.
 apps.dtic.mil
apps.dtic.mil
Compare the above to the situation when Iraq was up against a regional adversary in the 1980s. Iraqi forces managed to capture Khorramshahr in 1980 but lost this city to Iranian forces in 1982. Iranian forces could not capture a single Iraqi city in war that lasted 8 years on the other hand - not even Basra (1986 - 1987). Much of the war could be fought in open landscapes and ballistic missiles were used to attack different cities. This was the situation between adversaries that were evenly matched on the whole.
De-baathification of Iraq
De-Baathification of Iraq - similar to De-Nazification of Germany
 www.cambridge.org
www.cambridge.org
De-Baathification of Iraq presented considerable challenge to US-led forces in fact. Saddam regime was toppled in 2003 but Iraq produced a significant level of insurgency that claimed many lives through the years. US-led forces were moved to former Iraqi military bases but had to fight to recapture some of the Iraqi cities that were lost to various insurgent groups through the years.
Ramadi, Husaybah, Najaf, Samarra, Mosul, and Fallujah in 2004. Fighting was most violent and intense in Fallujah and the city was recaptured in second attempt but much of it was reduced to rubble in the process (Operation Phantom Fury).
Tal Afar in 2005
Ramadi in 2006
Karbala in 2007, and Basra and Sadr City in 2008. These battles were fought with Iran-backed Mehdi Army. This was a large and powerful insurgent group that claimed 600 American lives in the war but was defeated in 2008 and its leader Muqtada al-Sadr fled to Iran to avoid attempts on his life.
Reflections:
Moaddel, M., Tessler, M., & Inglehart, R. (2008). Saddam Hussein and the Sunni insurgency: Findings from values surveys. Political Science Quarterly, 123(4), 623-644.

 www.ictj.org
www.ictj.org
Fate of Saddam Hussein's two sons

 www.theguardian.com
www.theguardian.com
Leader of Al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI) killed in 2006

 www.nytimes.com
www.nytimes.com
Execution of Saddam Hussein

 www.theguardian.com
www.theguardian.com

 www.al-monitor.com
www.al-monitor.com
Reboot of Iraqi political system
Iraq is now a Federal Parliamentary Republic:
Fallujah - a case study of Urban Warfare

 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com

 mca-marines.org
mca-marines.org
Sadr City - a case study of Urban Warfare

 www.rand.org
www.rand.org
References

 www.brookings.edu
www.brookings.edu

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
Comments
Iraqi insurgency was a very violent and destructive development on the whole with Syria and Iran providing arms and guidance to different insurgent groups in Iraq, but US-led forces defeated all insurgent groups and stabilized the country in 2008 and Obama administration withdrew US-led forces from Iraq in 2011.

 www.theguardian.com
www.theguardian.com

 www.reuters.com
www.reuters.com
Muqtada al-Sadr returned to Iraq in 2011.
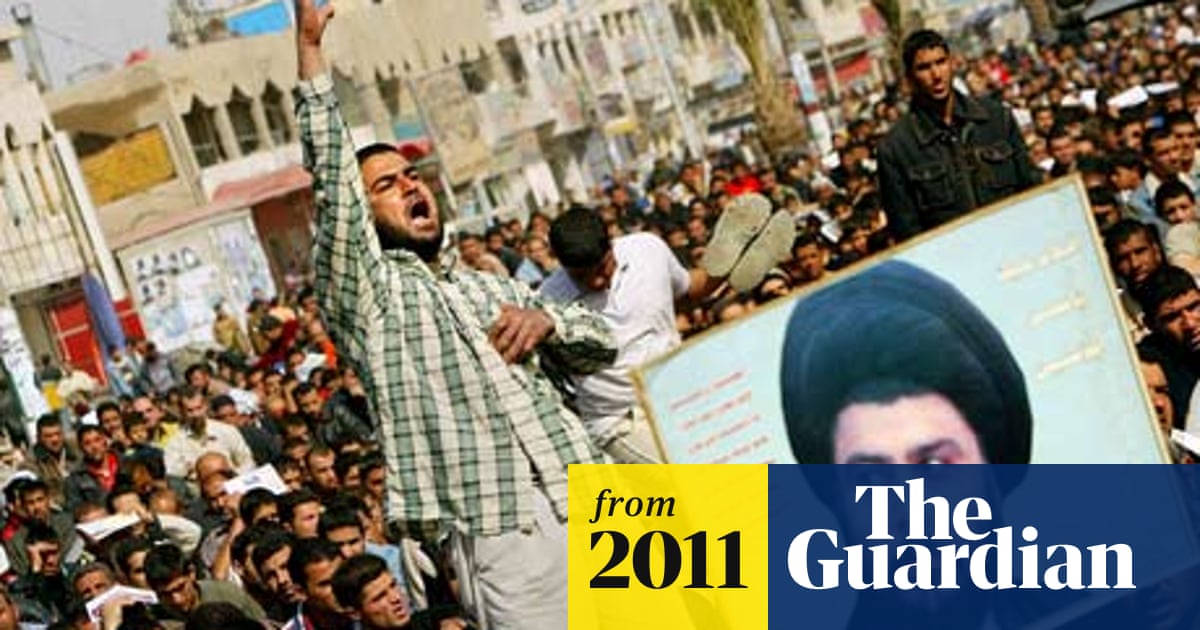

 www.theguardian.com
www.theguardian.com
US has reshaped political landscape of Iraq but the war has also allowed Iran to make political inroads into Iraq. This situation has opened a new chapter of conflict in the region by extension.

 www.iiss.org
www.iiss.org
11.3. Libya
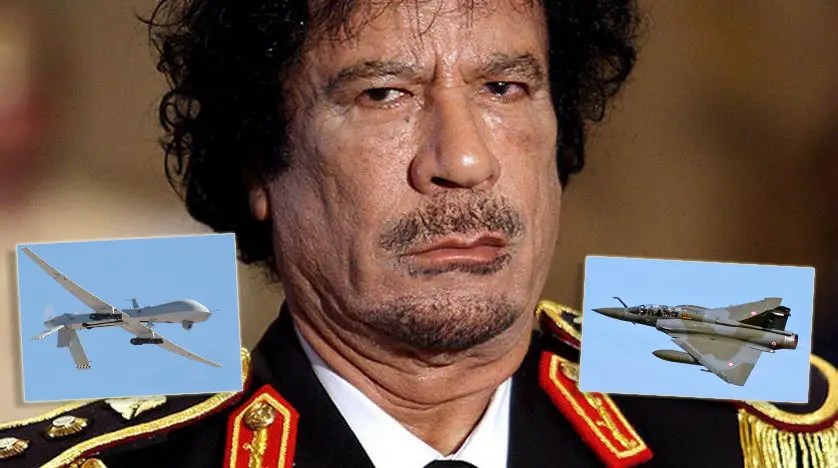
Fate of Muammar Qaddafi
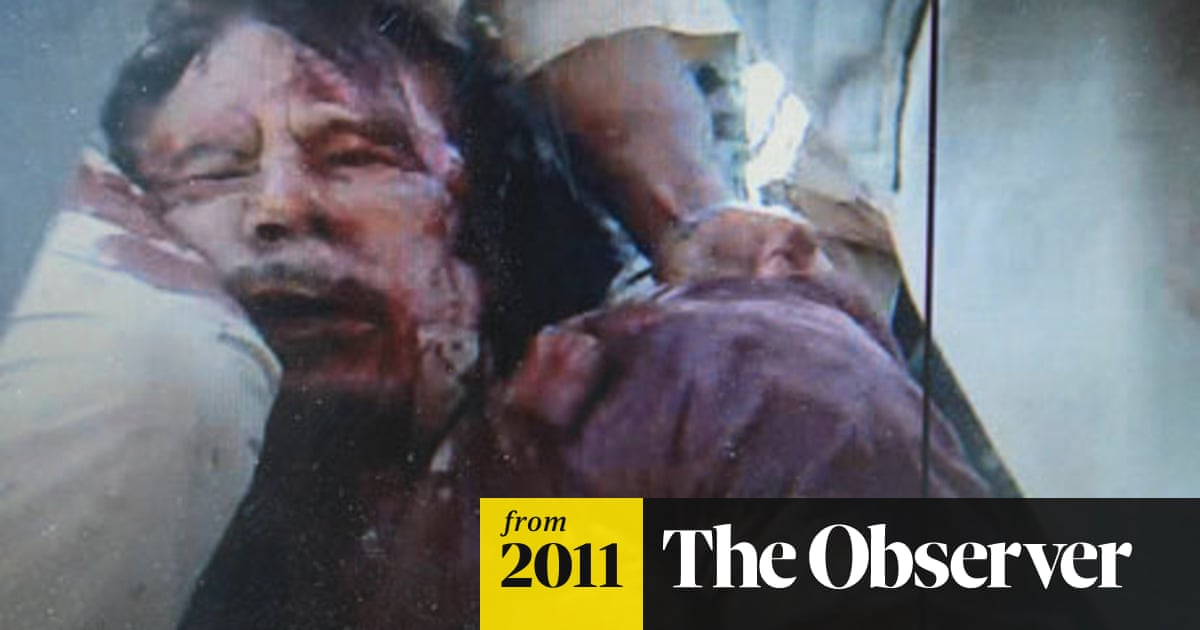

 www.theguardian.com
www.theguardian.com

 theaviationist.com
theaviationist.com
References

 www.rand.org
www.rand.org

 en.wikipedia.org
en.wikipedia.org
Comments
US conducted a shadow war to defeat ISIL elements in Sirte in 2016.

 theintercept.com
theintercept.com
11.4. Islamic State of Iraq and Levant (ISIL)
Main thread

Perspective
Poor security situation in Syria and political blunders of Maliki administration in Iraq allowed survivors of Saddam regime and Al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI) to regroup and establish the Islamic State of Iraq and Levant (ISIL) in 2013 and its call for jihad appealed to thousands from all over the world, and ISIL managed to spread across Syria and Iraq consequently.
NATO . Success in this mission is in part owed to local actors in Iraq and Syria who were willing to fight ISIL and stood firm in this cause.
Iraqi establishment called on the US to help liberate Iraqi lands and cities from ISIL forces in 2014. US troops returned to Iraq in 2014 to restructure localized resistance fronts and US-led forces liberated Mosul and Raqqa in 2017.
The Operation Inherent Resolve is a COIN masterpiece involving calculative application of local partners and Air Power to counter a formidable multinational terrorist network. The operation also underscore the commitment of local partners to the cause.
References

 www.rand.org
www.rand.org
Comments
1. ISIL defectors explain how ISIL emerged and managed its operations:
2. US established the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) bloc to help counter ISIL in Syria but this development led to tensions between US and Turkey due to involvement of PKK in SDF.
3. Iran-led forces also fought ISIL but independently.

 theintercept.com
theintercept.com
4. US continues to monitor situation in Syria.
------ ------ ------
The US has also defined modern warfare concepts for the rest of the world to emulate (if possible) or study at minimum.
Modern Warfare Theories:

 link.springer.com
link.springer.com
The US adopted this theory to plan and fight multiple limited-scale wars in post World War II times.
Boyd understood that victory in aerial engagements did not go to the faster or higher-flying aircraft but to the pilot whose aircraft had superior sustained turn performance, allowing maneuvers behind the prey. Boyd's Energy-Maneuverability Theory analysed how well an aircraft could change energy states involving speed, acceleration, kinetic and potential energy.

 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com
Boyd's the OODA Loop is a tool that explains how individuals and organizations can succeed in uncertain and chaotic environments. Boyd perceived four elements of command and control. These functions form the core of Boyd’s research of commanders and armies at war. In a dynamic environment, competitors with superior OODA capability out-think and out-maneuver lesser opponents. The model applies to fighter aircraft, military organizations, and private business.

 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com
Boyd's the OODA Loop provides the basis for Maneuver Warfare Theory and conceptualization of the (battle-tested) AirLand Battle Doctrine which was successfully applied on two separate occasions such as in 1991 to liberate Kuwait and in 2003 to topple Saddam regime in Iraq.
Modern Battle Doctrines:
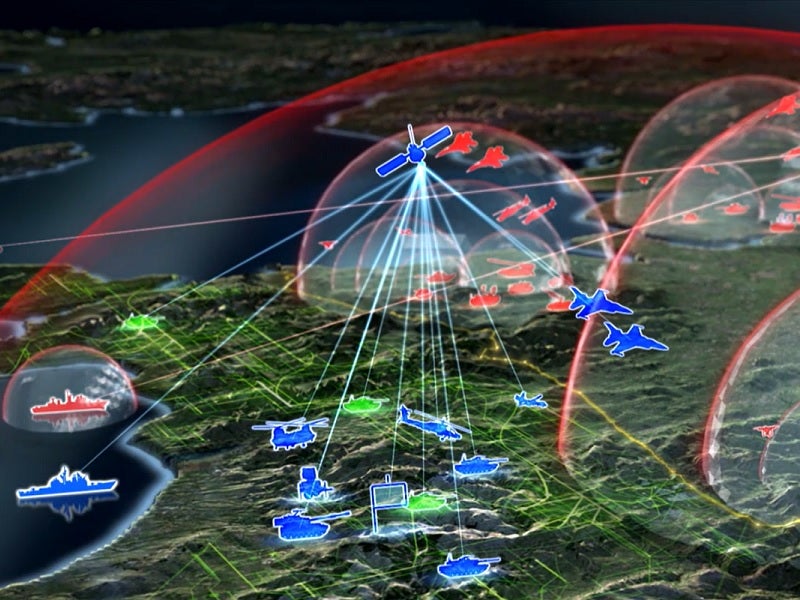
Towards Multi-Domain Operations Doctrine?

 www.ausa.org
www.ausa.org
 apps.dtic.mil
apps.dtic.mil

 www.army-technology.com
www.army-technology.com

 www.newamerica.org
www.newamerica.org

 www.lockheedmartin.com
www.lockheedmartin.com
American military publications in following link:
DETAILS of major wars in following link:
http://www.historycentral.com/wars.html
American KIA statistics of major wars from 1775 to 2022 in following link:

United States: war fatalities1775-2024 | Statista
The American Civil War is the conflict with the largest number of American military fatalities in history.
War outcomes in American context:
The US altered political landscape of a particular region = VICTORY = BLUE (Use of force); PURPLE (Other methods)
The opposing side recovered in a particular region or altered political landscape of a particular region = DEFEAT = RED
Victorious Camp in American Civil War = GREEN
Controversy = ORANGE
------ ------ ------
1. REVOLUTIONARY WAR
THE WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE
| Opponent | The British Empire |
| Allies | France |
| Duration | 1775 - 1783 |
| Outcome | American victory with Treaty of Paris [1] |
From [1]: "This treaty, signed on September 3, 1783, between the American colonies and Great Britain, ended the American Revolution and formally recognized the United States as an independent nation."
World Conflict situation
From [1]: "The American War for Independence (1775-1783) was actually a world conflict, involving not only the United States and Great Britain, but also France, Spain, and the Netherlands. The peace process brought a nascent United States into the arena of international diplomacy, playing against the largest and most established powers on earth."
Map of the United States post Treaty of Paris

References
Milestones in the History of U.S. Foreign Relations - Office of the Historian
history.state.gov 3.0 shell

Overview of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War is forever ingrained within our American identity, and provides all Americans a sense of who we are, or, at the very least, who we should be. Our forefathers fought for liberty, freedom, and republican ideals the likes of which had never before been seen in any...
Comments
1. USA is the only former colony of the mighty British Empire that fought for its independence and accomplished its objective in this manner. American (settlers) were good at fighting on average and decided to formulate a separate nation due to mistreatment from the British.
2. Territorial disputes with the British and Spanish were far from settled yet which led to additional wars in the region:

2. WAR OF 1812
THE WAR FOR EXPANSION OF THE HOMELAND
| Opponent | The British Empire* |
| Allies | |
| Duration | 1812 - 1815 (3 years) |
| Outcome | American victory with Treaty of Ghent [1] |
From [1]: "This "Treaty of Peace and Amity Between the United States and Great Britain" was signed on December 24, 1814. It ended the War of 1812, fought between Great Britain and the United States."
Decisive battle
References
Milestones in the History of U.S. Foreign Relations - Office of the Historian
history.state.gov 3.0 shell

A Brief Overview of the War of 1812
The War of 1812 brought the United States onto the world's stage in a conflict that ranged throughout the American Northeast, Midwest, and Southeast, into...
NMAH | The War of 1812
Although its events inspired one of the nation’s most famous patriotic songs, the War of 1812 is a relatively little-known war in American history. Despite its complicated causes and inconclusive outcome, the conflict helped establish the credibility of the young United States among other...
amhistory.si.edu
https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/the-10-things-you-didnt-know-about-the-war-of-1812-102320130/
Comments
1. USA actually fought a 4-front war with the British, Canada, Red Indian tribes, and the Spanish to reshape political landscape of the region.
2. This is the only war in history in which an opponent managed to burn the White House (the center of American politics and power).
3. MEXICAN - AMERICAN WAR
THE WAR FOR EXPANSION OF THE HOMELAND
| Opponent | Mexican Empire |
| Allies | |
| Duration | 1846 - 1848 (2 years) |
| Outcome | American victory with Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo [1] |

The Mexican-American War - Explained in 16 minutes
The Mexican-American War - Explained in 16 minutes♦Consider supporting the Channel : https://www.patreon.com/Knowledgia♦Please consider to SUBSCRIBE: https:/...
From [1]: "The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, that brought an official end to the Mexican-American War (1846-1848), was signed on February 2, 1848, at Guadalupe Hidalgo, a city north of the capital where the Mexican government had fled with the advance of U.S. forces. By its terms, Mexico ceded 55 percent of its territory, including parts of present-day Arizona, California, New Mexico, Texas, Colorado, Nevada, and Utah, to the United States. Mexico relinquished all claims to Texas, and recognized the Rio Grande as the southern boundary with the United States."
Map of the United States post Treaty of Gualalupe Hidalgo

References
Home Page | A Continent Divided: The U.S. Mexico War

The Mexican American War | American Experience | PBS
Determined to acquire the land, Polk sent American troops to Texas in January of 1846 to provoke the Mexicans into war.
www.pbs.org
Comments
The US - Mexico War (1846 - 1848) is the largest and most significant armed struggle between two nations in the western hemisphere. See references above for more information.
4. CIVIL WAR
DARK TIMES
| American factions | Union versus Confederate |
| Allies | |
| Duration | 1861 - 1865 (4 years) |
| Outcome | Union victory |
References

A Brief Overview of the American Civil War
The Civil War of 1861-1865 determined what kind of nation the United States would be.

The Westport Library Resource Guides: American Civil War: About
The Westport Library Resource Guides: American Civil War: About

37 maps that explain the American Civil War
150 years after Abraham Lincoln's assassination, these maps explain the origins of the Civil War, why the North won, and how the war transformed the United States.
 www.vox.com
www.vox.com
Comments
1. Americans turned their guns on each other this time (over the issue of legitimacy of slavery) and a brutal civil war ensued:
2. Between 1861 and 1865, 10,000 battles and engagements were fought across the continent, from Vermont to the New Mexico Territory, and beyond. The four-year struggle between north and south made heroes of citizen soldiers, forever changed the role of women in society, and freed more than 3 million slaves. In the end, 620,000 or more Americans were left dead in its wake. See references above for more information.
5. SPANISH - AMERICAN WAR
BECOMING A GREAT POWER
| Opponent | Spanish Empire |
| Allies | |
| Duration | 1898 (3 months) |
| Outcome | American victory with Treaty of Paris [1] |
Decisive battle
Battle of Santiago Bay
The Battle of Santiago Bay By late June it seemed almost certain that Santiago de Cuba, and the Spanish squadron of Adm. PascualCervera y Topete, would be captured. The North Atlantic Fleet instituted a rigorous and effective round-the-clock blockade of the harbor and in late June the United...
References
Milestones in the History of U.S. Foreign Relations - Office of the Historian
history.state.gov 3.0 shell
Spanish-American War - Ohio History Central

The Spanish-American War in the Philippines and the Battle for Manila | American Experience | PBS
Congress approved President McKinley's request for a declaration of war on April 25, 1898; yet the Spanish-American War was the culmination of decades of pressure toward U.S. expansionism.
www.pbs.org
American Imperialism: The Spanish-American War | DPLA
The Digital Public Library of America brings together the riches of America’s libraries, archives, and museums, and makes them freely available to the world.
Comments
1. Accident on and subsequent loss of the USS Maine in Havana, Cuba on February 15, 1898 set the stage for this war.
2. USA was able to cement its reputation as a "world power" by liberating several colonies of the Spanish Empire such as Cuba, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines. Spanish Empire was one of the greatest in the world for centuries.
6. WORLD WAR I
RESHAPING EUROPE
| Opponents | Central Powers (Germany; Austria-Hungary; Ottoman Empire; Bulgaria) |
| Allies | France; The British Empire; Russia; Italy; Japan |
| Duration | 1914 - 1918 (4 straight years) |
| Outcome | Allied victory with Treaty of Versailles [1] |
From [1]: "After four years of devastating fighting, the First World War came to an end in 1919 in Versailles. The treaty, which represented “peace” for some and a “diktat” for others, also sowed the seeds of the Second World War, which would break out twenty years later."
List of battles involving American troops
References
Milestones in the History of U.S. Foreign Relations - Office of the Historian
history.state.gov 3.0 shell
Comments
American intervention in 1917 ensured victory of Allied bloc (Russia; France; British Empire; and satellites) over Axis powers. Over 2 million American troops were deployed on the front-lines to help turn the tide. However, American intervention was restricted to the battlefield across Europe.
7. WORLD WAR II
SAVING THE WORLD
| Opponents | Axis Powers (Germany; Italy; Japan) |
| Allies | The British Empire; Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR); China |
| Duration | 1939 - 1945 (6 straight years) |
| Outcome | Allied victory with occupation and subsequent reconditioning of the Axis Powers |
Pacific War (1942 - 1945)
Japanese assault on Pearl Harbor in 1941 set the stage for American intervention in this war.
Major combat operations in the WEST
Operation Torch (1942)
Operation Torch: Invasion of North Africa
The Allied invasion of French North Africa in November 1942 was intended to draw Axis forces away from the Eastern Front, thus relieving pressure on the hard-pressed Soviet Union. The operation was a compromise between U.S. and British planners as the latter felt that the American-advocated...
Operation Avalanche (1943)
Landings at Salerno, Italy
After victories in North Africa in May 1943, the Allied high command looked to open a second front against the Axis on the European continent. Normandy was the first choice, but British insistence that a cross-channel attack would not be successful until 1944 left the Western Allied leadership...
Operation Overlord (1944)
Operation Overlord (D-Day): June 1944
Invasion of Normandy, France (Codename: Operation Overlord) On June 6, 1944, in Operation Overlord, the Allied forces landed troops on Normandy beaches for the largest amphibious assault in history, beginning the march eastward to defeat Germany. In a larger strategic sense, the successful...
List of battles involving American troops
US-led forces produced significant battlefield effects and played a key role in downfall of the Axis Powers around the world.
References
Comments
1. American Lend-Lease Act made it possible for the USSR to defeat German forces in the East:
https://historyplex.com/lend-lease-act-1941-facts-summary-significance
2. World War II led to creation of the Global Order in which USA and USSR were respective superpowers. This situation set the stage of Cold War between them (see section 8 below).
8. COLD WAR
THE CLASH OF CIVILIZATIONS
| Opponents | Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 1947 - 1991 |
| Outcome | Outcome # 1: South Korea is liberated by US-led forces (Coalition victory) Outcome # 2: North Korea is preserved by China (Communist Victory) Outcome # 3: Cuba is denuclearized with coercive diplomacy (American victory) Outcome # 4: South Vietnam is annexed by North Vietnam (Communist Victory) Outcome # 5: Afghanistan is liberated by US-backed Mujahideen (Coalition victory) Outcome # 6: Noriega regime is dismantled in Panama (American victory) Final Outcome: American victory with dissolution of the USSR |
Who Won the Cold War?
The U.S. and Soviet Union fought the Cold War for 45 years via proxy wars and a near-complete polarization of the rest of the world. But did either side really win?

The US Victory in the Cold War: Economic Strength, Foreign Policy Triumph or Both?
The economic strength of the US alone was not enough to secure victory, and the US foreign policy was frequently counter-productive. But when the disparity in economic strength was utilised by the US foreign policy it enabled the US to have a clear advantage over its enemy and negotiate from a...

Ronald Reagan and the Cold War: What Mattered Most - Texas National Security Review
Scholars, like contemporary observers, continue to argue heatedly over the quality of President Ronald Reagan’s strategy, diplomacy, and leadership. This paper focuses on a fascinating paradox of his presidency: By seeking to talk to Soviet leaders and end the Cold War, Reagan helped to win it...
Associated fronts and/or engagements:-
8.1. North Korea
| Opponents | North Korea; USSR; China |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 1950 - 1953 |
| Outcome | Outcome # 1: North Korea is preserved by China Final Outcome: Allied victory with Armistice Agreement for the Restoration of the South Korean State |
Main thread

The Korean War (1950 - 1953) - a visual guide
BACKGROUND North Korea and South Korea were split across the 38th parallel by USSR and USA after World War 2. USSR helped transform North Korea into an organized communist state with well-equipped armed forces in the (1945 - 1950) period. USA did not pay much attention to security needs...
defence.pk
References
Comments
China prevented downfall of North Korea with its military might (Chinese success story), but US-led forces managed to liberate South Korea from communist forces and ensure its independence.
8.2. Cuban Missile Crises
| Opponents | Cuba; USSR |
| Allies | |
| Duration | 1962 (13 days) |
| Outcome | American (coercive diplomacy) victory |
References
Milestones in the History of U.S. Foreign Relations - Office of the Historian
history.state.gov 3.0 shell
Comments
Soviet Union agreed to remove its nuclear umbrella from Cuba in-exchange of assurance from the USA to not invade Cuba and denuclearize Turkey.
8.3. Vietnam
| Opponents | North Vietnam; Cambodia; Laos |
| Allies | |
| Duration | 1955 - 1973 |
| Outcome | Outcome # 1: Use of force to compel North Vietnam to sign Paris Peace Accords and allow American withdrawal from the region in 1973. Final Outcome: North Vietnam annexed South Vietnam in 1975. |
Perspective
Vietnam War in retrospective
USA fought a war in Vietnam in the 1960s when its military technologies were nothing like in 1991 (vs. Iraq) and beyond. Vietcong and American troops could NOT defeat each other due to technological limitations and geographical factors and were locked in a stalemate for a long period of time.
Technological limitations
For perspective; USAF could NOT knock out a Vietnamese bridge (Dragon's Jaw) with "standard munitions" for a long period of time in Vietnam:
"At the outset of the Vietnam War, the US Joint Chiefs of Staff rated the Dragon’s Jaw as No. 14 on the list of the most important targets in North Vietnam. It carried the only railroad in the North Vietnamese panhandle and was a key link in the supply route supporting the war in the south. When the Rolling Thunder air campaign began in 1965, the bridge was selected for early attack.
On April 3, 1965, Lt. Col. Robinson Risner led a strike force of almost 80 aircraft from bases in Vietnam and Thailand against the Dragon’s Jaw. The actual attack was conducted by 31 F-105s from Korat Air Base in Thailand, half of them carrying Bullpup missiles and half with 750-pound general-purpose bombs.
Planners had expected the attack to drop the bridge. However, neither the missiles nor the bombs caused any appreciable damage. One pilot said the Bullpups, which had lightweight 250-pound warheads, simply “bounced off” the target.
The next day, Risner led a restrike by 46 F-105s. This time, they left the Bullpups at home and hit the bridge with some 300 bombs, but the results were no better than before. Two further strikes in May closed the bridge briefly for repairs. Large mines, dropped upriver by transport aircraft, floated into the bridge abutments but they had little effect.
By 1972, the Air Force and the Navy had sent 871 sorties against the Dragon’s Jaw, losing 11 aircraft but failing to knock out the bridge.

 www.airforcemag.com
www.airforcemag.com
Geographical factors

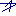
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Topographic-map-of-Vietnam_fig1_233808418
Source: https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn11483-coastal-living-a-growing-global-threat/
Vietnamese geography prevents mechanized thrusts in numerous sectors of the country. USA had NO choice but to use helicopters to insert troops in such sectors to confront Vietcong forces and/or to conduct bombing runs in numerous sectors to soften Vietcong infrastructure. American troops could win battles but gains on the ground remained limited.
Locked in a stalemate
Major battles of the war and their respective outcomes are identified as follows:
Although American military forces could win battles, Vietcong remained intact and launched Easter Offensive in another show of force to weaken South Vietnam in 1972.
Negotiations
Nixon administration was under domestic pressure to bring an end to war in Vietnam and ordered drawdown of American troops to signal its intent to do the needful but Vietcong saw an opportunity in this development to launch its Easter Offensive to weaken South Vietnam in 1972. This put Nixon administration in a predicament and it authorized use of overwhelming force to stop Vietcong in its tracks and bring it to the negotiation table instead: Operation Linebacker II was launched to achieve desired outcome in this case.

 www.youtube.com
www.youtube.com
Improvements in American military technology such as emergence of smart bombs made it possible for the USAF to achieve results that were NOT possible before. For example, USAF used smart bombs on the Vietnamese bridge Dragon's Jaw for a change:
The F-4s hit the bridge with 26 laser-guided bombs, several of them heavy 3,000-pounders, and did what all of the previous attacks had not been able to do. According to an Air Force review of the action, “The western span of the bridge had been knocked completely off its 40 foot thick concrete abutment and the bridge superstructure was so critically disfigured and twisted that rail traffic would come to a standstill for at least several months.”

 www.airforcemag.com
www.airforcemag.com
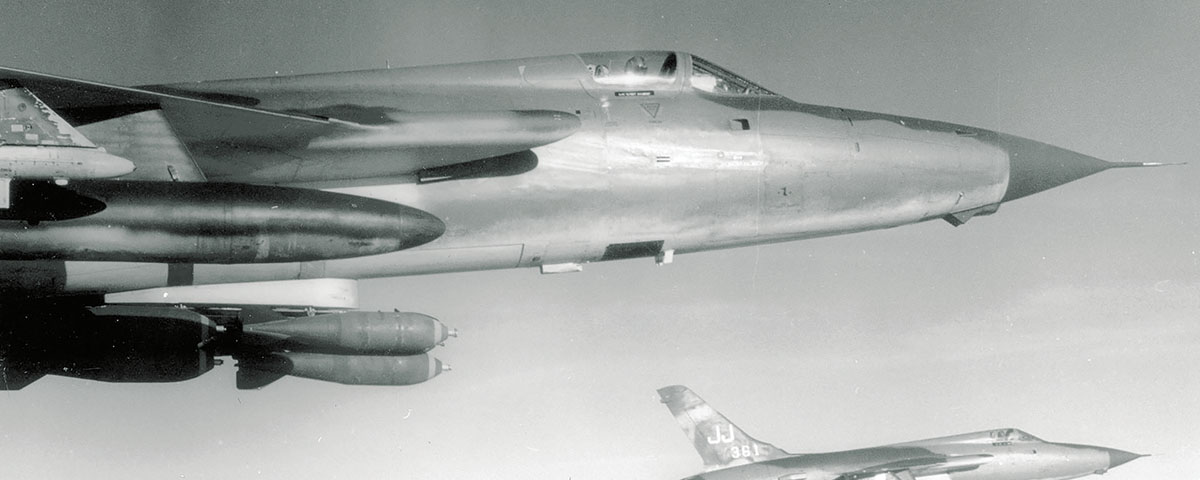
 www.historynet.com
www.historynet.com
- and Dragon's Jaw collapsed.
Operation Linebacker II showed that it was possible to defeat Vietcong but Nixon administration was not interested to stay on course.
USA fought a war in Vietnam in the 1960s when its military technologies were nothing like in 1991 (vs. Iraq) and beyond. Vietcong and American troops could NOT defeat each other due to technological limitations and geographical factors and were locked in a stalemate for a long period of time.
Technological limitations
For perspective; USAF could NOT knock out a Vietnamese bridge (Dragon's Jaw) with "standard munitions" for a long period of time in Vietnam:
"At the outset of the Vietnam War, the US Joint Chiefs of Staff rated the Dragon’s Jaw as No. 14 on the list of the most important targets in North Vietnam. It carried the only railroad in the North Vietnamese panhandle and was a key link in the supply route supporting the war in the south. When the Rolling Thunder air campaign began in 1965, the bridge was selected for early attack.
On April 3, 1965, Lt. Col. Robinson Risner led a strike force of almost 80 aircraft from bases in Vietnam and Thailand against the Dragon’s Jaw. The actual attack was conducted by 31 F-105s from Korat Air Base in Thailand, half of them carrying Bullpup missiles and half with 750-pound general-purpose bombs.
Planners had expected the attack to drop the bridge. However, neither the missiles nor the bombs caused any appreciable damage. One pilot said the Bullpups, which had lightweight 250-pound warheads, simply “bounced off” the target.
The next day, Risner led a restrike by 46 F-105s. This time, they left the Bullpups at home and hit the bridge with some 300 bombs, but the results were no better than before. Two further strikes in May closed the bridge briefly for repairs. Large mines, dropped upriver by transport aircraft, floated into the bridge abutments but they had little effect.
By 1972, the Air Force and the Navy had sent 871 sorties against the Dragon’s Jaw, losing 11 aircraft but failing to knock out the bridge.

The Emergence of Smart Bombs | Air & Space Forces Magazine
Precision-guided munitions in Vietnam wrote the book on ground attack.
Geographical factors

Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Topographic-map-of-Vietnam_fig1_233808418

Source: https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn11483-coastal-living-a-growing-global-threat/
Vietnamese geography prevents mechanized thrusts in numerous sectors of the country. USA had NO choice but to use helicopters to insert troops in such sectors to confront Vietcong forces and/or to conduct bombing runs in numerous sectors to soften Vietcong infrastructure. American troops could win battles but gains on the ground remained limited.
Locked in a stalemate
Major battles of the war and their respective outcomes are identified as follows:
| Battle of la Drang | 1965 | Indecisive |
| Battle of Khe Sanh | 1968 | Indecisive |
| Vietcong's Tet offensive | 1968 | Victory (US-led forces repel attack of Vietcong) |
| Operation Apache Snow including the battle of Hamburger hill | 1969 | Victory (US-led forces secure thung lũng A Sầu region but are withdrawn due to political reasons). |
Although American military forces could win battles, Vietcong remained intact and launched Easter Offensive in another show of force to weaken South Vietnam in 1972.
Negotiations
Nixon administration was under domestic pressure to bring an end to war in Vietnam and ordered drawdown of American troops to signal its intent to do the needful but Vietcong saw an opportunity in this development to launch its Easter Offensive to weaken South Vietnam in 1972. This put Nixon administration in a predicament and it authorized use of overwhelming force to stop Vietcong in its tracks and bring it to the negotiation table instead: Operation Linebacker II was launched to achieve desired outcome in this case.

Operation Linebacker II - The B-52s go to Hanoi, 1972 - Animated
Near the end of the Vietnam War and with time against him, President Nixon decides to use overwhelming military force to bring the North Vietnamese to the ne...
Improvements in American military technology such as emergence of smart bombs made it possible for the USAF to achieve results that were NOT possible before. For example, USAF used smart bombs on the Vietnamese bridge Dragon's Jaw for a change:
The F-4s hit the bridge with 26 laser-guided bombs, several of them heavy 3,000-pounders, and did what all of the previous attacks had not been able to do. According to an Air Force review of the action, “The western span of the bridge had been knocked completely off its 40 foot thick concrete abutment and the bridge superstructure was so critically disfigured and twisted that rail traffic would come to a standstill for at least several months.”

The Emergence of Smart Bombs | Air & Space Forces Magazine
Precision-guided munitions in Vietnam wrote the book on ground attack.

The North Vietnamese Bridge That Took Seven Years to Destroy
The road and railway bridge at Thanh Hoa south of Hanoi spanned the Ma River and was a vital link in the movement of communist troops and supplies. For the better part of a decade, U.S. Navy, Marine and Air Force aviators braved the flak-filled skies over North Vietnam on missions to destroy the...
- and Dragon's Jaw collapsed.
Operation Linebacker II showed that it was possible to defeat Vietcong but Nixon administration was not interested to stay on course.
My analysis shows that American military was learning from its battlefield experiences and began to produce results in every battle that was fought in Vietnam since 1968. More importantly, a new generation of technologies emerged and could be employed to devastating effect in Operation Linebacker II in 1972 - this operation showed that technological supremacy could help turn the tide of war in Vietnam but domestic pressure on Nixon administration to give up on Vietnam was immense and it followed through.
---
Dereliction of Duty: Lyndon Johnson, Robert McNamara, the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and the Lies That Led to Vietnam
By Charles E. Neu and H. R. McMaster, Published on 04/13/18
digital-commons.usnwc.edu
References

School of Advanced Military Studies Monographs
This monograph examines how the United States and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization employed air power to obtain national objectives in Operation Linebacker II, Operation Deliberate Force, and Operation Allied Force. Operation Linebacker II took place from 18-29 December 1972. It was the...
The Limits of Airpower or the Limits of Strategy: The Air Wars in Vietnam and Their Legaci
For most of the world’s population, America’s air wars in Vietnam are now ancient history. The first U.S. bombing raids against North Vietnam, conducted in response to attacks by North Vietnamese
ndupress.ndu.edu
Comments
1. Although American military forces were able to win battles in Vietnam, American leaders did not capitalize on such gains (see "My analysis of the Vietnam War" part above).
2. Vietnam War provided valuable lessons for restructuring and re-equipping American military to fight a competent adversary much more effectively at some point in the future. Vietnam War was particularly instructive for re-equipping American military forces and revisiting American battle doctrine in subsequent years.
AirLand Battle Doctrine - MERIP
The US Army has recently adopted an aggressive new warfighting doctrine called AirLand Battle. Its precepts now constitute the Army’s basic “how to fight” principles for a decade of “intense, deadly, and costly” battles. The Middle East is one of three major theaters—along with Europe and...
 merip.org
merip.org
8.4. Afghanistan
| Operation | Operation Cyclone |
| Allies | Pakistan |
| Duration | 1979 - 1989 |
| Outcome | Allied (proxy) victory with Geneva Accords of 1988 |
US made the war unwinnable for the Soviet Union in Afghanistan by providing massive assistance to the Mujahideen with collaboration of Pakistan.
References
Afghan War and the Stinger Saga: Lt. Col. (R) Mahmood Ahmed Ghazi Y. Bt.: 9789699225154: Amazon.com: Books
Afghan War and the Stinger Saga [Lt. Col. (R) Mahmood Ahmed Ghazi Y. Bt.] on Amazon.com. *FREE* shipping on qualifying offers. Afghan War and the Stinger Saga
www.amazon.com
Comments
Some of the Mujahideen banded together to establish Al-Qaeda Network in 1988. This development would set the stage for another war in Afghanistan (see section 11 below).
8.5. Panama
| Enemy | Noriega regime |
| Operation | Operation Just Cause |
| Allies | |
| Duration | 1989 - 1990 (42 days) |
| Outcome | American victory (Noriega regime is dismantled in Panama) |
This was the largest and most complex military operation since Vietnam.
Perspective
Operation Just Cause: A Historical Analysis
On September 7, 2007, seventeen years after Manuel Noriega’s violent removal from power in Panama, a legal order for his release was issued in Miami; however, to this day, the former Panamanian strongman remains imprisoned in a Florida jail as both France and Panama battle for him to be...
www.coha.org
---

The truth behind US’ Operation Just Cause in Panama
The more history that can be exhumed, the harder it will be for the US to hide behind noble intentions in the future.
---
---
3 Little-Known Stories from Operation Just Cause
On Dec. 20, 1989, the United States military invaded Panama, code-named Operation Just Cause, in an effort to oust Panamanian narco-dictator Manuel Noriega from power.
References

Operation Just Cause and the U.S. Policy Process
This Note examines the policy process that led the United States to intervene in Panama.
Defense Technical Information Center

Operation Just Cause: Lessons for Operations Other Than War
The study of past operations is helpful in defining U.S. Army roles and functions in military operations other than war (OOTW) and in assessing the range of missions and requirements the Army is likely to face in the future.
MI Library Home: Battle SOUTHCOM: Operation Just Cause
MI Library Home: Battle SOUTHCOM: Operation Just Cause
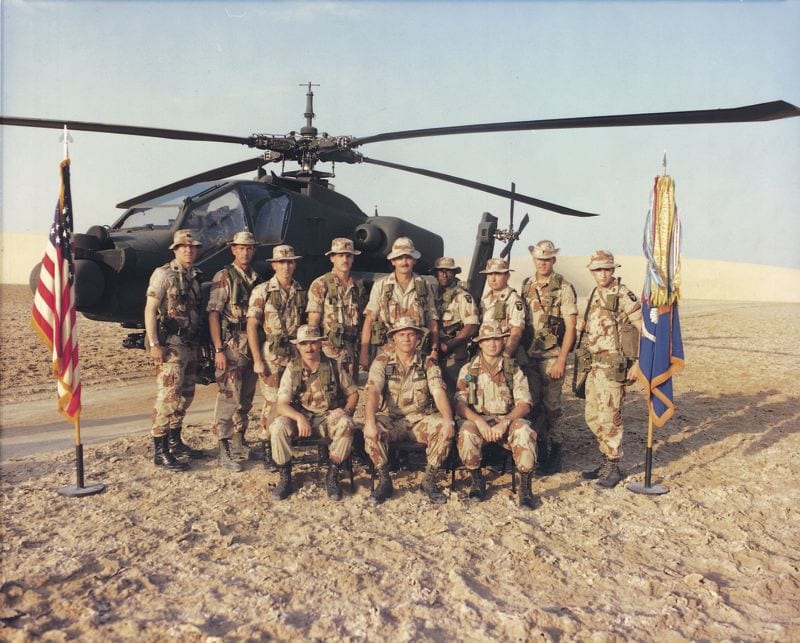
9. Iraq
| Operation | Operation Desert Storm |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 1991 (45 days) |
| Outcome | US-led coalition victory with Liberation of Kuwait |
Perspective

How The Tomahawk Missile Shocked The World In The Gulf War | Battlezone | War Stories
During the First Gulf War, coalition forces unleashed a massive assaults on Iraqi forces. At the heart of these attacks was a new weapon....the Tomahawk Miss...
References

Desert Storm at 30: Aerospace Power and the U.S. Military - War on the Rocks
Feb. 28 marked the 30th anniversary of the end of offensive operations in Operation Desert Storm. Desert Storm was a sustained 43-day air campaign
warontherocks.com
Comments
1. US-led coalition defeated Iraq in the war (and liberated Kuwait by extension) through combination of a well-planned military operation involving a deception plan and tactics and technological supremacy with surprises in the mix.
2. This is the FIRST war in which US applied its AirLand Battle Doctrine to devastating effect.
Defense Technical Information Center

The Evolution of U.S. Army Doctrine: from Active Defense to Airland Battle and Beyond
This study explains the recent evolution of U.S. Army doctrine. During the last two decades, the Army revised its capstone manual--FM 100-5, Operations--three times in 1976, 1982, and 1986. A fourth revision is underway in 1991. This thesis chronicles the change in doctrine by analyzing the...
apps.dtic.mil
10. Yugoslavia
| Operation | Operation Allied Force |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 1999 (78 days) |
| Outcome | US-led coalition victory with Liberation of Kosovo |
Perspective
Yugoslavian A2/AD arrangements were among the finest in Europe shaped by lessons drawn from Operation Desert Storm with a network of radar systems that were collectively optimized to detect Low Observable (LO) aircraft and cruise missiles. Earliest examples of IMAD setups in fact.
"Air Force and NATO aircraft faced significantly more effective air defenses than what they had recently encountered in Iraq, and pilots were initially instructed to stay above 15,000 feet to minimize risk."
1999 - Operation Allied Force
NATO's air campaign against the former Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) and its forces deployed in Kosovo. During this operation NATO used a wide range of aircraft and naval weapons against the FRY.
www.afhistory.af.mil
But NATO humbled Yugoslavian A2/AD arrangements and lost only two aircraft over Yugoslavia:
"After 65 days of operations, NATO had lost to enemy fire only two aircraft–an F-117 and an F-16–with no casualties."
Washington Watch: Victory in Kosovo | Air & Space Forces Magazine
In late May, NATO shifted gears in Operation Allied Force. The air campaign soon saw the results of th
B-2A bomber proved its mettle in Yugoslavia:
"The combat effectiveness of the B-2 was proved in Operation Allied Force, where it was responsible for destroying 33 percent of all Serbian targets in the first eight weeks, by flying nonstop to Kosovo from its home base in Missouri and back."
B-2 Spirit
The B-2 Spirit is a multi-role bomber capable of delivering both conventional and nuclear munitions. A dramatic leap forward in technology, the B-2 brings massive firepower to bear, in a short time,
www.af.mil
"In its first combat test, the B-2 bomber defeated not only the Serbian air defense system but also the critics who for years had insisted it would not work as advertised or would never be risked in real war."
With Stealth in the Balkans | Air & Space Forces Magazine
The performance of the B-2 exceeded the expectations of even its most ardent fan.
Related Discussion
Russian Air Force Is Very Effective In Ukraine
Poor operational performance and tactics - inadequate real world experience or relevant training other than very senior pilots. Non existent cooperation with combined force elements - even coordinating within VKS has been terrible. Lastly, the entire operational plan and execution was poor...
defence.pk
References

Kosovo Air Campaign (March-June 1999)
NATO launched an air campaign, Operation Allied Force, in March 1999 to halt the humanitarian catastrophe that was then unfolding in Kosovo. The decision to intervene followed more than a year of fighting within the province and the failure of international efforts to resolve the conflict by...
Operation Allied Force
On 24 March 1999, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) launched air campaign Operation Allied Force against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia to stop the humanitarian catastrophe that was then unfolding in Kosovo. The campaign was launched after all diplomatic avenues had failed. Operation...
1999 - Operation Allied Force
NATO's air campaign against the former Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) and its forces deployed in Kosovo. During this operation NATO used a wide range of aircraft and naval weapons against the FRY.
www.afhistory.af.mil

Operation Allied Force: Lessons for the Future
RAND researcher Benjamin S. Lambeth offers a thorough appraisal of Operation Allied Force, with a view toward shedding light both on the operation's strengths and on its most salient weaknesses.
Operation Allied Force | Air & Space Forces Magazine
How airpower won the war for Kosovo.
Operation Allied Force (Kosovo, 1999) from Misfortunes of War: Press and Public Reactions to Civilian Deaths in Wartime on JSTOR
Operation Allied Force (Kosovo, 1999), Misfortunes of War, pp. 63-124
11. WAR ON TERROR
GLOBAL WAR ON TERRORISM
| Opponents | Various |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 2001 - 2021 |
| Outcome | Outcome # 1: Perpetrators of 9/11 eliminated in AfPak (NATO victory) Outcome # 2: Afghan Taliban return to power in Afghanistan (Renaissance Diplomacy*) Outcome # 3: Saddam regime is dismantled in Iraq (NATO victory) Outcome # 4: Qaddafi regime is dismantled in Libya (NATO victory) Outcome # 5: Islamic State of Iraq and Levant (ISIL) is dismantled across Syria and Iraq (NATO victory) Final Outcome: American victory (US managed to eliminate perpetrators of 9/11 and dismantle one of the most dangerous multinational terrorist groups in the world); monitoring of relevant regions continues. |
| Controversies | 1. War in Iraq is one of the most controversial developments in modern times. Critics contend that this war was unnecessary. 2. Involvement of The Kurdistan Workers' Party (PKK) in American mission to defeat ISIL in Syria fueled tensions between US and Turkey. 3. War Profiteering |
Al-Qaeda Network (a multinational terrorist group) was deemed responsible for horrendous acts of terrorism on American soil on September 11, 2001. This event propelled US to launch its War On Terror to degrade or defeat Al-Qaeda Network around the world. US also created the Department of Homeland Security to prevent terror attacks on American soil. But US decided to settle scores with perceived enemies in Iraq and Libya on the side.
Timeline of elimination of the most influential members of the Al-Qaeda Network around the world:
- Abu Musab al-Zarqawi was assassinated in Iraq in 2006
- Osama Bin Laden was assassinated in Pakistan in 2011
- Abu al-Khayr al-Masri was assassinated in Syria in 2017
- Hamza Bin Laden was assassinated in undisclosed location in 2019
- Abu Muhammad al-Masri was assassinated in Iran in 2021
- Ayman al-Zawahiri was assassinated in Afghanistan in 2022
US used drones to assassinate a large number of terrorists in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Somalia, and Yemen respectively:
Drone Warfare
The role of NSA in Drone Warfare:

The NSA's Secret Role in the U.S. Assassination Program
The National Security Agency is using complex analysis of electronic surveillance, rather than human intelligence, as the primary method to locate targets for lethal drone strikes – an unreliable tactic that results in the deaths of innocent or unidentified people.
Killed in action (KIA):
Associated fronts and/or engagements:-
11.1. Afghanistan
| Opponents | Al-Qaeda Network (Primary) Afghan Taliban (Secondary) |
| Operation | Operation Enduring Freedom |
| Allies | Various |
| Gateway to Afghanistan | Pakistan |
| Duration | 2001 - 2021 |
| Outcome | Outcome # 1: Perpetrators of 9/11 eliminated in AfPak Outcome # 2: Afghan Taliban return to power Final Outcome: MIXED with US - Taliban agreement |
Toppling Taliban regime
This mission was accomplished in the (October 2001 - June 2002) period.

Toppling the Taliban
This report describes the preparations for Operation Enduring Freedom, Army operations and support activities, coalition issues, and civil-military operations in Afghanistan from October 2001 through June 2002.
US applied its AirLand Battle doctrine to defeat Al-Qaeda Network in Tora Bora Mountains in 2002 (Operation Anaconda).
Defense Technical Information Center
Notable efforts to dismantle Al-Qaeda Network
Pakistani contribution to this end in times of Musharraf administration is documented in following book:
---
Operation Neptune Spear
This operation is discussed at length in following links:
LibGuides: Special Operations Forces: Operation Neptune Spear
This research guide provides information and resources such as journal articles, book titles, websites, and government reports/papers on the subject of Special Operations Forces.

How did the Osama bin Laden strike mission maintain stealth in Pakistani airspace if they flew giant Chinook helicopters in addition to t...
Dan Rosenthal's answer: The Chinooks were not known to be particularly modified for low observability in the way that the 160th SOAR “stealth” Black Hawks (I’m just gonna call them Ghosthawks, since that seems to be the most common nickname) were. They were just standard MH-47E’s at least as far ...
Wirtz, J. J. (2022). The Abbottabad raid and the theory of special operations. Journal of Strategic Studies, 45(6-7), 972-992.
DataSpace: Bin Laden Dossier [Abbottabad Commission Report on Killing of Osama bin Laden]
This operation set in motion a chain of tragic events in Pakistan:
https://acleddata.com/2017/02/07/the-fallout-of-operation-neptune-spear/
Additional pointers in following links:
1. CIA 3D model of the Abbottabad compound
2. Dr. Shakeel Afridi
3. Dead bodies found in the compound; these people are identified in the Abbottabad Commission Report
4. Documents recovered from the Abbottabad compound
5. General Ehsan ul Haq's account
6. Pakistan showing the preserved part of the crashed helicopter to a Chinese team
7. Osama Bin Laden's family
Seymour Hersh account is disputed and/or refuted in here, here, here, and here.
---

The death of Hamza bin Laden and the weakness of al-Qaida | Brookings
Hamza bin Laden’s death is a blow to al-Qaida’s attempts to regain its momentum and restore its position as leader of the global jihadi cause. More important, it illustrates al-Qaida’s many problems and the successes, however incomplete, of U.S. counterterrorism.
---
US continues to monitor activity of Al-Qaeda remnants in Afghanistan and assassinated Ayman al-Zawahiri using over-the-horizon strike approach.

The Killing of al-Zawahiri: Repercussions for the Taliban
Following the drone strike against al-Qaeda leader Ayman al-Zawahiri, many variables are up in the air that could significantly alter the stability of a Taliban-controlled Afghanistan as well as the future of the al-Qaeda framework.
Nation Building Failure

Why Nation-Building Failed in Afghanistan | by Daron Acemoglu - Project Syndicate
Daron Acemoglu explains why the West's top-down approach to establishing state institutions was bound to end in tears.
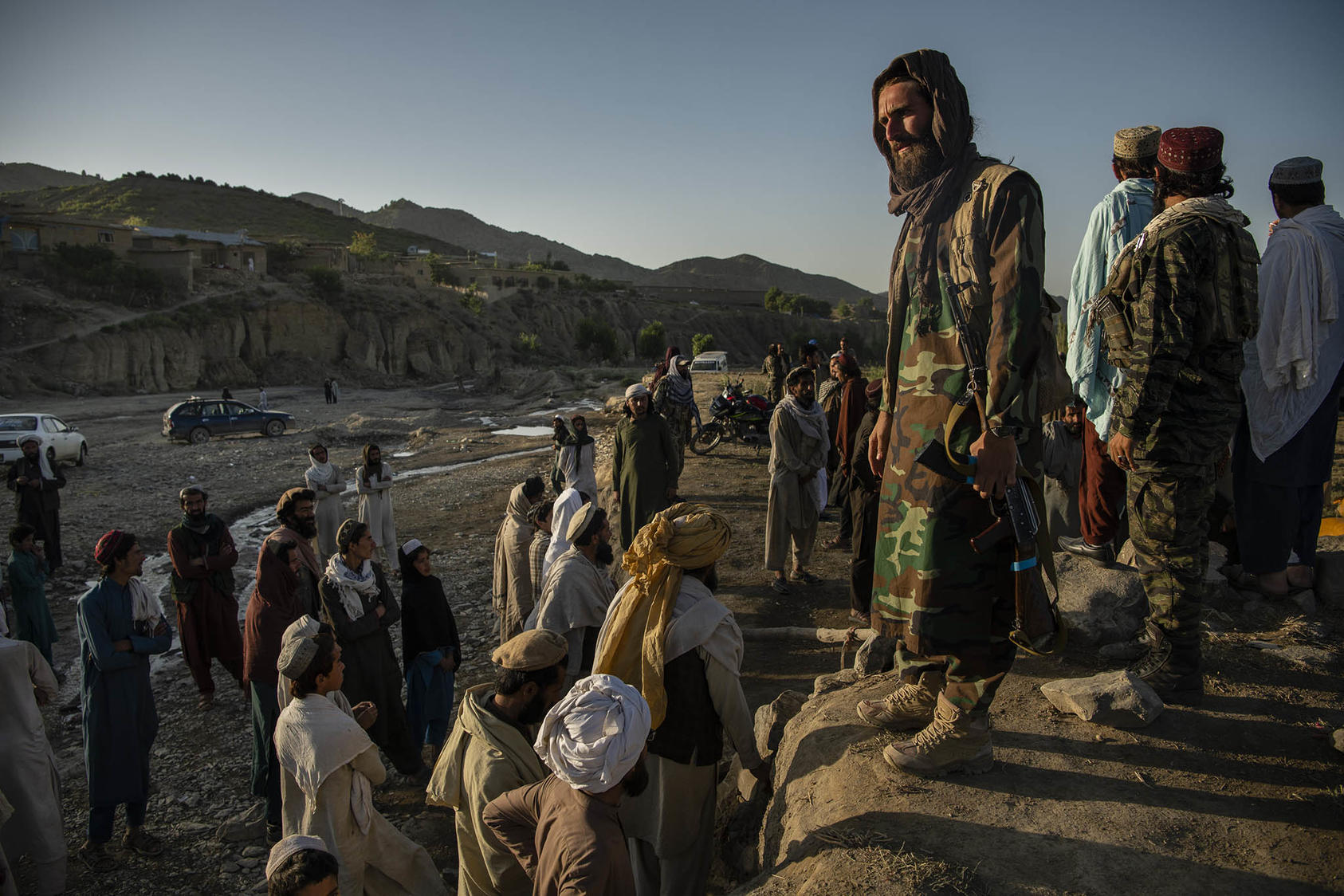
Afghan Taliban were able to regroup in Pakistan and Iran and plot their return. Pakistan was reluctant to act against Afghan Taliban for various reasons.

Why did the USA fail in Afghanistan | Complete inside story unrevealed by Faisal Warraich
#fsw #Afghanistan #USAââââââââââââââââððð Contacts for ads and marketingð© imfaisalwarraich@gmail.comððð Social Mediað· Twitter https://twitter.com/FS...
Afghan Taliban demonstrated incredible proficiency in the art of insurgency warfare and continued to assert themselves as a stakeholder in Afghan political affairs. Afghan Taliban and US eventually came to an understanding in US - Taliban agreement.
Perspective
How the Taliban won - It will be passed down for generations, all the lost limbs and the money lost
No I have talked to them, usually they are pro-Pakistan. I am talking about the Pathans. The Pathans from Afghanistan are literally the most anti-Pakistan out of the lot... You don't need to talk to them but just watch what they say, their culture is based around hating Pakistan, Gul Khans...
defence.pk
---

Here's Who REALLY Won the War in Afghanistan
The war in Afghanistan made these people very richThis video is sponsored by BetterHelp. Get 10% off your first month of BetterHelp: https://BetterHelp.com/J...
---
References

Air Power Vital to the Conduct of Operation Enduring Freedom
The U.S. conducted Operation Enduring Freedom from land and sea bases far from the war zone in Afghanistan. Al Qaeda's terrorist infrastructure and the Taliban regime were destroyed largely through the use of networked ground-aided air attacks that are now the cutting edge of American combat style.
Comments
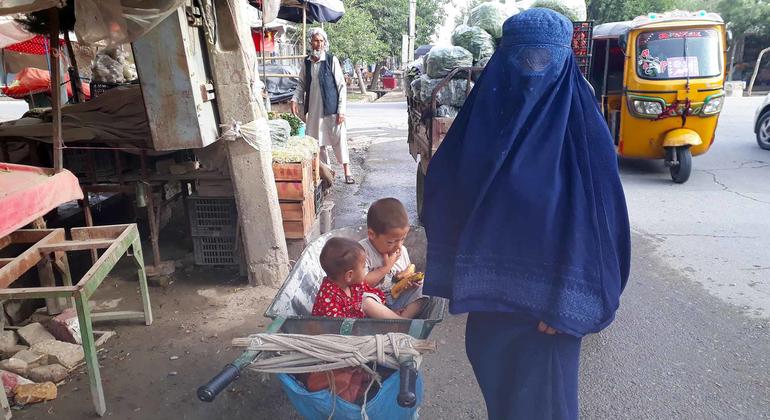
1. Afghan Taliban returned to power in Afghanistan with American nod but US has withdrawn its financial assistance to the country. Afghanistan finds itself in a period of significant economic crisis in the present.

Ten years of Afghan economic growth, reversed in just 12 months: UNDP
A year on from the Taliban takeover in Kabul, Afghanistan is gripped by “cascading crises”, including a crippled economy that humanitarian aid alone cannot address, according to a new report from the UN Development Programme (UNDP) on Wednesday.

One Year Later, Taliban Unable to Reverse Afghanistan’s Economic Decline
Afghanistan’s economy was already deteriorating before the Taliban takeover of the country on August 15, 2021, suffering from severe drought, the COVID-19 pandemic, declining confidence in the previous government, falling international military spending as U.S. and other foreign troops left...
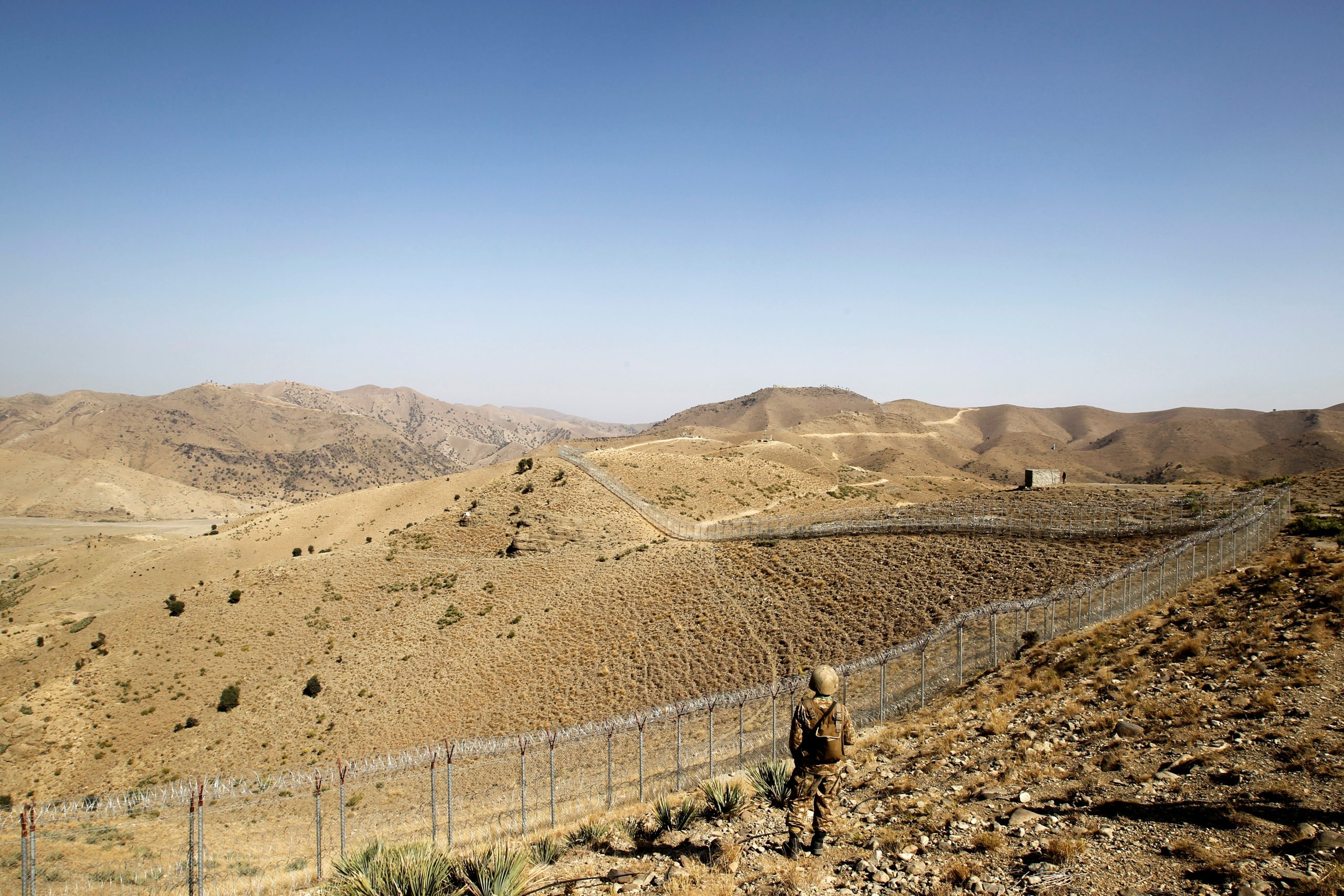
3. Pakistan continues to face security challenges emanating from Afghanistan in spite of fencing Durand Line.

As Pakistan's Afghanistan policy fails, the Afghan Taliban moves against Islamabad
Islamabad’s long standing objective—to have a dependent government in Kabul—has finally burned to the ground.

Pakistan’s troubled ties with the Taliban
Pakistan must continue to treat Afghanistan as a policy priority, despite its own internal issues.
Pakistan insists on addressing problems of Afghanistan, nevertheless.
11.2. Iraq
| Opponents | Saddam regime |
| Operation | Operation Iraqi Freedom |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 2003 - 2011 |
| Outcome | US-led coalition victory (Saddam regime is toppled / dismantled and Iraq is transformed into a Federal Parliamentary Republic) |
Toppling Saddam regime
"The U.S. victory in Iraq makes the German blitzkrieg look positively incompetent by comparison." - Boot (2003)
Urban warfare was central to combat strategy of Saddam regime due to lack of options for its forces in open landscapes in 2003 as noted in here and here. American tanks could survive in Iraqi urban spaces - this dynamic coupled with excellent precision strike capability and good intel was a winning combination. US-led forces toppled Saddam regime in a matter of days in a stunningly effective application of Blitzkrieg in modern times.
"Coalition forces in the second Gulf War were less than half the size of those deployed in the first one. Yet they achieved a much more ambitious goal-occupying all of Iraq, rather than just kicking the Iraqi army out of Kuwait-in almost half the time, with one-third the casualties, and at one-fourth the cost of the first war. Many will argue, in retrospect, that Saddam Hussein's forces were not all that formidable to begin with, and there is no doubt a great deal of truth in this. But they were capable enough when they fought the Iranian army to a draw in the 1980s and put down Kurdish and Shi'ite insurgencies in the 1990s. And, on paper at least, the Baathist regime's military enjoyed a big numerical advantage over U.S. and British forces. Although the Iraqi army was much degraded from its pre-1991 heyday, it still deployed more than 45o,ooo troops, including para-military units, the Republican Guard, and the Special Republican Guard, whose loyalty had been repeatedly demonstrated. Traditionally, war colleges have taught that to be sure of success, an attacking force must have a 3 to 1 advantage-a ratio that goes up to 6 to 1 in difficult terrain such as urban areas. Far from having a 3 to 1 advantage in Iraq, coalition ground forces (which never numbered more than ioo,ooo) faced a 3 to 1 or 4 to 1 disadvantage.
That the United States and its allies won anyway-and won so quickly-must rank as one of the signal achievements in military history. Previously, the gold standard of operational excellence had been the German blitzkrieg through the Low Countries and France in 1940. The Germans managed to conquer France, the Netherlands, and Belgium in just 44 days, at a cost of "only" 27,000 dead soldiers. The United States and Britain took just 26 days to conquer Iraq (a country 80 percent of the size of France), at a cost of 161 dead, making fabled generals such as Erwin Rommel and Heinz Guderian seem positively incompetent by comparison."
Boot, M. (2003). The new American way of war. Foreign Affairs, 41-58.
US applied its AirLand Battle doctrine to topple Saddam regime in 2003.
Defense Technical Information Center
Compare the above to the situation when Iraq was up against a regional adversary in the 1980s. Iraqi forces managed to capture Khorramshahr in 1980 but lost this city to Iranian forces in 1982. Iranian forces could not capture a single Iraqi city in war that lasted 8 years on the other hand - not even Basra (1986 - 1987). Much of the war could be fought in open landscapes and ballistic missiles were used to attack different cities. This was the situation between adversaries that were evenly matched on the whole.
De-baathification of Iraq
De-Baathification of Iraq - similar to De-Nazification of Germany
From Prague to Baghdad: Lustration Systems and their Political Effects1 | Government and Opposition | Cambridge Core
From Prague to Baghdad: Lustration Systems and their Political Effects1 - Volume 41 Issue 3
De-Baathification of Iraq presented considerable challenge to US-led forces in fact. Saddam regime was toppled in 2003 but Iraq produced a significant level of insurgency that claimed many lives through the years. US-led forces were moved to former Iraqi military bases but had to fight to recapture some of the Iraqi cities that were lost to various insurgent groups through the years.
Ramadi, Husaybah, Najaf, Samarra, Mosul, and Fallujah in 2004. Fighting was most violent and intense in Fallujah and the city was recaptured in second attempt but much of it was reduced to rubble in the process (Operation Phantom Fury).
Tal Afar in 2005
Ramadi in 2006
Karbala in 2007, and Basra and Sadr City in 2008. These battles were fought with Iran-backed Mehdi Army. This was a large and powerful insurgent group that claimed 600 American lives in the war but was defeated in 2008 and its leader Muqtada al-Sadr fled to Iran to avoid attempts on his life.
Reflections:
Moaddel, M., Tessler, M., & Inglehart, R. (2008). Saddam Hussein and the Sunni insurgency: Findings from values surveys. Political Science Quarterly, 123(4), 623-644.

A Bitter Legacy: Lessons of De-Baathification in Iraq | International Center for Transitional Justice
Based on significant field research and interviews with the Higher National de-Baathification Commission, this report focuses on Iraq’s purge of members of Saddam Hussein’s Baath Party, which is the most well-known example of large-scale and politically based dismissals in the Middle East and...
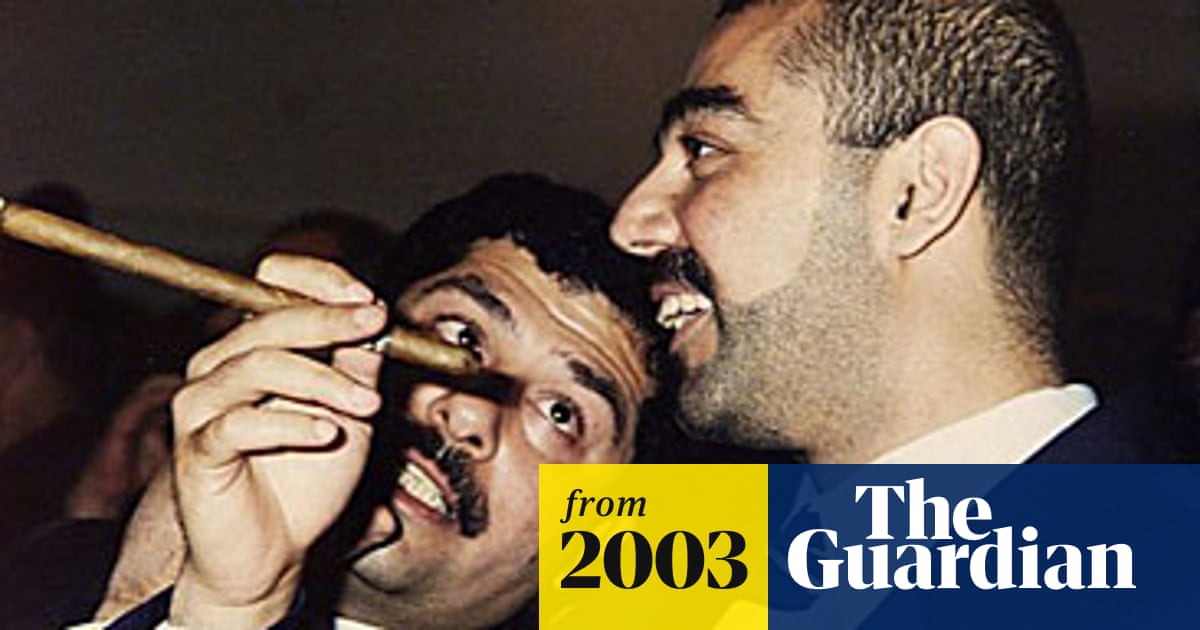
Fate of Saddam Hussein's two sons

Dead: the sons of Saddam
Uday and Qusay, Saddam Hussein's sons and his most feared lieutenants, were killed yesterday in a gun battle at their hideout in the northern Iraqi town of Mosul.
Leader of Al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI) killed in 2006

U.S. Strike Hits Insurgent at Safehouse (Published 2006)
Iraq's prime minister and the top U.S. commander in Iraq said Abu Musab al-Zarqawi's body had been positively identified by fingerprints, "facial recognition" and "known scars."
Execution of Saddam Hussein

How Saddam died on the gallows
Camera footage of the final minutes of Saddam Hussein released yesterday shows him being taunted by Shia hangmen and witnesses, a scene that risks increasing sectarian tension in Iraq.

13 years later, Iraq passes de-Baathification law
The Iraqi parliament passed a de-Baathification law to ban any political activity by the Baath Party, but its consequences are still unknown as warnings continue about potential destabilizing effects.
Reboot of Iraqi political system
Iraq is now a Federal Parliamentary Republic:
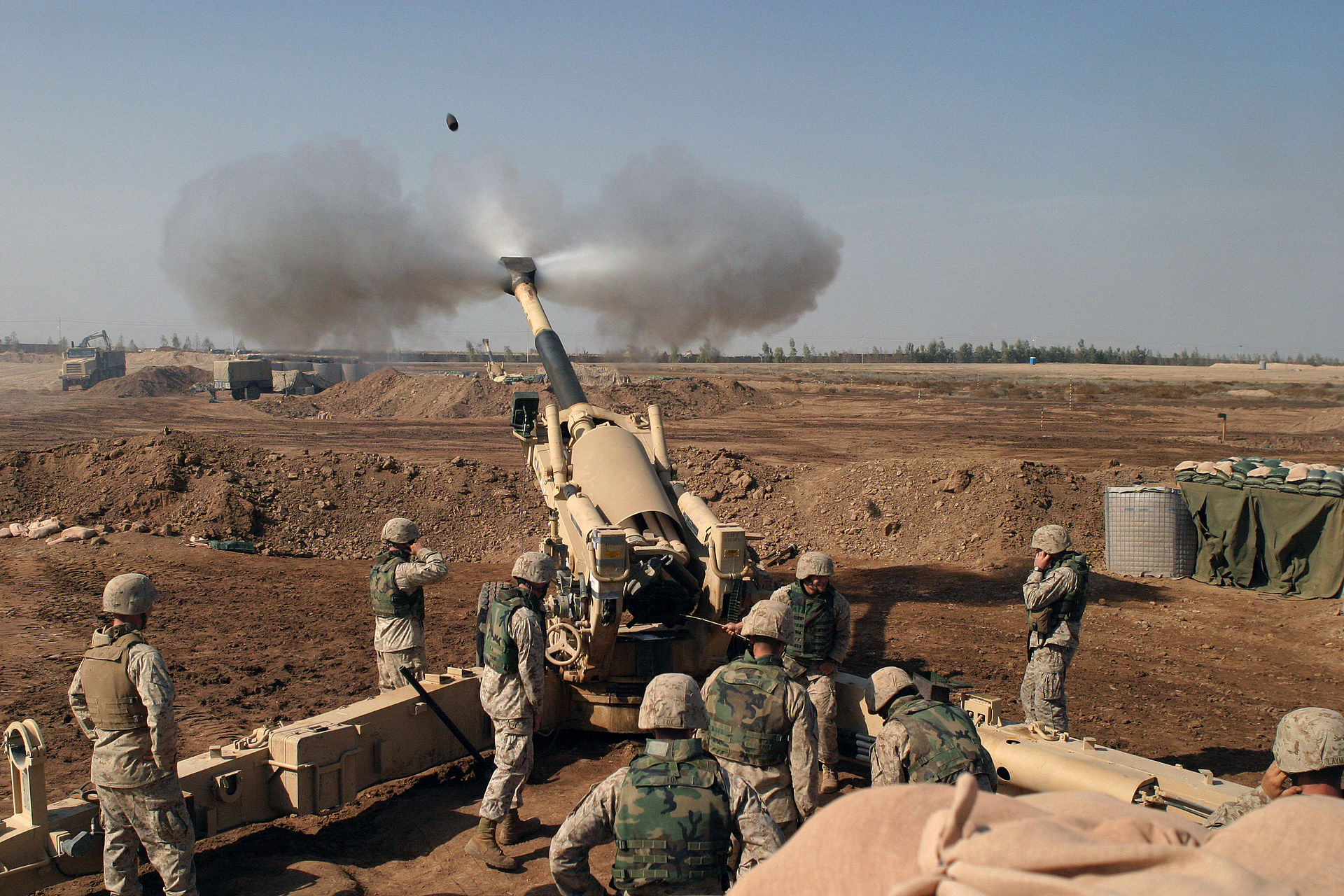
Fallujah - a case study of Urban Warfare

Brutal Urban Combat: Battle of Fallujah (2004) | Animated History
Sign up for Bright Cellars today and save 50% off of your first 6-bottle box of wine: https://www.brightcellars.com/armchair/NEW Poster: https://store.armcha...

Battle of Fallujah - Phantom Fury - Marine Corps Association
The Marine Corps Gazette and Leatherneck Magazine archives have more than 100 years of articles. Click the buttons below to read articles about the Second
 mca-marines.org
mca-marines.org
Operation Phantom Fury: The Assault and Capture of Fallujah, Iraq: Camp, Dick: Amazon.com: Books
Operation Phantom Fury: The Assault and Capture of Fallujah, Iraq [Camp, Dick] on Amazon.com. *FREE* shipping on qualifying offers. Operation Phantom Fury: The Assault and Capture of Fallujah, Iraq
www.amazon.com
Sadr City - a case study of Urban Warfare

Urban Warfare
The authors identify factors critical to the coalition victory over Jaish al-Mahdi in the 2008 Battle of Sadr City and describe a new model for dealing with insurgent control of urban areas.
References

Operation Iraqi Freedom and the Future of the U.S. Military | Brookings
Iraq Memo #17 by Michael E. O'Hanlon for the Saban Center (6/19/03)

Iraq War - Wikipedia
Comments
Iraqi insurgency was a very violent and destructive development on the whole with Syria and Iran providing arms and guidance to different insurgent groups in Iraq, but US-led forces defeated all insurgent groups and stabilized the country in 2008 and Obama administration withdrew US-led forces from Iraq in 2011.

Barack Obama announces total withdrawal of US troops from Iraq
President says 'America's war in Iraq will be over' with decision to pull all troops from Iraq by the end of the year

Last U.S. troops leave Iraq, ending war
The last convoy of U.S. soldiers pulled out of Iraq on Sunday, ending nearly nine years of war that cost almost 4,500 American and tens of thousands of Iraqi lives, and left a country grappling with political uncertainty.
Muqtada al-Sadr returned to Iraq in 2011.

Moqtada al-Sadr returns to Iraq after exile
Cleric who has spent three years in Iran goes back less than fortnight after helping usher in new government
US has reshaped political landscape of Iraq but the war has also allowed Iran to make political inroads into Iraq. This situation has opened a new chapter of conflict in the region by extension.

Iran’s Networks of Influence in Iraq | Abu Mahdi al-Muhandis
Iraq continues to pose a threat to Iranian national security, which is why Iran is intent on shaping Iraq’s domestic politics and strategic orientation.
11.3. Libya
| Opponents | Qaddafi regime |
| Operation | Operation Odyssey Dawn |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 2011 (7 months) |
| Outcome | US-led coalition victory (Qaddafi regime is toppled / dismantled) |
Fate of Muammar Qaddafi

Gaddafi's last words as he begged for mercy: 'What did I do to you?'
As National Transitional Council fighters fought their way into Sirte, radio intercepts spoke of 'an asset' in the besieged city. But no one knew until the final moments that the deposed dictator was within their grasp

The Air Strike That Led To The Capture (And Subsequent Killing) Of Muammar Gaddafi 10 Years Ago Today
On this day in 2011, an air strike by NATO aircraft contributed to the capture of Col. Gaddafi. Here's how it went. Although NATO’s Operation Unified
References

Airpower in the Libyan Civil War
In 2011, a coalition of nations waged a war against Muammar Qaddafi's regime that reversed the tide of Libya's civil war. The intervention's central element was a relatively small air campaign. What lessons did each nation glean from the experience?

Operation Odyssey Dawn - Wikipedia
Comments
US conducted a shadow war to defeat ISIL elements in Sirte in 2016.

The U.S. Has Conducted 550 Drone Strikes in Libya Since 2011 — More Than in Somalia, Yemen, or Pakistan
Libya has served as a laboratory for new drone warfare tactics.
11.4. Islamic State of Iraq and Levant (ISIL)
| Opponents | Islamic State of Iraq and Levant (ISIL) |
| Operation | Operation Inherent Resolve |
| Allies | Various |
| Duration | 2014 - 2021 |
| Outcome | US-led coalition victory (ISIL is dismantled) |
Main thread

Mapping the kinetic aspect of the Operation Inherent Resolve to defeat ISIL (Updated)
BACKGROUND AND ORIGINS OF THE ISIL "At its peak, IS ruled over 88,000 sq km (34,000 sq miles) stretching across the Iraq-Syria border." - BBC* Syria and Iraq contemplated merger to create the United Arab Republic in the 1960s...
defence.pk
Perspective
Poor security situation in Syria and political blunders of Maliki administration in Iraq allowed survivors of Saddam regime and Al-Qaeda in Iraq (AQI) to regroup and establish the Islamic State of Iraq and Levant (ISIL) in 2013 and its call for jihad appealed to thousands from all over the world, and ISIL managed to spread across Syria and Iraq consequently.
NATO . Success in this mission is in part owed to local actors in Iraq and Syria who were willing to fight ISIL and stood firm in this cause.
Iraqi establishment called on the US to help liberate Iraqi lands and cities from ISIL forces in 2014. US troops returned to Iraq in 2014 to restructure localized resistance fronts and US-led forces liberated Mosul and Raqqa in 2017.
The Operation Inherent Resolve is a COIN masterpiece involving calculative application of local partners and Air Power to counter a formidable multinational terrorist network. The operation also underscore the commitment of local partners to the cause.
References

Operation Inherent Resolve
This report, which outlines four battles within Operation Inherent Resolve (OIR) and reviews U.S. ground force contributions to those battles, is intended to address gaps both in analysis and in the common understanding of OIR.
Comments
1. ISIL defectors explain how ISIL emerged and managed its operations:
2. US established the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) bloc to help counter ISIL in Syria but this development led to tensions between US and Turkey due to involvement of PKK in SDF.
Istanbul bombing: Turkiye 'rejects' US condolences hours before G20 summit
who is going to attack Israel without American protection? Dubai with Burj Khalifa? almost all Arab countries are Israeli allies and those that are hostile cant even protect theirown Capitals. Once US leaves, those countries will change stances in a heartbeat, they still hate Israel, they may...
defence.pk
3. Iran-led forces also fought ISIL but independently.

While U.S.-Led Forces Dropped Bombs, Iran Waged Its Own Covert Campaign Against the Islamic State
Iran’s spies cheered U.S. bombings in the war against ISIS while covertly arming the Kurdish Peshmerga and penetrating the Islamic State’s leadership.
4. US continues to monitor situation in Syria.
------ ------ ------
The US has also defined modern warfare concepts for the rest of the world to emulate (if possible) or study at minimum.
Modern Warfare Theories:
| Theory of Limited War | Major Michael Cannon |

The Theory of Limited War
Until 1991 the theory of limited war was shaped by the experience of two critical conflicts — Korea and Vietnam. Korea was responsible for a concept geared to an east-west confrontation and dependent on the limitation of objectives in order to have any...
The US adopted this theory to plan and fight multiple limited-scale wars in post World War II times.
| Energy-Maneuverability Theory | Colonel John Boyd |
| The OODA Loop | Colonel John Boyd |
Boyd understood that victory in aerial engagements did not go to the faster or higher-flying aircraft but to the pilot whose aircraft had superior sustained turn performance, allowing maneuvers behind the prey. Boyd's Energy-Maneuverability Theory analysed how well an aircraft could change energy states involving speed, acceleration, kinetic and potential energy.

Ft. Leavenworth: John Boyd and Air Power Theory
Christopher Johnson, Assistant Professor at U.S. Army Command and General Staff College in Fort Leavenworth, joins us for a conversation on the unsung yet le...
Boyd's the OODA Loop is a tool that explains how individuals and organizations can succeed in uncertain and chaotic environments. Boyd perceived four elements of command and control. These functions form the core of Boyd’s research of commanders and armies at war. In a dynamic environment, competitors with superior OODA capability out-think and out-maneuver lesser opponents. The model applies to fighter aircraft, military organizations, and private business.

The Ultimate Guide to the OODA Loop
The OODA loop was a tool developed by military strategist John Boyd to explain how individuals and organizations can win in uncertain and chaotic environment...
Boyd's the OODA Loop provides the basis for Maneuver Warfare Theory and conceptualization of the (battle-tested) AirLand Battle Doctrine which was successfully applied on two separate occasions such as in 1991 to liberate Kuwait and in 2003 to topple Saddam regime in Iraq.
Modern Battle Doctrines:
| Active Defense Doctrine | General DePuy | 1976 |
| AirLand Battle Doctrine | General Donn A. Starry | 1982 |
| Multi Domain Operations Doctrine | Lt Gen Norman Seip | 2017 |
Towards Multi-Domain Operations Doctrine?

Distinctly Different Doctrine: Why Multi-Domain Operations Isn’t AirLand Battle 2.0
Those who have watched the Army’s concept for Multi-Domain Operations evolve since the fall of 2017 have experienced an odd sense of d
Defense Technical Information Center
Multi-Domain Operations: Bridging the Gaps for Dominance
This article will take a quick look at how warfare has evolved and why we have headed toward the multi-domain operations (MDO) doctrine. Additionally, the article provides a framework as a rudimentary
www.airuniversity.af.edu

Multi-domain operations in the future battlespace
With diplomatic tensions and conflict commanding the world’s attention, it is clear that a new age of military operations beckons.

The Army and Multi-Domain Operations: Moving Beyond AirLand Battle
Dennis Wille explains the evolution of AirLand battle in the Army and where Army doctrine could take us next.

Multi-Domain Operations/Joint All-Domain Operations
Discover Lockheed Martin's advanced JADO and JADC2 solutions for unmatched defense across land, air, sea, space, and cyber, ensuring rapid threat deterrence.