JSCh
ELITE MEMBER

- Joined
- Jun 9, 2011
- Messages
- 13,235
- Reaction score
- 2
- Country
- Location
Acercando Naciones » Chinese company installed in a space observatory Neuquén

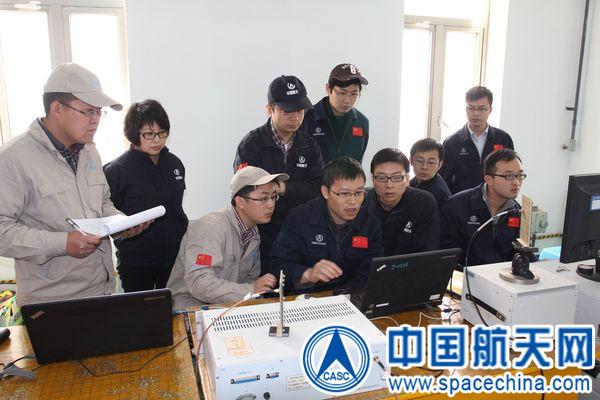
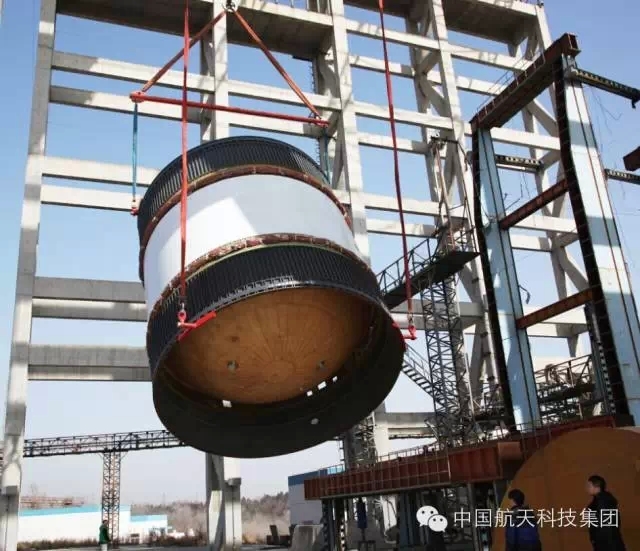
CLTC Chinese company confirmed Tuesday that the station for deep space observation building in the province of Neuquén, with an investment of 300 million dollars, will be operational in 2016.
In addition, year to begin construction of the antennas, as indicated by the Asian company Federal Planning Minister Julio De Vido, who is in Beijing on an official visit.
The Chinese observation station deep space, located in Neuquén, aims to “carry out monitoring, control and data download under the Chinese program of missions to explore the moon and space,” said Federal Planning .
In a statement, the Ministry said the station “is the third in a network and the first outside Chinese territory, with an antenna 35 meters in diameter and associated facilities to its observation, making it the most modern of the three “.
The technical counterpart of Argentina, the National Commission on Space Activities (CONAE), you can access “at least 10 percent of the time available for the development of their research projects with advanced technology”, according to official information.





CLTC Chinese company confirmed Tuesday that the station for deep space observation building in the province of Neuquén, with an investment of 300 million dollars, will be operational in 2016.
In addition, year to begin construction of the antennas, as indicated by the Asian company Federal Planning Minister Julio De Vido, who is in Beijing on an official visit.
The Chinese observation station deep space, located in Neuquén, aims to “carry out monitoring, control and data download under the Chinese program of missions to explore the moon and space,” said Federal Planning .
In a statement, the Ministry said the station “is the third in a network and the first outside Chinese territory, with an antenna 35 meters in diameter and associated facilities to its observation, making it the most modern of the three “.
The technical counterpart of Argentina, the National Commission on Space Activities (CONAE), you can access “at least 10 percent of the time available for the development of their research projects with advanced technology”, according to official information.