rezangahir
BANNED

- Joined
- Dec 5, 2014
- Messages
- 634
- Reaction score
- -9
- Country
- Location
Understanding Spy Satellites
Spy satellites are a special type of artificial satellites intended primarily for espionage purposes.
A body orbiting a planet is known as a satellite. For example Moon is Earths natural satellite. Artificial satellites are man-made satellites orbiting earth and other planets for the purpose of information gathering and its relay.
Artificial satellites are extremely useful not only for espionage purposes but also for transmission of telephone and television signals.
Artificial Satellites
There are different types of artificial satellites. Biosatellites are designed to carry living organisms to space. Miniaturized satellites are extremely small and light weight; they could be as light as 10 kg. To monitor Earths climate and weather, weather satellites are used.
Spy -or Espionage- satellites are used for intelligence purposes. They are also known as reconnaissance or recon satellites. Communications satellites are helpful in relaying radio signals to various parts of the world. Some satellites are lunched in space to study distant stars, planets and galaxies, they are known as astronomical satellites. Navigation satellites help in pinpointing exact location of a certain object. For example GPS satellites provide GPS facilities in several cars and handheld devices.
Some satellites are powered by sunlight, they dont use conventional fossil fuel, and instead rays from the sun help them to accomplish their tasks. Some satellites are launched to destroy enemys satellite; such satellites are known as Killer Satellites. They are armed with particle and energy weapons.
Orbit of a Satellite
The path of a satellite is known as its orbit. A satellite is launched in its orbit either by a rocket or by the help of cargo bay of a space shuttle. Orbit of a satellite can help in its classification. Following are some important orbits:
Spy satellites are a special type of artificial satellites intended primarily for espionage purposes.
Historical Background
The very first artificial satellite ever was launched by Russia in 1957, it was known as Sputnik 1. Explorer 1 was launched by US in 1958. Spy satellites were used for spying since the 1970s. These satellites recorded the required data and ejected it in a canisters. These canisters were retrieved by intelligence agencies.
The first series of US spy satellites, code named Corona, was launched in 1959. This satellite ejected the collected data in a canister which was collected successfully. With the advancement in radio technology, satellites started using the new technology. Samos launched in 1960 used radio technology to relay data along with the old canister technology. Due to bottlenecks of technology, at that time, some of the relayed images were not unto the mark. Subsequently, US government launched Argon (1961), Lanyard (1963), and Gambit (1963) and Hexagon Big Bird (1971). Crystal Kennan, lunched in 1976 used digital imaging technology. This was the first known recon satellite to use this technology. Ikon Improved Crystal, launched in 1990 offered live data reception. 8X EIS are using state of the technology. Although a little information is available on them, some people think that these satellites use radar and stealth technology.
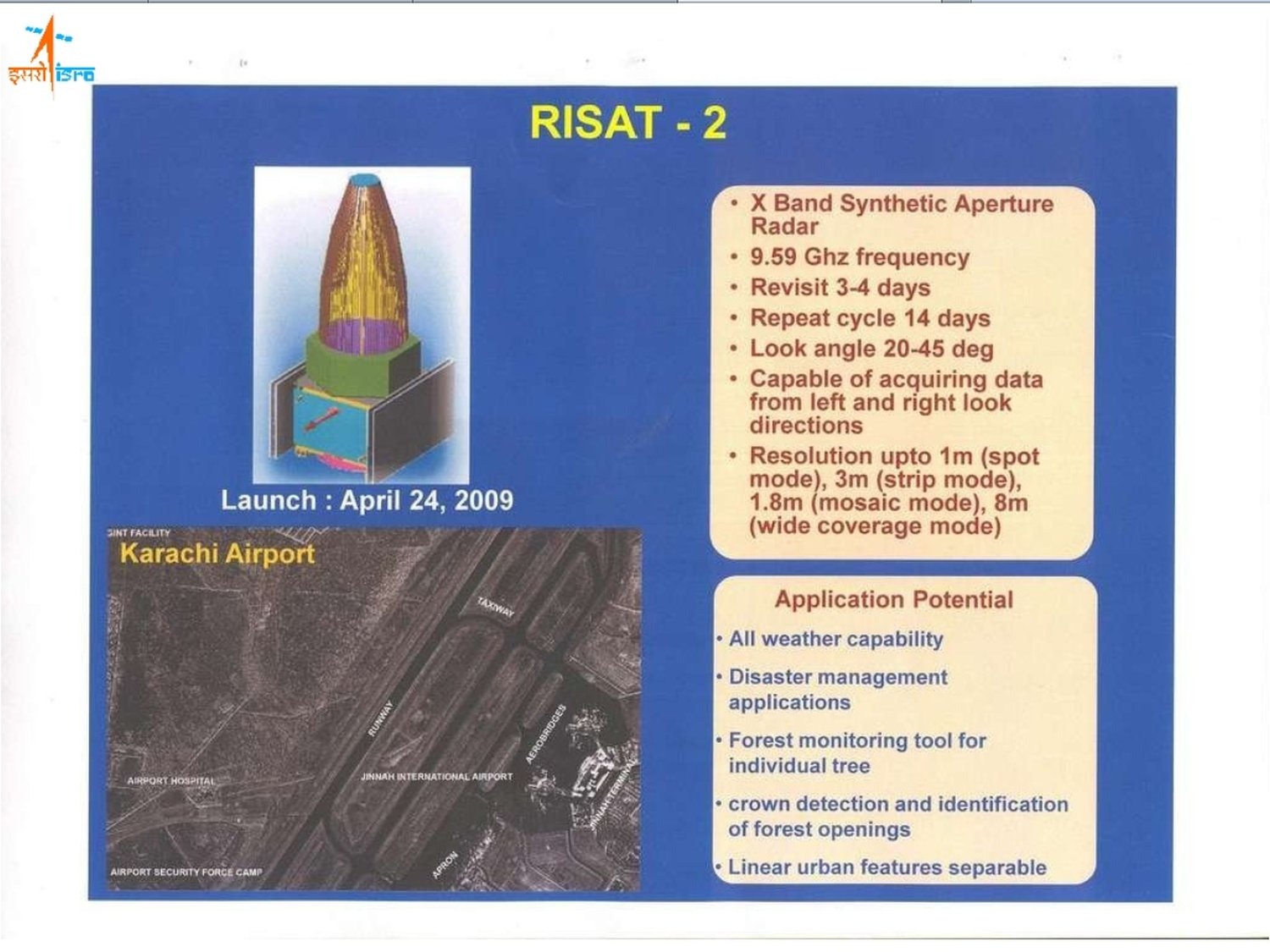
Apart from US, many other countries have launched their own satellites as well. Russia, formerly know as Soviet Union, launched Zenit, Yantar, Almaz and Cosmos. Ofeq was launched by Israel. United Kingdom Launched Zircon. Helios 1B and Helios 2A were launched by French government. Germany launched a satellite known as SAR-Lupe 1-5. Technology Experiment Satellite was launched by India. (India is the second country in the world after the USA that can offer images with one-metre resolution and it enabled ISRO the images of the war in Afghanistan, official sources maintain.)
Hiding from a satellite
Orbits of most of the old fashioned spy satellites can be predicted. Furthermore building underground nuclear and other top classified facilities makes spying from these satellites very difficult. Some facilities also used camouflage techniques to hide from a spy satellite.
Your Very Own Spy Satellite
Some satellites like IKONOS allow people to use it as their very own spy satellite. IKONOS was launched by Space Imaging of Denver. Images capered by this satellite are also used for news reporting. The satellite possesses a sophisticated camera weighing 240 pounds. On a customers desire the camera can rotate a few degrees east or west. All you need to do is to give them your desired coordinates; the satellite owners will send you your images. This service is not currently available for free. Images captured by IKONOS have a resolution of one square meter per pixel.
Currently there are other personal satellites available to public; some of them have capability of capturing an image of resolution half-meter square per pixel. More advanced cameras with far more level of detail are being used for espionage purposes and they are not yet available to consumers. Some softwares like Google Earth and NASA World Wind also allow their users to view previously captured images from a satellite. These services are available for free and require a PC with a good internet connection.
Understanding Spy Satellites
Spy satellites are a special type of artificial satellites intended primarily for espionage purposes.
A body orbiting a planet is known as a satellite. For example Moon is Earths natural satellite. Artificial satellites are man-made satellites orbiting earth and other planets for the purpose of information gathering and its relay.
Artificial satellites are extremely useful not only for espionage purposes but also for transmission of telephone and television signals.
Artificial Satellites
There are different types of artificial satellites. Biosatellites are designed to carry living organisms to space. Miniaturized satellites are extremely small and light weight; they could be as light as 10 kg. To monitor Earths climate and weather, weather satellites are used.
Spy -or Espionage- satellites are used for intelligence purposes. They are also known as reconnaissance or recon satellites. Communications satellites are helpful in relaying radio signals to various parts of the world. Some satellites are lunched in space to study distant stars, planets and galaxies, they are known as astronomical satellites. Navigation satellites help in pinpointing exact location of a certain object. For example GPS satellites provide GPS facilities in several cars and handheld devices.
Some satellites are powered by sunlight, they dont use conventional fossil fuel, and instead rays from the sun help them to accomplish their tasks. Some satellites are launched to destroy enemys satellite; such satellites are known as Killer Satellites. They are armed with particle and energy weapons.
Orbit of a Satellite
The path of a satellite is known as its orbit. A satellite is launched in its orbit either by a rocket or by the help of cargo bay of a space shuttle. Orbit of a satellite can help in its classification. Following are some important orbits:
- HEO-High Earth Orbit (more than 35786 km above Earths surface)
- GSO-Geostationary Orbit (35764 km above Earths surface)
- GEO-Geosynchronous Orbit (35786 km above Earths surface)
- MEO or ICO-Medium Earth Orbit (1200 to 35286 km above Earths surface)
- LEO-Low Earth Orbit (200 to 1200 km above Earths surface)
Spy satellites are a special type of artificial satellites intended primarily for espionage purposes.
Historical Background
The very first artificial satellite ever was launched by Russia in 1957, it was known as Sputnik 1. Explorer 1 was launched by US in 1958. Spy satellites were used for spying since the 1970s. These satellites recorded the required data and ejected it in a canisters. These canisters were retrieved by intelligence agencies.
The first series of US spy satellites, code named Corona, was launched in 1959. This satellite ejected the collected data in a canister which was collected successfully. With the advancement in radio technology, satellites started using the new technology. Samos launched in 1960 used radio technology to relay data along with the old canister technology. Due to bottlenecks of technology, at that time, some of the relayed images were not unto the mark. Subsequently, US government launched Argon (1961), Lanyard (1963), and Gambit (1963) and Hexagon Big Bird (1971). Crystal Kennan, lunched in 1976 used digital imaging technology. This was the first known recon satellite to use this technology. Ikon Improved Crystal, launched in 1990 offered live data reception. 8X EIS are using state of the technology. Although a little information is available on them, some people think that these satellites use radar and stealth technology.
Apart from US, many other countries have launched their own satellites as well. Russia, formerly know as Soviet Union, launched Zenit, Yantar, Almaz and Cosmos. Ofeq was launched by Israel. United Kingdom Launched Zircon. Helios 1B and Helios 2A were launched by French government. Germany launched a satellite known as SAR-Lupe 1-5. Technology Experiment Satellite was launched by India. (India is the second country in the world after the USA that can offer images with one-metre resolution and it enabled ISRO the images of the war in Afghanistan, official sources maintain.)
Hiding from a satellite
Orbits of most of the old fashioned spy satellites can be predicted. Furthermore building underground nuclear and other top classified facilities makes spying from these satellites very difficult. Some facilities also used camouflage techniques to hide from a spy satellite.
Your Very Own Spy Satellite
Some satellites like IKONOS allow people to use it as their very own spy satellite. IKONOS was launched by Space Imaging of Denver. Images capered by this satellite are also used for news reporting. The satellite possesses a sophisticated camera weighing 240 pounds. On a customers desire the camera can rotate a few degrees east or west. All you need to do is to give them your desired coordinates; the satellite owners will send you your images. This service is not currently available for free. Images captured by IKONOS have a resolution of one square meter per pixel.
Currently there are other personal satellites available to public; some of them have capability of capturing an image of resolution half-meter square per pixel. More advanced cameras with far more level of detail are being used for espionage purposes and they are not yet available to consumers. Some softwares like Google Earth and NASA World Wind also allow their users to view previously captured images from a satellite. These services are available for free and require a PC with a good internet connection.
Understanding Spy Satellites