SvenSvensonov
PROFESSIONAL

- Joined
- Oct 15, 2014
- Messages
- 1,617
- Reaction score
- 207
- Country
- Location

In the early days of electronic espionage, the US intelligence community didn't have the benefit of all-seeing spy satellites—it had to intercept and interpret high-frequency radio waves transmitted by the Soviet Union. To do so, the Americans relied on a network of mysterious structures whose real purpose was kept highly classified throughout the Cold War.
Nicknamed "Elephant Cages" by outside observers, these structures were actually high-frequency antenna arrays, part of the US military's AN/FLR-9 "Iron Horse" system. These arrays, commonly known as "Wullenweber" antennas—and named after German WWII scientist, Dr. Hans Rindfleisch was Wullenwever—are a type of Circularly Disposed Antenna Array (CDAA). They can be used for a variety of purposes from intelligence gathering and identifying high-value targets to navigation and search and rescue operations.
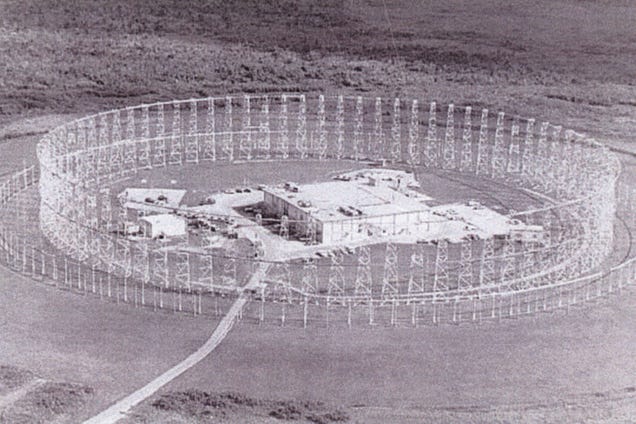
Each elephant cage consisted of an inner ring of antennas tuned for high frequency waves surrounded by one or more outer rings tuned for lower frequencies. These antennas would listen for HF radio waves bouncing off the ionosphere (which is what also allows HF radios to communicate beyond the horizon) and triangulate the precise location of the signal's source.
Per the AN/FLR-9 Operation and Service Manual:
The antenna array is composed of three concentric rings of antenna elements. Each ring of elements receives rf signals for an assigned portion of the 1.5 to 30-MHz radio spectrum. The outer ring normally covers the 2 to 6-MHz range (band A), but also provides reduced coverage down to 1.5 MHz. The center ring covers the 6 to 18-MHz range (band B) and the inner ring covers the 18 to 30-MHz range (band C). Band A contains 48 sleeve monopole elements spaced 78.4 feet apart (7.5 degrees). Band B contains 96 sleeve monopole elements spaced 37.5 feet (11.43 m) apart (3.75 degrees). Band C contains 48 antenna elements mounted on wooden structures placed in a circle around the central building. Bands A and B elements are vertically polarized. Band C elements consist of two horizontally polarized dipole antenna subelements electrically tied together, and positioned one above the other.
This setup enabled each array to operate over a range of up to 3,100 miles (5,000 km). In fact, the Iron Horse program actually ran clear around the planet with a total of six such arrays situated in strategic locations throughout the US and its allied nations. Since the system relied on signals bouncing down from the ionosphere, each array was at the mercy of the weather and prevailing topographical conditions.

As such, the Iron Horse system quickly fell out of favor once we started launching ISR satellites to spy on the Soviets from space. Today, a majority of the existing elephant cages have already been dismantled including those at RAF Chicksands in the UK and Clark Air Base in the Philippines. Crews have just started deconstructing the cage at Misawa Air Base in Japan after a two year delay, leaving the system at Joint Base Elmendorf-Richardson in Alaska as the only operational AN/FLR-9 unit in existence.
From This Electronic Stonehenge Once Divined the Secrets of Soviet Radio


 . Part of EMSEC is intercepting plain, uencrypted signals without the targets knowledge. While we typically think of signals being anything we intend to have happen, such as sending an email intentionally by pushing the send button, an email that would be encrypted once and only once that button is pushed. For those in EMSEC we specialize in gathering plain signals from unintentional sources, such as electo-magnetic leakage from a computer monitor or keyboard, which can't be encrypted, but can be pieced together into a picture of what activity is being done. Encryption is good, it's not going to stop an intelligence, law enforcement or military agency, no matter how much the FBI wants to complain, as these groups can get both encrypted and unencrypted signals.
. Part of EMSEC is intercepting plain, uencrypted signals without the targets knowledge. While we typically think of signals being anything we intend to have happen, such as sending an email intentionally by pushing the send button, an email that would be encrypted once and only once that button is pushed. For those in EMSEC we specialize in gathering plain signals from unintentional sources, such as electo-magnetic leakage from a computer monitor or keyboard, which can't be encrypted, but can be pieced together into a picture of what activity is being done. Encryption is good, it's not going to stop an intelligence, law enforcement or military agency, no matter how much the FBI wants to complain, as these groups can get both encrypted and unencrypted signals.