Indus Falcon
SENIOR MEMBER

- Joined
- Mar 4, 2011
- Messages
- 6,910
- Reaction score
- 107
- Country
- Location
Rio 2016: Brazil Looks to Russia for Air Defense Systems
Jun 12, 2014 by Defense Industry Daily staff
World Cup begins, no missiles.
June 12/14: Not in time.Russia’s Aleksander Fomin says of the Brazilian deal:
“Apparently, we are not managing in time by the beginning of the championship, but we continue the dialogue with our counterparts, the project is in its active phase…. Our counterparts had to observe certain procedures, lice tenders, reasons for choosing a counterpart, the samples and so on. All those procedures have taken time, and most of them are being finalized now. We have been contacting actively, but, unfortunately, the contract is not in place yet.”
He’s hopeful that they’ll be able to do a deal in time to deploy them for the 2016 Olympics. Sources: ITAR-TASS, “Russia’s surface-to-air-missiles not to guard Brazil’s sky during World Cup”.
Brazil needs to upgrade its ground-based air defenses, and has chosen Russian equipment to do so. Protecting the 2016 Olympics in Rio de Janeiro is very much on Brazil’s mind, and so is improving anti-aircraft defenses beyond the current stock of SA-18 Igla shoulder-fired missiles and Gepard mobile anti-aircraft guns. What they’re buying won’t give them anything close to a comprehensive IADS system, but it will upgrade their mobile and short-range options.
Brazil’s Choices
Brazil has good, established relations with competing providers, including Britain (Starstreak VSHORAD and Rapier, which protected the 2012 Olympics), France (Mistral VSHORAD and VL-MICA mobile), and Israel (Spyder). Nevertheless, they chose a pair of Russian products.
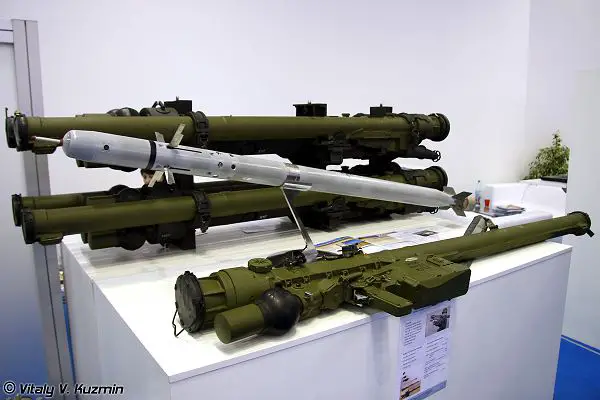
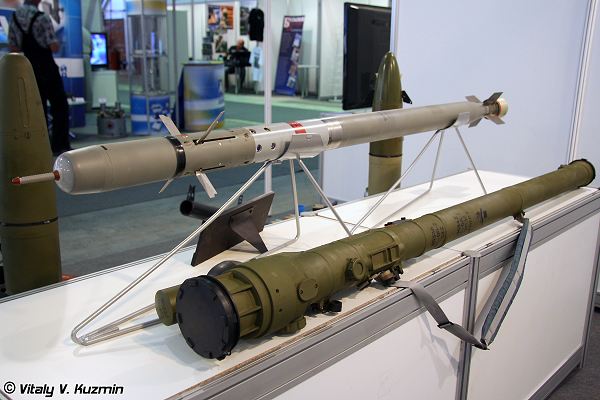
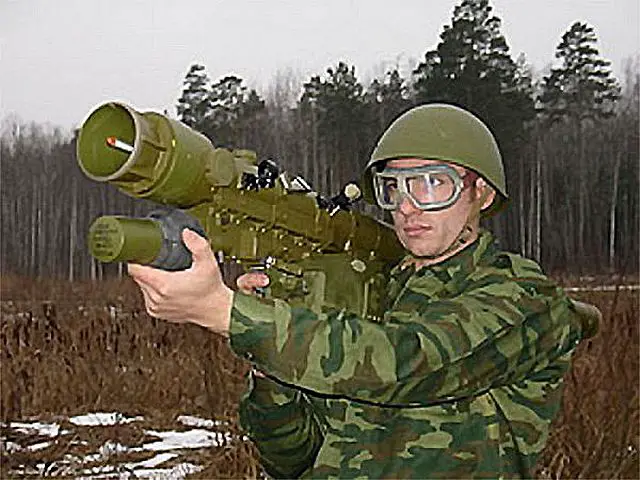
The SA-24 Igla-S
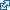 is an upgraded version of the SA-18, with a proximity fuze and other enhancements. It can be carried and fired by troops in the field, or mounted on vehicles or helicopters using Strelets 4-missile launchers. Note that Brazil’snew Mi-35M/ AH-2 Sabreattack helicopters aren’t an integrated platform.
is an upgraded version of the SA-18, with a proximity fuze and other enhancements. It can be carried and fired by troops in the field, or mounted on vehicles or helicopters using Strelets 4-missile launchers. Note that Brazil’snew Mi-35M/ AH-2 Sabreattack helicopters aren’t an integrated platform.
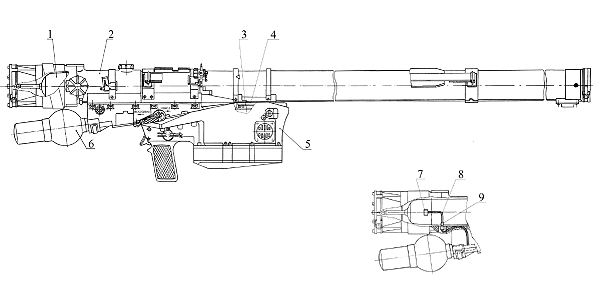
The SA-22 Pantsir S1
 is designed for mobile low-level air defense, and can be mounted on trucks, wheeled armored vehicles, and tracked vehicles. It combines twin 30mm guns with 12 57E6 radar-guided surface-to-air missiles that reach out to 12 km/ 10 miles, and up to 10,000m altitude. Sensors include targeting and tracking radars, with an electro-optical system for passive scanning.
is designed for mobile low-level air defense, and can be mounted on trucks, wheeled armored vehicles, and tracked vehicles. It combines twin 30mm guns with 12 57E6 radar-guided surface-to-air missiles that reach out to 12 km/ 10 miles, and up to 10,000m altitude. Sensors include targeting and tracking radars, with an electro-optical system for passive scanning.
It’s more of a low-level air defense system than a remedy against enemies who can use precision bombing from altitude, and its use of radio command guidance (RCG) means that its attacks can be defeated with jamming, or by killing the launcher. Nevertheless, it has been exported to Algeria and the UAE, and ordered by Iraq. There are reports that Jordan and Syria are also customers, and that some of the Syrian systems found their way to Iran.
The Pantsirs will be integrated into a system that includes Russian SA-18 missiles, ex-German army Gepard 1A2 self-propelled anti-aircraft guns, and Brazil’s own CTEx M-60 SABER radars with a range of up to 60 km.

Pantsir S1 mobile air defense systems
Rio 2016: Brazil Looks to Russia for Air Defense Systems
Jun 12, 2014 by Defense Industry Daily staff
World Cup begins, no missiles.
June 12/14: Not in time.Russia’s Aleksander Fomin says of the Brazilian deal:
“Apparently, we are not managing in time by the beginning of the championship, but we continue the dialogue with our counterparts, the project is in its active phase…. Our counterparts had to observe certain procedures, lice tenders, reasons for choosing a counterpart, the samples and so on. All those procedures have taken time, and most of them are being finalized now. We have been contacting actively, but, unfortunately, the contract is not in place yet.”
He’s hopeful that they’ll be able to do a deal in time to deploy them for the 2016 Olympics. Sources: ITAR-TASS, “Russia’s surface-to-air-missiles not to guard Brazil’s sky during World Cup”.
Brazil needs to upgrade its ground-based air defenses, and has chosen Russian equipment to do so. Protecting the 2016 Olympics in Rio de Janeiro is very much on Brazil’s mind, and so is improving anti-aircraft defenses beyond the current stock of SA-18 Igla shoulder-fired missiles and Gepard mobile anti-aircraft guns. What they’re buying won’t give them anything close to a comprehensive IADS system, but it will upgrade their mobile and short-range options.
Brazil’s Choices
Brazil has good, established relations with competing providers, including Britain (Starstreak VSHORAD and Rapier, which protected the 2012 Olympics), France (Mistral VSHORAD and VL-MICA mobile), and Israel (Spyder). Nevertheless, they chose a pair of Russian products.
The SA-24 Igla-S
The SA-22 Pantsir S1
It’s more of a low-level air defense system than a remedy against enemies who can use precision bombing from altitude, and its use of radio command guidance (RCG) means that its attacks can be defeated with jamming, or by killing the launcher. Nevertheless, it has been exported to Algeria and the UAE, and ordered by Iraq. There are reports that Jordan and Syria are also customers, and that some of the Syrian systems found their way to Iran.
The Pantsirs will be integrated into a system that includes Russian SA-18 missiles, ex-German army Gepard 1A2 self-propelled anti-aircraft guns, and Brazil’s own CTEx M-60 SABER radars with a range of up to 60 km.

Pantsir S1 mobile air defense systems
Rio 2016: Brazil Looks to Russia for Air Defense Systems


 Back to top
Back to top