Chanakya's_Chant
SENIOR MEMBER
- Joined
- Jul 22, 2013
- Messages
- 3,395
- Reaction score
- 28
- Country
- Location
A look at India's achievements in military systems in 2014

The Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) continued on the path of building self-reliance. The production value of DRDO developed systems inducted or cleared for acquisition (excluding strategic systems) crossed Rs 1,70,000 crores.
The Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) continued on the path of building self-reliance. The production value of DRDO developed systems inducted or cleared for acquisition (excluding strategic systems) crossed Rs 1,70,000 crores ($27 Billion). The year 2014 witnessed yet another series of accomplishments with enormous potential to further enhance the level of self-reliance in defence technologies.
The Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) continued on the path of building self-reliance. The production value of DRDO developed systems inducted or cleared for acquisition (excluding strategic systems) crossed Rs 1,70,000 crores.

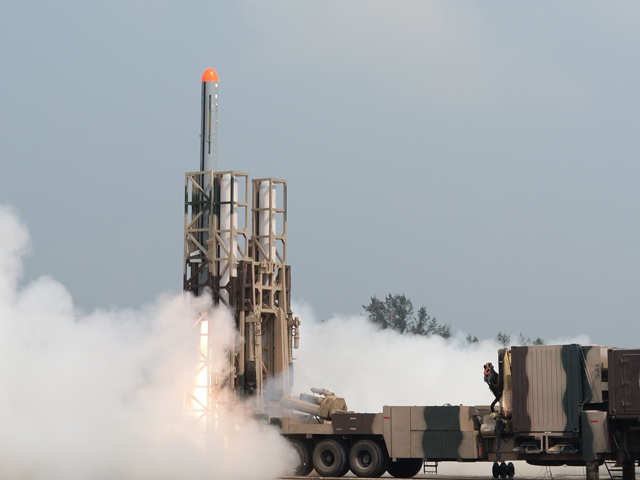
AGNI-4
The 4,000 km range road mobile ballistic missile AGNI-4, was successfully flight tested twice. Among the development flights, the flight test on 20 January 2014 paved the way for flight test on 02 December, 2014 by the armed forces. Agni 4 is equipped with the state-of-the-art avionics, 5th Generation On board Computer and Distributed Architecture. It is also equipped with the latest features to correct and guide it for inflight disturbances. With Agni 1, 2, 3 and Prithvi already in India’s arsenal, Agni 4 further extends the reach and enhances effective deterrence capability. Besides, practice cum training launches of strategic missiles which are already inducted, such as Agni-1, Agni-2, P-II and Dhanush were carried out by the armed forces.

Nirbhay Sub-Sonic Cruise Missile
Nirbhay, the 1000 km class long range sub-sonic cruise missile was successfully flight tested on 17 October, 2014. The flight lasted over one hour and met all the mission objectives with the missile following the predefined trajectory with very high accuracy throughout its path. The maiden flight of PDV exo-atmospheric interceptor on 27 April 2014 was a significant milestone in the direction of developing a two layered Ballistic Missile Defence System. In addition to the interceptor itself, the two stage target for mimicking a "hostile Ballistic Missile approaching from more than 2000 km away" too was specially developed for the mission.
Akash SAM
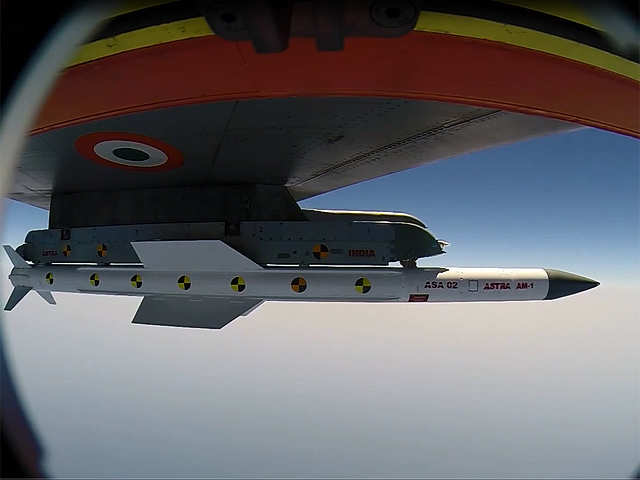
Production and induction of Akash, the medium range air defence system with multi-target, multi directional capability was another remarkable achievement. Several squadrons of Akash (Air Force) have been inducted, with specified number of missiles from each production lot undergoing comprehensive flight tests in various operational modes before acceptance of the lot. Akash (Army) has been accepted and is undergoing its induction process. LRSAM, the Long Range Surface-to-Air Missile was successfully tested against a flying target in Israel on 10 November 2014. Successful trials of Helina, a “Lock-On Before Launch (Fire & Forget)” third generation Anti-tank Guided missile that can attack in both direct and top attack mode was integrated with Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH). The missile with capability to defeat futuristic armors underwent successful field trials on 27 June 2014. ASTRA-BVR (Beyond Visual Range) Air-to-Air missile was successfully tested from a Su-30 MKI by the Indian Air Force, demonstrating interception of an electronically simulated target at long range. The series of tests conducted have demonstrated the aerodynamic characteristics of the missiles and its repeatability, robustness and endurance capability as a weapon system. A 1,000 kg class Guided Glide Bomb was designed, developed and successfully tested. The bomb, after getting released by the aircraft and guided by onboard navigation system is capable of gliding accurately to its target even 100 km away. Over thirty missions such as launches of strategic and tactical guided missiles kept the Integrated Test Range, the only one in the country, heavily engaged with activities throughout the year.
HAL LCH
A four km long Rail Track Rocket Sled (RTRS) Penta Rail Supersonic Track, a national test facility was established and made operational, bringing India among a handful of countries in the world now possessing this unique test facility. The RTRS will facilitate testing and evaluation of a wide range of critical systems such as payload for manned missions of ISRO, the navigation system for missiles and aircrafts, proximity fuses for advanced warheads, fuses for armament systems parachutes for payload delivery and arrester systems for aircraft such as LCA.
ARJUN MARK II MBT
An Advanced Parachute System meeting stringent requirements of Human Space Program (HSP-II) was designed, developed and successfully evaluated by DRDO. The system developed for India’s manned space missions was successfully proven with the recovery of Moon Mission Crew Capsule flown into space by the GSLV Mk-III on 18 December 2014. The parachute deployment system functioned perfectly and achieved the required descent rate. A Heavy Drop System (P-16) for dropping from IL 76 heavy lift aircraft was developed and is undergoing user assisted trials. The system consisting of a platform system suitably designed for harnessing and mounting of variety of payloads of 16 tones class and a highly advanced parachute system to drop loads. The load typically consists of military stores such as vehicles (including BMP class), supplies and ammunition. The first indigenously designed and developed Inflatable Radom to serve as a shelter to provide controlled environment for effective and continuous 24x7 functioning of sensitive systems such as RADARs for civil and military applications was installed. The inflatable structure consists of hemispherical envelope of coated fabrics with airlock tunnel, centrifugal air blowers, packaged air conditioners, electrical control system and emergency generator.

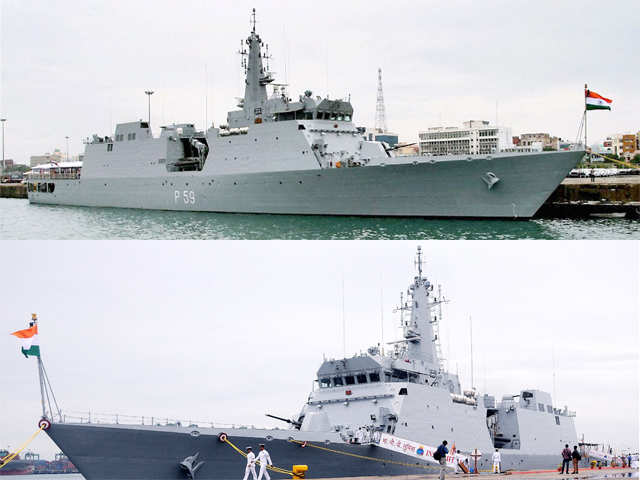
INS KOLKATA
Phase-IV of user trials of Arjun Main Battle Tank Mk-II, that included trench crossing and step climbing capabilities, were successfully completed. Development of Arjun Catapult 130mm Self-Propelled Artillery Gun, a blend of 130 mm SP Art Gun with Arjun chassis has been completed as per GSQR. DRDO internal trial validation has been completed and the Arjun Catapult is ready for user trials. User demo trials of Pinaka Mk- II rockets with enhanced range were successfully conducted.

DRDO Airborne Early Warning & Control (AEW&C)
Successful User Assisted Technical Trials (UATT) of CBRN Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) and Multi-Purpose Decontamination System (MPDS) were carried out. User and DGQA trials of BMCS (Bi-Modular Charge System) using both Soltam and Bofors guns were completed and the trials included validation of manufacturing process. Dynamic trials of 120mm Penetration-cum-Blast (PCB) ammunition for MBT Arjun Mk II were conducted successfully.
A man-portable modular military bridging system suitable for rapid deployment in mountainous regions and capable of bridging gaps up to 35m successfully completed user assisted technical trials. The modules weighing less than 18 kg each allow the bridge to be constructed from near-bank without any access to far-bank. A 35m bridge can be launched in about one hour.
“NABHRATHNA”, a Flying Test Bed (FTB) based on a Dornier aircraft acquired from HAL was realized. The FTB serves as a test bed platform for evaluation of airborne Radars. FTB sorties with Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and Maritime Patrol Airborne Radar (MPAR) have been taken up successfully.
A man-portable modular military bridging system suitable for rapid deployment in mountainous regions and capable of bridging gaps up to 35m successfully completed user assisted technical trials. The modules weighing less than 18 kg each allow the bridge to be constructed from near-bank without any access to far-bank. A 35m bridge can be launched in about one hour.
“NABHRATHNA”, a Flying Test Bed (FTB) based on a Dornier aircraft acquired from HAL was realized. The FTB serves as a test bed platform for evaluation of airborne Radars. FTB sorties with Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) and Maritime Patrol Airborne Radar (MPAR) have been taken up successfully.

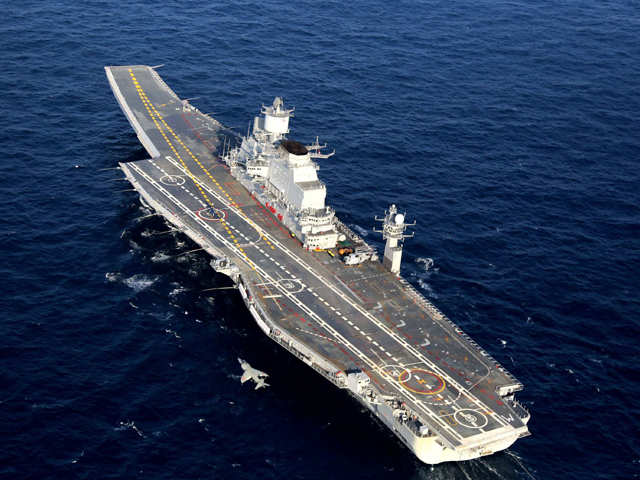
INS VIKRANT (IAC I) Under Construction
Dhruva-3, the latest in a series of indigenous High Performance Computing Systems designed for solving mission critical Defence R&D applications and one of the fastest computing facilities in the country became operational.
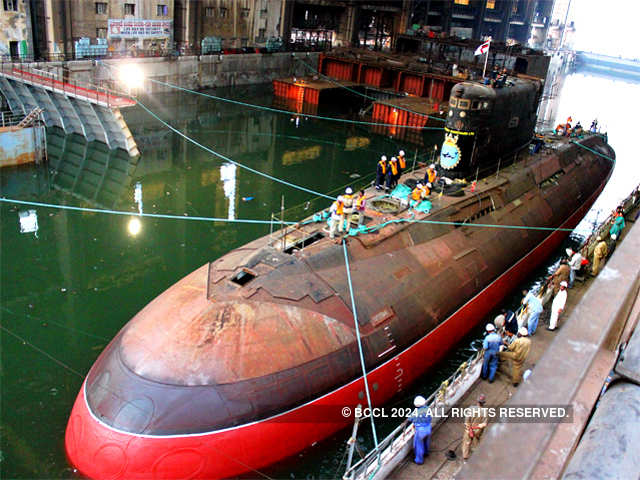
ALTAS was realized with establishment of Towed array SONAR technology with 100% indigenous capabilities with two production centres. The system is designed to detect and identify submarines and underwater weapons. First technical trial on ALTAS has been conducted with satisfactory results. ABHAY and HUMSA-UG compact sonars, ideal for fitment on smaller platforms for surveillance purposes and having advantages of reduced installation and maintenance load on the technical personnel were installed on two platforms and are undergoing technical trials. The hull mounted sonar HUMSA-NG has been installed onboard INS Kolkata and INS Komorta. Varunastra, the heavy weight torpedo and Maareech, the decoy system for defence against torpedo attacks successfully completed 10 and 12 sets of user evaluation trials respectively.

The life sciences labs of DRDO continued its efforts with full vigour to develop soldier support systems and processes to help the soldiers perform effectively in diverse and harsh terrain and climatic conditions in the country. Submarine Escape Set 120 M to assist safe escape from underwater vessels from depths up to 120m is undergoing trials. Mark I version is already in production. ‘Telemedicine System’ has been accepted for induction in Indian Navy. The system capable of exchange of vital medical information and advice in a secure manner through multiple channels (including Satcom) will be installed in various Indian Navy ships as well as remote naval units.
Source:- Defence News - A look at India's achievements in military systems in 2014
Last edited:
















