Techy
FULL MEMBER
- Joined
- Apr 18, 2015
- Messages
- 222
- Reaction score
- 5
- Country
- Location
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is now aiming for an October-end launch for the Reusable Launch Vehicle-Technology Demonstrator (RLV-TD), a scaled-down model of the proposed ‘space shuttle’. Earlier, the space agency was planning to have the mission in July. K Sivan, director, Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), said the construction of the space plane portion of RLV-TD is in its final phase at VSSC, Thumba. “Tests are progressing. We are planning to have the launch in the second half of October,” he said. ISRO chairman A S Kiran Kumar, who is due for a visit to VSSC on Monday, will review the progress of work on this mission which is crucial for India’s future in the space race. This mission will be the first of several tests conducted ahead of building India’s own space shuttle.
The scale model weighs 1.5 tonnes and will fly up to a height of 70 kilometres before dropping down to the Bay of Bengal. For the first RLV-TD experimental flight, the space plane part will be rigged atop a solid booster rocket.The ISRO chairman will also review the progress of work on the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III (GSLV Mk-III) project.
‘UK Satellites in Good Health’
All five British satellites that were put in orbit by the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle C-28 (PSLV c-28) on Friday night are in “good health,” VSSC director K Sivan, who arrived back in Thiruvananthapuram from the Sriharikota spaceport on Saturday morning, said. At one go, ISRO had placed in orbit three identical DMC3 earth observation satellites, the CBNT-1 earth observation micro satellite and a nano satellite – De-OrbitSail.
RLV-TD Introduction
ISRO is developing fully Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV) technology for two stage to orbit (TSTO) capability.
The first stage will be powered by a semi cryogenic winged booster capable of flying back and landing on a runway near the launch site like a conventional aircraft after burnout.
The second stage will be cryogenic. It will deliver the satellite into orbit, de-orbit and re-enter the atmosphere and parachute down to a soft landing on balloons.
The RLV has been conceived by ISRO as a space launch system that will significantly cut down launch cost from the present level of around $5,000 / kg to around $500 / kg.
Phased Development
Reusable Launch Vehicle technology will be developed in phases through a series of trial flights.
The first in the series of trials is the hypersonic flight experiment (HEX) followed by the landing experiment (LEX), return flight experiment (REX) and scramjet propulsion experiment (SPEX).
Hypersonic Flight Experiment (HEX)
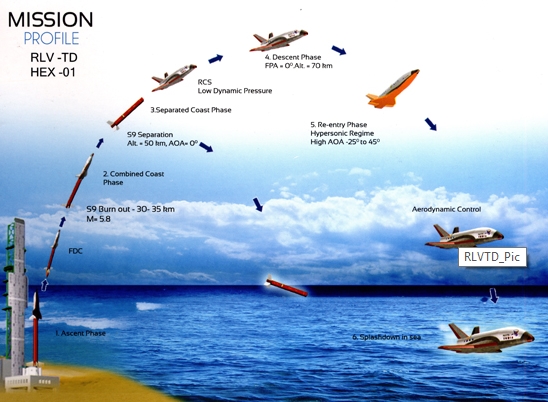
Flight testing will start with RLV-TD (HEX). During the mission, a booster rocket (Single strap-on solid booster of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) with 9 tonne fuel.) will take the 1.5 tonne RLV scale model to 70-km altitude and release it. The booster rocket will fall back into the sea.
The lofted RLV will re-enter the atmosphere independently travelling at around 2-km / sec. The descent speed would be controlled using the fins. The RLV has protective tiles to dissipate frictional heat during re-entry.
In the first trial-flight, the RLV will not be recovered from sea because it will not be cost-effective to do so. ISRO will instead use telemetry data data on the re-entry, deceleration and return.
Landing Experiment (LEX)
In the second phase RLV will be tested without its scramjet engine. After burnout, the booster will separate and fall away, and the RLV-TD will go on to make an unpowered ascent.
The RLV-TD will then re-enter the atmosphere at hypersonic speed and use aerodynamic breaking to decelerate. It will perform a range maneuver at 15-km, a 2g turn towards its launch site. Once the TD reaches 0.8 M, it will light up a turbofan engine to cruise back to its launch site at 0.6M and make a horizontal landing on a runway.
Return Flight Experiment (REX)
In this phase, the RLV-TD will be launched to orbit and then de-orbited for a landing on a runway.
Scramjet Propulsion Experiment (SPEX)
Eventually, the RLV will be powered by an air breathing scram jet which is being developed under a separate project called Air Breathing Propulsion Project (ABPP).
RLV-TD HEX-01
ISRO has a hypersonic wind tunnel facility at VSSC, Trivandrum installed by Hind High Vacuum (HHV) Bangalore. The system comprises three Horton Spheres, each 16.3m dia. and 2200 cu m capacity. The system has two parallel pumping trains, each with two mechanical booster pumps with pumping speed of 30,000 cu m / hr backed successively by a 14,000 cu m / hr and 7,000 cu m / hr booster pump and finally by three rotary piston pumps, each with a pumping speed of 1325 cu m / hr.




